Inquiry-based science encourages students to explore questions, conduct experiments, and develop critical thinking skills through hands-on learning, while textbook science typically relies on memorization and passive reading. Students engaged in inquiry-based learning often demonstrate deeper understanding and retention of scientific concepts. This approach promotes curiosity and active participation, making science more engaging and relevant to young learners.
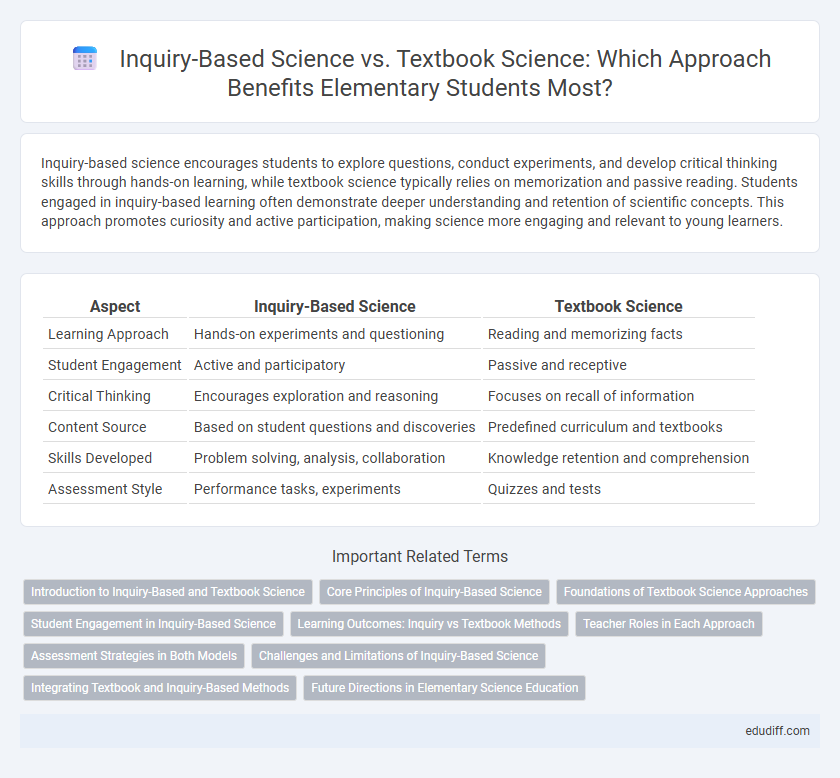
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Science | Textbook Science |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Approach | Hands-on experiments and questioning | Reading and memorizing facts |
| Student Engagement | Active and participatory | Passive and receptive |
| Critical Thinking | Encourages exploration and reasoning | Focuses on recall of information |
| Content Source | Based on student questions and discoveries | Predefined curriculum and textbooks |
| Skills Developed | Problem solving, analysis, collaboration | Knowledge retention and comprehension |
| Assessment Style | Performance tasks, experiments | Quizzes and tests |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based and Textbook Science
Inquiry-Based Science engages elementary students by encouraging hands-on exploration and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding through active participation. Textbook Science relies on structured content and predefined concepts, primarily focusing on memorization and passive learning. Emphasizing inquiry promotes curiosity and scientific reasoning, essential for developing problem-solving skills at an early age.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Science
Inquiry-Based Science emphasizes student-driven exploration, prioritizing hands-on experiments and critical thinking to foster deeper understanding of scientific concepts. Core principles include formulating questions, conducting investigations, analyzing data, and drawing evidence-based conclusions. This approach contrasts with traditional Textbook Science, which often relies on passive reading and memorization of facts.
Foundations of Textbook Science Approaches
Textbook science approaches in elementary education emphasize structured content delivery, focusing on established scientific facts and standardized assessments to build foundational knowledge. These methods prioritize clear objectives, organized chapters, and reproducible experiments that align with curriculum standards. The foundations of textbook science rely on sequential learning, ensuring students master core concepts before progressing to more complex topics.
Student Engagement in Inquiry-Based Science
Inquiry-based science significantly boosts student engagement by encouraging active participation through experiments and hands-on activities. Unlike traditional textbook science, it fosters curiosity and critical thinking, allowing students to explore concepts deeply. This interactive approach leads to better retention and enthusiasm for learning scientific principles in elementary education.
Learning Outcomes: Inquiry vs Textbook Methods
Inquiry-based science promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and deeper conceptual understanding by engaging students in hands-on experiments and exploration. Textbook science often emphasizes memorization and passive learning, which may limit students' ability to apply knowledge practically. Studies show inquiry methods improve retention and foster scientific reasoning skills more effectively than traditional textbook approaches.
Teacher Roles in Each Approach
Inquiry-based science positions teachers as facilitators who guide students to explore and discover scientific concepts through hands-on experiments and questioning. In textbook science, teachers primarily act as knowledge transmitters, delivering structured content and ensuring students understand established facts. The shift highlights a move from passive learning to active engagement, with inquiry fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Assessment Strategies in Both Models
Inquiry-Based Science assessments emphasize student-generated explanations, hands-on experiments, and critical thinking skills to gauge understanding, promoting deeper cognitive engagement. Textbook Science assessments typically rely on standardized tests, multiple-choice questions, and memorization of facts, focusing on content retention and accuracy. Combining formative assessment methods in inquiry models and summative evaluations in textbook approaches offers a balanced strategy to measure both conceptual understanding and factual knowledge.
Challenges and Limitations of Inquiry-Based Science
Inquiry-based science in elementary education often faces challenges such as limited classroom time and insufficient teacher training, which can hinder effective implementation. Students may struggle with open-ended questions and inquiry processes without foundational knowledge typically provided by textbooks. Additionally, resource constraints and standardized testing pressures limit the depth and frequency of inquiry-based activities in many elementary schools.
Integrating Textbook and Inquiry-Based Methods
Integrating textbook and inquiry-based science methods in elementary education enhances student engagement and comprehension by combining structured knowledge with hands-on exploration. Textbooks provide essential foundational content and vocabulary, while inquiry-based activities encourage critical thinking and real-world application of concepts. This blended approach supports diverse learning styles and fosters deeper understanding of scientific principles.
Future Directions in Elementary Science Education
Inquiry-based science encourages elementary students to engage actively with experiments and real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and curiosity. Future directions in elementary science education emphasize integrating technology and hands-on activities to personalize learning and promote scientific literacy. Shifting from traditional textbook-centered methods to inquiry-based approaches aims to prepare students for complex problem-solving in a rapidly changing world.
Inquiry-Based Science vs Textbook Science Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com