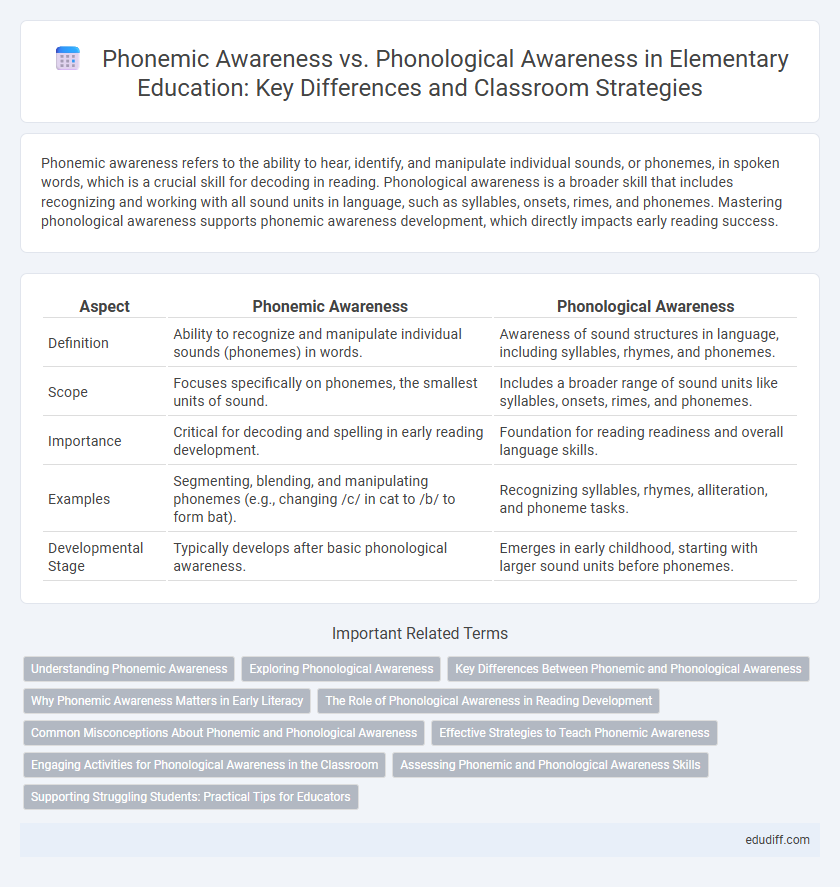
Phonemic awareness refers to the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate individual sounds, or phonemes, in spoken words, which is a crucial skill for decoding in reading. Phonological awareness is a broader skill that includes recognizing and working with all sound units in language, such as syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes. Mastering phonological awareness supports phonemic awareness development, which directly impacts early reading success.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Phonemic Awareness | Phonological Awareness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to recognize and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in words. | Awareness of sound structures in language, including syllables, rhymes, and phonemes. |
| Scope | Focuses specifically on phonemes, the smallest units of sound. | Includes a broader range of sound units like syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes. |
| Importance | Critical for decoding and spelling in early reading development. | Foundation for reading readiness and overall language skills. |
| Examples | Segmenting, blending, and manipulating phonemes (e.g., changing /c/ in cat to /b/ to form bat). | Recognizing syllables, rhymes, alliteration, and phoneme tasks. |
| Developmental Stage | Typically develops after basic phonological awareness. | Emerges in early childhood, starting with larger sound units before phonemes. |
Understanding Phonemic Awareness
Phonemic awareness is a critical aspect of reading development that involves recognizing and manipulating individual sounds, or phonemes, within spoken words. Mastery of phonemic awareness enables elementary students to decode words effectively by connecting sounds to letters, which is foundational for spelling and reading fluency. This skill differs from broader phonological awareness, which includes recognizing larger sound units such as syllables and rhymes.
Exploring Phonological Awareness
Phonological awareness involves recognizing and manipulating larger sound units in language, such as syllables, onsets, and rimes, which lays the foundation for reading skills in elementary students. This skill encompasses identifying rhymes, segmenting words into syllables, and blending sounds, essential for developing decoding abilities. Exploring phonological awareness supports early literacy by enhancing students' ability to connect sounds with written letters, improving word recognition and spelling proficiency.
Key Differences Between Phonemic and Phonological Awareness
Phonemic awareness specifically involves the ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds, or phonemes, within words, while phonological awareness encompasses a broader range of sound recognition skills, including syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes. Key differences include that phonemic awareness targets the smallest units of sound crucial for decoding, whereas phonological awareness covers larger sound units important for early reading development. Mastering phonemic awareness is essential for spelling and decoding, while phonological awareness supports overall language and literacy skills in elementary learners.
Why Phonemic Awareness Matters in Early Literacy
Phonemic awareness, the ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds in words, is a critical skill in early literacy that directly supports decoding and spelling. Unlike broader phonological awareness, which includes recognizing larger sound units like syllables and rhymes, phonemic awareness targets the smallest sound units, enabling children to connect sounds to letters effectively. Developing strong phonemic awareness improves reading fluency and comprehension, laying the foundation for successful literacy acquisition in elementary students.
The Role of Phonological Awareness in Reading Development
Phonological awareness, encompassing the ability to recognize and manipulate sounds in spoken language, plays a critical role in reading development by enabling children to decode words accurately. This skill includes recognizing syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes, which directly supports the acquisition of phonics and spelling strategies in early education. Strong phonological awareness predicts better reading fluency and comprehension, making it foundational for literacy success in elementary students.
Common Misconceptions About Phonemic and Phonological Awareness
Phonemic awareness specifically refers to the ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken words, while phonological awareness encompasses a broader range of sound structures such as syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes. A common misconception is that phonemic awareness and phonological awareness are interchangeable terms, which can lead to overlooking important developmental milestones in reading instruction. Understanding the distinction is crucial for educators to design effective literacy interventions targeting precise sound recognition and manipulation skills in early learners.
Effective Strategies to Teach Phonemic Awareness
Effective strategies to teach phonemic awareness in elementary students include using sound isolation, segmentation, and blending activities that highlight individual phonemes within words. Incorporating multisensory approaches, such as tapping, clapping, or using manipulatives, strengthens students' ability to identify and manipulate sounds. Consistent practice with phoneme substitution and deletion tasks enhances students' understanding of how sounds function in spoken language, supporting early reading development.
Engaging Activities for Phonological Awareness in the Classroom
Engaging activities for phonological awareness in elementary classrooms include rhyming games, syllable clapping, and sound isolation tasks that build students' ability to recognize and manipulate sounds in spoken language. Teachers can incorporate interactive read-alouds and songs that emphasize alliteration and phoneme segmentation to strengthen auditory discrimination skills. These activities support literacy development by enhancing children's capacity to hear, identify, and work with phonological units essential for reading and spelling.
Assessing Phonemic and Phonological Awareness Skills
Assessing phonemic awareness involves tasks like identifying and manipulating individual sounds in words, such as phoneme segmentation and deletion. Phonological awareness assessment covers broader skills including rhyme recognition, syllable counting, and onset-rime identification, which help gauge a child's ability to detect sound structures beyond phonemes. Effective evaluation of these skills informs targeted instruction to support reading development in elementary learners.
Supporting Struggling Students: Practical Tips for Educators
Supporting struggling students in phonemic awareness involves focused activities like segmenting sounds and blending phonemes to build decoding skills crucial for reading. Phonological awareness instruction should include rhyming, syllable counting, and sound manipulation exercises to strengthen overall auditory discrimination. Consistent practice using multisensory techniques and individualized interventions can significantly improve struggling learners' ability to recognize and manipulate sound units in spoken language.
Phonemic Awareness vs Phonological Awareness Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com