Push-in support occurs when educators assist students within the general classroom setting, promoting inclusivity and peer interaction. Pull-out support involves taking students to a separate location for individualized instruction, allowing for focused attention on specific skills. Both methods aim to address learning needs but differ in integration and environment.
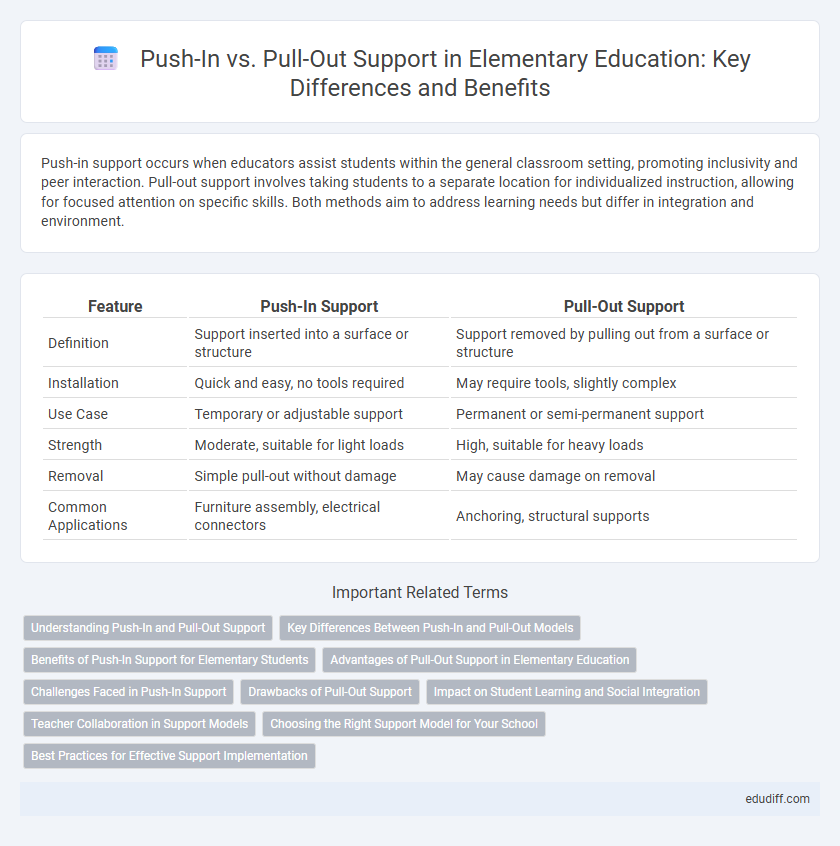
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Push-In Support | Pull-Out Support |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Support inserted into a surface or structure | Support removed by pulling out from a surface or structure |
| Installation | Quick and easy, no tools required | May require tools, slightly complex |
| Use Case | Temporary or adjustable support | Permanent or semi-permanent support |
| Strength | Moderate, suitable for light loads | High, suitable for heavy loads |
| Removal | Simple pull-out without damage | May cause damage on removal |
| Common Applications | Furniture assembly, electrical connectors | Anchoring, structural supports |
Understanding Push-In and Pull-Out Support
Push-in support involves fastening or pressing a component directly into place, providing secure and immediate stability, often used in applications requiring quick assembly without extra tools. Pull-out support refers to the resistance against forces attempting to remove or extract a component, crucial for ensuring long-term durability and load-bearing capacity. Understanding these concepts helps in selecting the right fasteners for construction or mechanical projects, balancing ease of installation with strength and reliability.
Key Differences Between Push-In and Pull-Out Models
Push-In support involves inserting components directly into connectors or sockets, providing quick, reliable electrical connections without additional tools, often used in wiring and electronic assemblies. Pull-Out support requires components to be physically pulled out from their mounted positions, which may need tools or additional effort, commonly found in modular electronic systems or circuit boards. The key difference lies in ease of installation and removal, where push-in models offer faster, tool-free assembly while pull-out models provide secure positioning but potentially slower maintenance access.
Benefits of Push-In Support for Elementary Students
Push-In Support for elementary students enhances learning by allowing specialized educators to collaborate directly within the general classroom environment, promoting inclusivity and reducing stigma. This approach supports immediate intervention and tailored instruction, fostering better engagement and social integration among peers. Students benefit from consistent support without missing core academic activities, improving both academic achievement and self-confidence.
Advantages of Pull-Out Support in Elementary Education
Pull-Out Support in elementary education offers personalized attention by allowing students to work in a smaller, focused setting tailored to their specific learning needs. This method supports targeted skill development, particularly for students requiring intervention in reading, math, or language arts. Pull-Out Support enhances engagement and progress monitoring, leading to measurable improvements in academic performance.
Challenges Faced in Push-In Support
Push-In Support often faces challenges such as limited engagement time between support staff and students due to the presence of the general classroom teacher. Managing varying student needs simultaneously in a crowded setting can reduce the effectiveness of individualized assistance. Distractions and interruptions in a shared learning environment may also hinder focused support during Push-In sessions.
Drawbacks of Pull-Out Support
Pull-out support often creates gaps in learning by removing students from the general classroom environment, which can lead to social isolation and decreased engagement. This method may cause students to miss important instruction time, resulting in fragmented understanding of core subjects. Pull-out support can also reduce the opportunity for teachers to collaborate effectively and adapt lessons to meet individual needs within the classroom setting.
Impact on Student Learning and Social Integration
Push-in support allows students to receive specialized assistance within the general classroom, promoting seamless inclusion and fostering peer interactions that enhance social integration. Pull-out support provides targeted, individualized instruction outside the classroom, which can improve academic skills but may limit opportunities for social engagement with peers. Balancing both approaches optimizes student learning outcomes and supports meaningful social connections in elementary education.
Teacher Collaboration in Support Models
Push-in support involves special education teachers collaborating directly within the general classroom, promoting real-time co-teaching and seamless integration of instructional strategies. Pull-out support removes students from the classroom for targeted intervention, allowing teachers to focus intensively on individual or small group needs. Effective teacher collaboration in push-in models enhances inclusive education by fostering continuous communication and shared planning.
Choosing the Right Support Model for Your School
Choosing the right support model for your elementary school involves evaluating the benefits of Push-In Support and Pull-Out Support based on student needs and classroom dynamics. Push-In Support allows special educators or support staff to work within the general education classroom, promoting inclusion and real-time assistance. Pull-Out Support provides targeted, individualized instruction outside the classroom, ideal for students requiring focused intervention without distractions.
Best Practices for Effective Support Implementation
Push-in support ensures lateral stability by directly resisting forces perpendicular to the supported element, making it ideal for lightweight structures or where minimal displacement is critical. Pull-out support provides anchorage against tensile forces, securing elements subjected to uplifting or withdrawal loads, often used in foundation anchoring. Best practices include selecting support types based on load directions, material compatibility, and ensuring proper installation to maintain structural integrity and durability.
Push-In Support vs Pull-Out Support Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com