Multiage classrooms combine students of different ages and grade levels, promoting peer learning and social development through collaboration. Single-grade classrooms group students by age, allowing instruction to be tailored to a specific developmental stage and curriculum focus. Both models offer unique benefits, with multiage settings fostering flexibility and mentorship while single-grade classrooms provide targeted academic pacing.
Table of Comparison
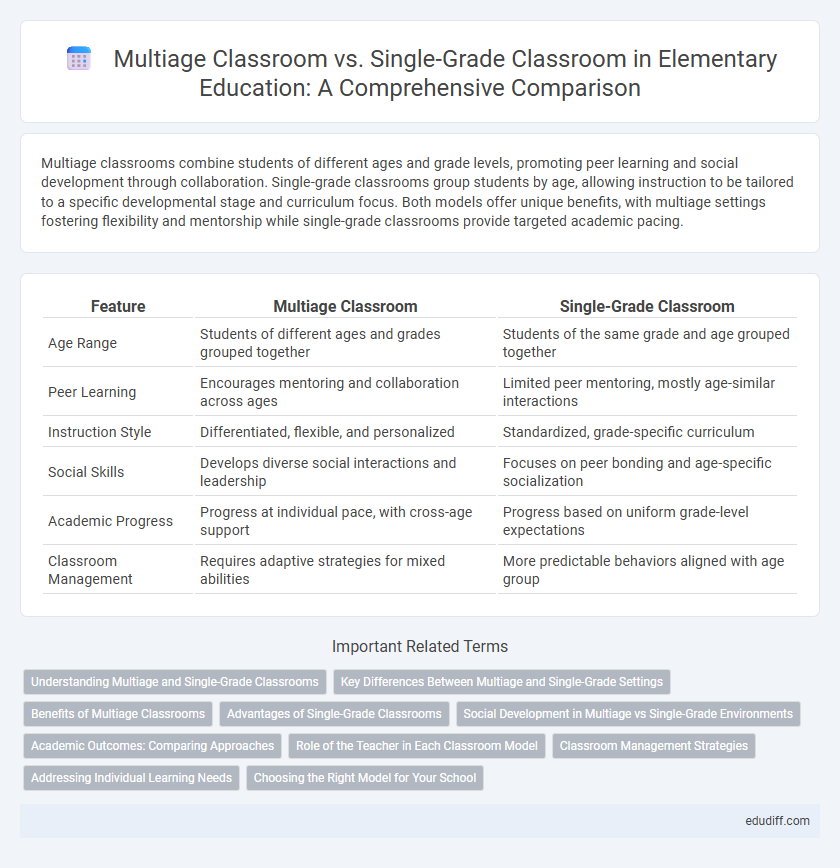
| Feature | Multiage Classroom | Single-Grade Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Age Range | Students of different ages and grades grouped together | Students of the same grade and age grouped together |
| Peer Learning | Encourages mentoring and collaboration across ages | Limited peer mentoring, mostly age-similar interactions |
| Instruction Style | Differentiated, flexible, and personalized | Standardized, grade-specific curriculum |
| Social Skills | Develops diverse social interactions and leadership | Focuses on peer bonding and age-specific socialization |
| Academic Progress | Progress at individual pace, with cross-age support | Progress based on uniform grade-level expectations |
| Classroom Management | Requires adaptive strategies for mixed abilities | More predictable behaviors aligned with age group |
Understanding Multiage and Single-Grade Classrooms
Multiage classrooms combine students from different grade levels, promoting peer learning and individualized instruction that supports diverse developmental stages. Single-grade classrooms group students by age or grade, allowing for a structured curriculum tailored to specific academic standards and developmental milestones. Understanding these models helps educators design learning environments that best meet students' social, emotional, and cognitive needs.
Key Differences Between Multiage and Single-Grade Settings
Multiage classrooms group students of different ages and grade levels together, promoting peer learning and social development through collaboration, while single-grade classrooms separate students strictly by age and grade. Multiage settings offer flexible, personalized instruction tailored to individual student needs, whereas single-grade environments follow a standardized curriculum targeted at a specific age group. Research shows multiage classrooms can enhance academic achievement, social skills, and self-regulation compared to traditional single-grade models.
Benefits of Multiage Classrooms
Multiage classrooms enhance social skills by encouraging peer learning and collaboration across different age groups, fostering empathy and communication. They support personalized instruction, allowing teachers to tailor lessons to varied developmental levels, which improves student engagement and academic growth. Research shows multiage settings reduce behavioral issues and increase students' adaptability and confidence compared to single-grade classrooms.
Advantages of Single-Grade Classrooms
Single-grade classrooms offer focused instruction tailored to a specific age group, allowing teachers to target developmental milestones and curriculum standards precisely. This environment promotes a cohesive social experience where students share similar cognitive and emotional stages, fostering peer connections and group activities suited to their level. Standardized assessments and lesson pacing are streamlined, ensuring consistent academic progress and easier benchmarking within the grade.
Social Development in Multiage vs Single-Grade Environments
Multiage classrooms foster enhanced social development by encouraging peer mentoring and collaboration among students of varying ages, promoting empathy and leadership skills. In contrast, single-grade classrooms often limit social interactions to same-age peers, which can restrict opportunities for diverse social learning experiences. Research indicates multiage settings support stronger social bonds and adaptability through exposure to multiple developmental stages within the learning environment.
Academic Outcomes: Comparing Approaches
Multiage classrooms foster personalized learning by allowing students to progress at their own pace, often resulting in improved critical thinking and social skills compared to single-grade classrooms. Single-grade classrooms provide a structured environment aligned with standardized curricula, facilitating targeted instruction and easier assessment of academic milestones. Research shows that multiage settings can enhance collaboration and motivation, while single-grade classrooms may better support focused skill development and standardized testing readiness.
Role of the Teacher in Each Classroom Model
In multiage classrooms, teachers act as facilitators by tailoring instruction to diverse developmental levels and encouraging peer learning among students. In single-grade classrooms, teachers often focus on delivering grade-specific content with structured lesson plans designed for uniform learning goals. The role shifts from guiding varied individual progress in multiage settings to maintaining curriculum consistency and pacing in single-grade environments.
Classroom Management Strategies
Multiage classrooms foster peer learning and collaboration, requiring teachers to implement flexible grouping and differentiated instruction to manage diverse skill levels effectively. Single-grade classrooms benefit from uniform pacing, allowing for consistent routines and targeted behavior management strategies tailored to a specific age group. Effective classroom management in multiage settings emphasizes adaptability and communication, while single-grade classrooms focus on structure and uniform expectations.
Addressing Individual Learning Needs
Multiage classrooms support tailored instruction by grouping students of various ages, allowing teachers to customize lessons based on individual skill levels and learning paces. Single-grade classrooms often use standardized pacing, which may not address diverse student needs as effectively. Research highlights that multiage settings promote personalized learning plans, fostering academic growth by targeting each child's unique strengths and challenges.
Choosing the Right Model for Your School
Multiage classrooms promote collaboration and social development by grouping students of varying ages and abilities together, fostering peer learning and flexibility in instruction. Single-grade classrooms offer structured, grade-specific curricula that align with standardized testing and targeted skill progression. Schools should evaluate their community needs, teacher expertise, and available resources when choosing between multiage and single-grade models to optimize student growth and engagement.
Multiage Classroom vs Single-Grade Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com