Silent reading encourages independent comprehension by allowing students to engage with the text at their own pace, enhancing vocabulary and fluency. Guided reading provides structured support from the teacher, helping students develop decoding skills and improve comprehension through targeted feedback. Combining both methods creates a balanced approach to literacy development in elementary education.
Table of Comparison
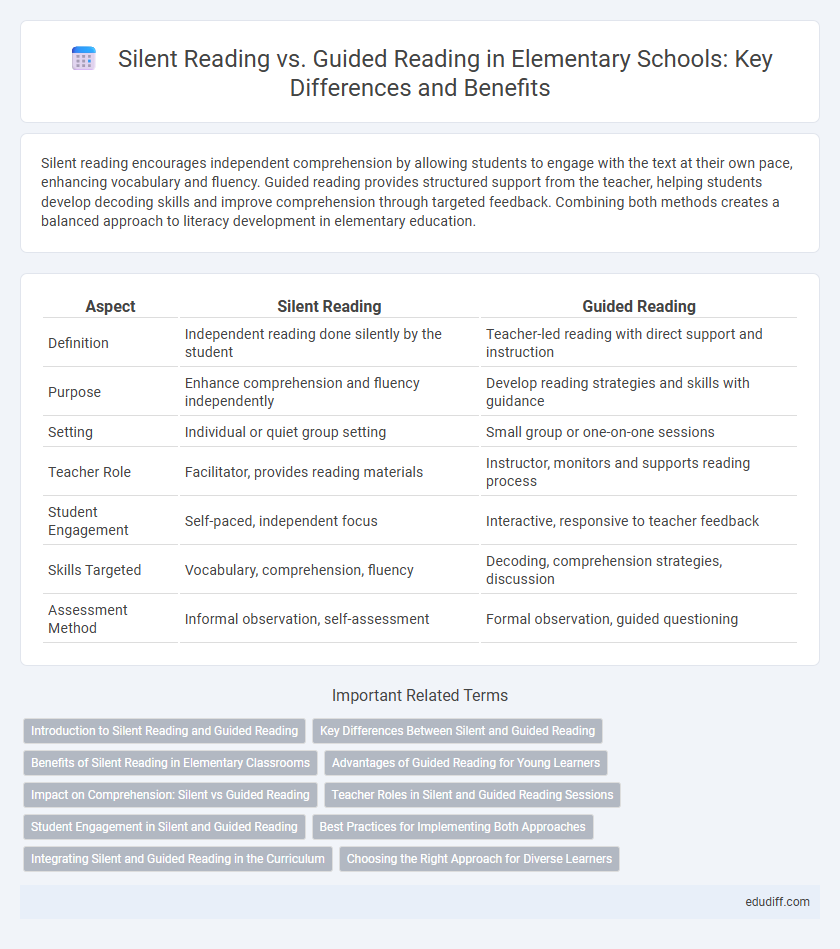
| Aspect | Silent Reading | Guided Reading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Independent reading done silently by the student | Teacher-led reading with direct support and instruction |
| Purpose | Enhance comprehension and fluency independently | Develop reading strategies and skills with guidance |
| Setting | Individual or quiet group setting | Small group or one-on-one sessions |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator, provides reading materials | Instructor, monitors and supports reading process |
| Student Engagement | Self-paced, independent focus | Interactive, responsive to teacher feedback |
| Skills Targeted | Vocabulary, comprehension, fluency | Decoding, comprehension strategies, discussion |
| Assessment Method | Informal observation, self-assessment | Formal observation, guided questioning |
Introduction to Silent Reading and Guided Reading
Silent reading allows elementary students to engage with text independently, fostering improved vocabulary, comprehension, and fluency at their own pace. Guided reading provides structured support from teachers, focusing on targeted skills and strategies to enhance understanding and reading proficiency. Both methods serve distinct roles in developing early literacy by balancing autonomy and instructional guidance.
Key Differences Between Silent and Guided Reading
Silent reading allows elementary students to develop independent comprehension skills by reading text quietly at their own pace. Guided reading involves teacher-led sessions where students receive targeted instruction, immediate feedback, and support in decoding and understanding more complex text. Key differences include the level of teacher involvement, the focus on fluency in guided reading, and the emphasis on self-regulation during silent reading.
Benefits of Silent Reading in Elementary Classrooms
Silent reading in elementary classrooms fosters independent comprehension skills, allowing students to process text at their own pace and enhance vocabulary acquisition. This practice promotes concentration and critical thinking by encouraging individual engagement with diverse reading materials. Research shows that regular silent reading increases reading fluency and builds a lifelong habit of self-directed learning.
Advantages of Guided Reading for Young Learners
Guided reading supports young learners by providing targeted instruction that addresses their individual reading levels and needs, fostering better comprehension and fluency. This method encourages interaction and immediate feedback, which helps develop critical thinking skills and confidence in reading. Teachers can monitor progress closely and adjust lessons to ensure continuous growth in literacy skills for elementary students.
Impact on Comprehension: Silent vs Guided Reading
Silent reading allows students to process text at their own pace, enhancing individual understanding and internalizing vocabulary. Guided reading provides targeted support, enabling educators to scaffold comprehension skills and address specific misunderstandings. Research shows that combining both approaches leads to improved overall reading comprehension in elementary students.
Teacher Roles in Silent and Guided Reading Sessions
In silent reading sessions, teachers primarily monitor student engagement and provide individualized support to foster independent comprehension skills. During guided reading, teachers actively facilitate discussion, model fluency, and offer targeted feedback to address specific reading strategies. Effective teacher roles in both settings enhance student literacy development by balancing autonomy with structured guidance.
Student Engagement in Silent and Guided Reading
Silent reading fosters individual student engagement by allowing learners to develop personal comprehension skills and self-paced focus, while guided reading promotes active participation through teacher-led discussions and targeted support. Research indicates that guided reading sessions enhance student interaction with texts and improve critical thinking, whereas silent reading encourages independent vocabulary growth and reading stamina. Balancing both approaches caters to diverse learning styles, maximizing overall student engagement in elementary classrooms.
Best Practices for Implementing Both Approaches
Silent reading enhances fluency and comprehension by allowing students to engage independently with texts at their own pace, making it essential to provide diverse and level-appropriate materials. Guided reading supports targeted skill development through small group instruction and teacher feedback, requiring careful assessment and planning to meet individual reading needs. Combining both approaches with consistent monitoring and scaffolding maximizes literacy growth in elementary students.
Integrating Silent and Guided Reading in the Curriculum
Integrating silent and guided reading in the elementary curriculum enhances literacy development by balancing independent comprehension with teacher-supported skill building. Silent reading fosters fluency and personal engagement with texts, while guided reading provides targeted instruction tailored to individual student needs. Combining both approaches ensures a comprehensive reading program that supports diverse learning styles and promotes continuous growth in reading proficiency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Silent reading allows elementary students to develop independent comprehension skills and build confidence at their own pace, while guided reading offers targeted support through teacher-led discussions and monitoring. Choosing the right approach depends on individual learner needs, such as reading level, attention span, and language proficiency, ensuring personalized instruction. Combining both methods can enhance literacy development by addressing diverse learning styles and promoting fluency and critical thinking.
Silent Reading vs Guided Reading Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com