Socratic questioning encourages critical thinking through open-ended questions that lead students to explore ideas deeply. Direct instruction provides clear, structured guidance by delivering information and explanations directly to learners. Combining both methods can enhance understanding by promoting active engagement and ensuring foundational knowledge.
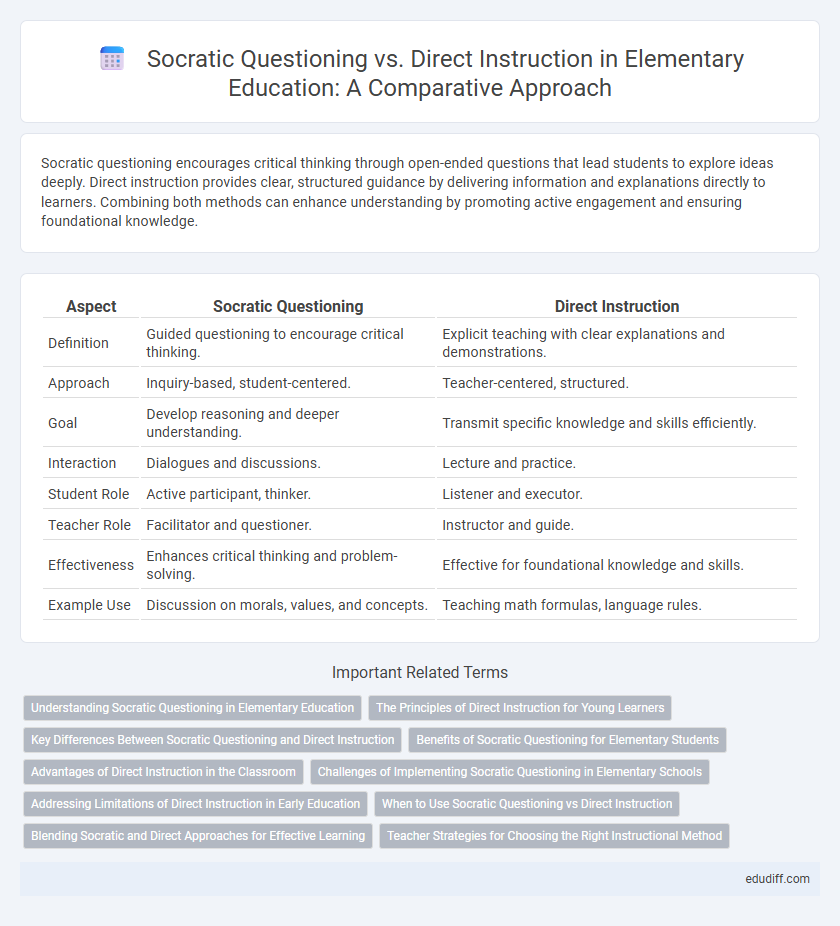
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Socratic Questioning | Direct Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guided questioning to encourage critical thinking. | Explicit teaching with clear explanations and demonstrations. |
| Approach | Inquiry-based, student-centered. | Teacher-centered, structured. |
| Goal | Develop reasoning and deeper understanding. | Transmit specific knowledge and skills efficiently. |
| Interaction | Dialogues and discussions. | Lecture and practice. |
| Student Role | Active participant, thinker. | Listener and executor. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and questioner. | Instructor and guide. |
| Effectiveness | Enhances critical thinking and problem-solving. | Effective for foundational knowledge and skills. |
| Example Use | Discussion on morals, values, and concepts. | Teaching math formulas, language rules. |
Understanding Socratic Questioning in Elementary Education
Socratic questioning enhances critical thinking and comprehension in elementary students by promoting dialogue, curiosity, and deeper analysis of concepts. This method encourages learners to explore ideas through guided questions, fostering independent thought more effectively than direct instruction. Teachers using Socratic questioning create a dynamic classroom environment where students actively construct knowledge rather than passively receive information.
The Principles of Direct Instruction for Young Learners
Direct Instruction for young learners emphasizes clear, structured teaching with explicit objectives and step-by-step guidance to build foundational skills effectively. It relies on frequent practice, immediate feedback, and mastery checks to ensure student comprehension and retention. This approach supports early development by providing predictable routines that reinforce learning through repetition and active teacher involvement.
Key Differences Between Socratic Questioning and Direct Instruction
Socratic questioning engages students through guided inquiry, encouraging critical thinking and deeper understanding by posing thoughtful questions rather than providing answers. Direct instruction delivers clear, structured teaching with explicit explanations aimed at quickly conveying specific knowledge or skills. The primary difference lies in the active student participation and exploration promoted by Socratic questioning versus the teacher-centered, straightforward approach of direct instruction.
Benefits of Socratic Questioning for Elementary Students
Socratic questioning encourages elementary students to develop critical thinking skills by prompting them to explore ideas deeply and articulate their understanding. This method fosters active learning, enhancing student engagement and promoting curiosity through open-ended questions. By nurturing reasoning abilities early, Socratic questioning supports better problem-solving skills and long-term academic success.
Advantages of Direct Instruction in the Classroom
Direct Instruction provides clear, structured guidance that helps elementary students grasp foundational concepts efficiently. It ensures consistent coverage of curriculum standards and promotes measurable academic progress through systematic practice. Teachers can easily identify and address learning gaps, enhancing overall student mastery and confidence.
Challenges of Implementing Socratic Questioning in Elementary Schools
Socratic questioning in elementary schools faces challenges due to students' limited critical thinking development and shorter attention spans. Teachers may struggle to balance open-ended inquiry with curriculum requirements and standardized testing pressures. Effective implementation requires extensive teacher training to foster inquiry-based learning while ensuring foundational knowledge is conveyed.
Addressing Limitations of Direct Instruction in Early Education
Direct instruction in early education often limits critical thinking by focusing on rote memorization and teacher-led explanations. Socratic questioning encourages young learners to explore ideas deeply, fostering curiosity and independent reasoning skills. By integrating Socratic methods, educators can address the passive learning habits formed through direct instruction and promote active engagement.
When to Use Socratic Questioning vs Direct Instruction
Socratic questioning is ideal for fostering critical thinking and deep understanding in elementary students by encouraging them to explore ideas and develop reasoning skills through guided dialogue. Direct instruction works best when new information, basic skills, or clear procedures need to be conveyed efficiently and with minimal confusion. Choosing between these methods depends on the learning objectives: use Socratic questioning for conceptual exploration and problem-solving, and direct instruction for foundational knowledge and skill acquisition.
Blending Socratic and Direct Approaches for Effective Learning
Blending Socratic questioning with direct instruction in elementary education enhances critical thinking and knowledge retention by encouraging active engagement and clear guidance. Teachers can prompt students with thought-provoking questions while systematically delivering key concepts to ensure comprehension. This approach fosters deeper understanding and supports diverse learning styles by integrating inquiry-based dialogue with structured teaching methods.
Teacher Strategies for Choosing the Right Instructional Method
Teachers selecting between Socratic questioning and direct instruction assess student engagement levels and learning objectives to optimize comprehension. Socratic questioning encourages critical thinking and deeper understanding by prompting students to explore ideas, while direct instruction offers clear, structured explanations suitable for introducing new content or foundational skills. Effective strategies balance these methods by adapting to classroom dynamics and individual learner needs, enhancing overall educational outcomes.
Socratic Questioning vs Direct Instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com