Rote memorization involves repeatedly practicing information until it is memorized, which can help with short-term recall but often leads to shallow learning. Conceptual understanding requires grasping the underlying principles and relationships, enabling students to apply knowledge to new situations and solve problems effectively. Emphasizing conceptual understanding in elementary education fosters critical thinking and long-term retention, preparing students for more complex subjects ahead.
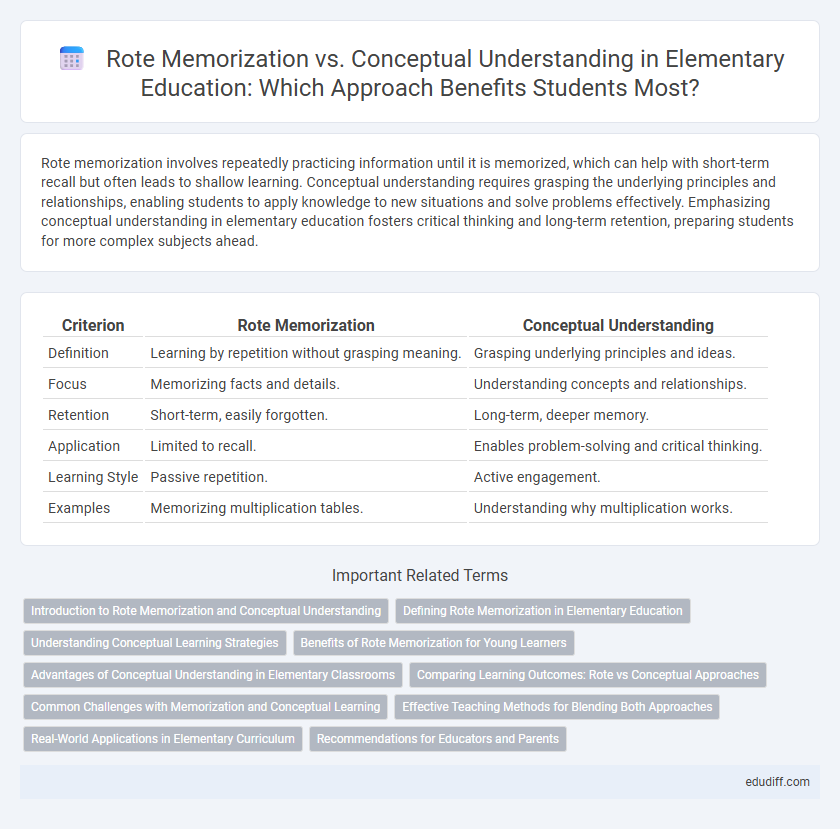
Table of Comparison
| Criterion | Rote Memorization | Conceptual Understanding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning by repetition without grasping meaning. | Grasping underlying principles and ideas. |
| Focus | Memorizing facts and details. | Understanding concepts and relationships. |
| Retention | Short-term, easily forgotten. | Long-term, deeper memory. |
| Application | Limited to recall. | Enables problem-solving and critical thinking. |
| Learning Style | Passive repetition. | Active engagement. |
| Examples | Memorizing multiplication tables. | Understanding why multiplication works. |
Introduction to Rote Memorization and Conceptual Understanding
Rote memorization involves repetitive learning to recall facts exactly, supporting quick retention of basic information such as multiplication tables and spelling. Conceptual understanding emphasizes grasping underlying principles and relationships, enabling students to apply knowledge flexibly to new problems. Balancing rote memorization with conceptual understanding enhances foundational skills and deeper cognitive development in elementary education.
Defining Rote Memorization in Elementary Education
Rote memorization in elementary education refers to the process of repeatedly practicing facts or information until they can be recalled exactly without understanding their meaning. This method emphasizes surface learning, such as memorizing multiplication tables or spelling words, which can help build a foundation of basic knowledge. However, it often lacks connection to deeper comprehension, making it challenging for students to apply information in different contexts.
Understanding Conceptual Learning Strategies
Conceptual learning strategies emphasize grasping underlying principles and relationships rather than memorizing isolated facts, enhancing long-term retention and application. Techniques such as using visual aids, analogies, and interactive activities promote deeper comprehension and critical thinking skills. This approach supports students in connecting new information to prior knowledge, fostering meaningful and adaptable learning experiences.
Benefits of Rote Memorization for Young Learners
Rote memorization helps young learners quickly recall essential facts such as multiplication tables, spelling words, and basic vocabulary, providing a strong foundation for further learning. This method improves memory retention and builds confidence by enabling children to answer questions accurately and promptly. Frequent repetition during rote memorization reinforces neural pathways, aiding long-term recall and automaticity in foundational skills.
Advantages of Conceptual Understanding in Elementary Classrooms
Conceptual understanding in elementary classrooms fosters critical thinking, allowing students to connect new information with prior knowledge for deeper learning. This approach encourages problem-solving skills and adaptability, essential for mastering complex subjects over time. Emphasizing conceptual understanding supports long-term retention compared to rote memorization, which often leads to short-term recall without meaningful comprehension.
Comparing Learning Outcomes: Rote vs Conceptual Approaches
Rote memorization often leads to quick recall of facts but may result in shallow understanding and difficulty applying knowledge in new situations. Conceptual understanding promotes deeper comprehension, enabling students to make connections between ideas and solve problems effectively. Studies show that learners with strong conceptual foundations perform better on critical thinking tasks and retain information longer than those relying solely on memorization.
Common Challenges with Memorization and Conceptual Learning
Rote memorization often leads to difficulty in applying knowledge to new situations, as students may struggle to connect facts without deeper understanding. Conceptual learning challenges include the time and effort required to grasp underlying principles, which can be overwhelming without proper guidance. Both approaches can cause frustration, but combining them improves retention and critical thinking skills in elementary students.
Effective Teaching Methods for Blending Both Approaches
Effective teaching methods for blending rote memorization and conceptual understanding in elementary education include using spaced repetition alongside hands-on activities that promote critical thinking. Incorporating visual aids and real-life examples helps students memorize facts while grasping underlying concepts. Balancing drill exercises with interactive discussions ensures retention and deeper comprehension, fostering long-term learning success.
Real-World Applications in Elementary Curriculum
Real-world applications in elementary curriculum enhance conceptual understanding by linking math and science concepts to everyday experiences, such as measuring ingredients during cooking or observing plant growth. Unlike rote memorization, which emphasizes repetition without context, experiential learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for practical use. Integrating hands-on activities with curriculum standards supports long-term retention and meaningful knowledge transfer.
Recommendations for Educators and Parents
Encourage active learning strategies that promote critical thinking over passive memorization, such as project-based activities and open-ended questions. Provide opportunities for students to connect new information to prior knowledge to enhance conceptual understanding and retention. Foster a supportive environment where mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities, helping children develop deeper comprehension and long-term skills.
Rote Memorization vs Conceptual Understanding Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com