Inquiry-based learning encourages students to explore concepts through questions and hands-on activities, fostering critical thinking and deeper understanding. Rote memorization emphasizes repetition and recall, which may help in short-term retention but often limits long-term comprehension and creativity. Emphasizing inquiry-based learning in elementary education supports curiosity and problem-solving skills essential for future academic success.
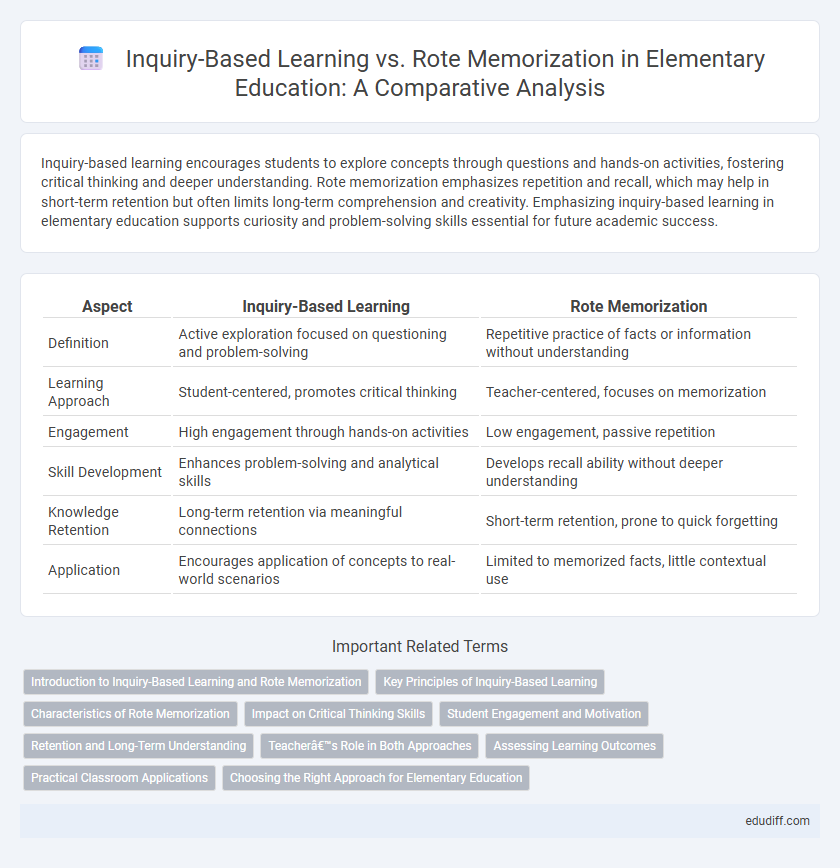
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Rote Memorization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active exploration focused on questioning and problem-solving | Repetitive practice of facts or information without understanding |
| Learning Approach | Student-centered, promotes critical thinking | Teacher-centered, focuses on memorization |
| Engagement | High engagement through hands-on activities | Low engagement, passive repetition |
| Skill Development | Enhances problem-solving and analytical skills | Develops recall ability without deeper understanding |
| Knowledge Retention | Long-term retention via meaningful connections | Short-term retention, prone to quick forgetting |
| Application | Encourages application of concepts to real-world scenarios | Limited to memorized facts, little contextual use |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Rote Memorization
Inquiry-Based Learning encourages elementary students to engage actively by asking questions, exploring, and discovering concepts deeply. Rote Memorization relies on repetitive practice to recall facts quickly, often without understanding underlying principles. Inquiry-Based Learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving, whereas rote memorization primarily enhances short-term retention of information.
Key Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes active student engagement, encouraging children to ask questions and explore topics deeply to build critical thinking skills. This approach fosters curiosity and problem-solving by allowing learners to investigate real-world scenarios rather than passively receiving information. It promotes understanding and retention through discovery, contrasting with rote memorization's focus on repetitive recall without contextual comprehension.
Characteristics of Rote Memorization
Rote memorization in elementary education emphasizes repetitive practice and memorizing facts without understanding underlying concepts, leading to surface-level knowledge retention. This method relies heavily on drills, flashcards, and recitation to reinforce memory through repetition rather than application. While efficient for mastering basic skills like multiplication tables or spelling, rote memorization often limits critical thinking and problem-solving abilities in young learners.
Impact on Critical Thinking Skills
Inquiry-based learning enhances critical thinking skills in elementary students by encouraging exploration, questioning, and problem-solving. Rote memorization mainly focuses on repetition and recall, which limits opportunities for deep analysis and understanding. Research shows that students engaged in inquiry-based methods develop stronger reasoning and adaptability compared to those relying solely on memorization.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Inquiry-Based Learning enhances student engagement by encouraging curiosity, critical thinking, and active participation in exploring topics, leading to deeper understanding and retention. Rote memorization often results in passive learning, which can decrease motivation due to lack of meaningful interaction with the material. Research shows students in inquiry-based environments demonstrate higher motivation and improved problem-solving skills compared to those relying solely on memorization techniques.
Retention and Long-Term Understanding
Inquiry-Based Learning enhances retention and long-term understanding by engaging students in active problem-solving and critical thinking, fostering deeper cognitive connections. Rote memorization leads to short-term retention but often fails to support meaningful comprehension or the application of knowledge over time. Studies show that students involved in inquiry-based approaches demonstrate improved mastery and recall compared to those relying solely on memorization techniques.
Teacher’s Role in Both Approaches
In inquiry-based learning, teachers act as facilitators who guide students to explore, ask questions, and discover knowledge through hands-on activities and critical thinking. In rote memorization, teachers primarily deliver information for students to memorize through repetition and drills, with less emphasis on understanding. The teacher's role shifts from information provider to learning coach, fostering curiosity and deeper comprehension in inquiry-based settings.
Assessing Learning Outcomes
Inquiry-based learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore and understand concepts deeply, leading to more meaningful retention and application. Rote memorization primarily supports the recall of facts, which may result in surface-level understanding and limited transfer of knowledge to new situations. Assessing learning outcomes in inquiry-based learning often involves evaluating analytical skills and creativity, while rote memorization assessments typically focus on accuracy and speed of fact retrieval.
Practical Classroom Applications
Inquiry-based learning encourages elementary students to explore concepts through hands-on activities and critical thinking, enhancing deep understanding and retention. Rote memorization emphasizes repetition and recall, useful for foundational facts like multiplication tables or spelling. Implementing inquiry-based approaches in lessons fosters curiosity and problem-solving skills, while rote techniques support memorization of essential information.
Choosing the Right Approach for Elementary Education
Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging elementary students to explore concepts through questions and hands-on activities. Rote memorization emphasizes repetition and recall, which helps reinforce fundamental facts but may limit creativity and problem-solving skills. Selecting the right approach depends on curricular goals, student needs, and balancing foundational knowledge with opportunities for active discovery.
Inquiry-Based Learning vs Rote Memorization Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com