Homeroom classrooms involve students rotating to different subject teachers throughout the day, allowing them to experience various teaching styles and specialized instruction. Self-contained classrooms keep the same teacher with the students all day, fostering strong relationships and a consistent learning environment. Both models support student growth differently, depending on individual needs and school resources.
Table of Comparison
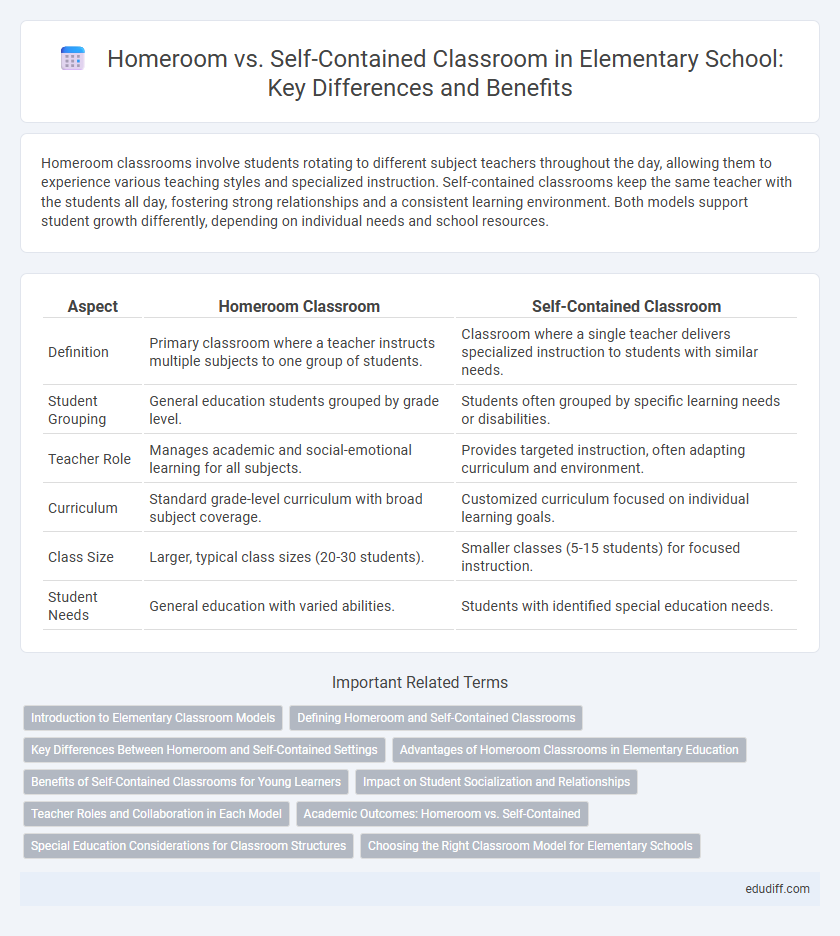
| Aspect | Homeroom Classroom | Self-Contained Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Primary classroom where a teacher instructs multiple subjects to one group of students. | Classroom where a single teacher delivers specialized instruction to students with similar needs. |
| Student Grouping | General education students grouped by grade level. | Students often grouped by specific learning needs or disabilities. |
| Teacher Role | Manages academic and social-emotional learning for all subjects. | Provides targeted instruction, often adapting curriculum and environment. |
| Curriculum | Standard grade-level curriculum with broad subject coverage. | Customized curriculum focused on individual learning goals. |
| Class Size | Larger, typical class sizes (20-30 students). | Smaller classes (5-15 students) for focused instruction. |
| Student Needs | General education with varied abilities. | Students with identified special education needs. |
Introduction to Elementary Classroom Models
Elementary classroom models include homeroom and self-contained setups, each designed for different learning environments. Homeroom classrooms have students rotate between specialized teachers for subjects, promoting focused expertise and varied instruction. Self-contained classrooms feature one teacher responsible for all subjects, fostering consistent relationships and tailored support throughout the school day.
Defining Homeroom and Self-Contained Classrooms
Homeroom is a designated classroom period where students gather for attendance, announcements, and brief instruction but typically transition to different classes for subjects. Self-contained classrooms house the same group of elementary students with one teacher managing most or all subjects throughout the day. The self-contained model promotes consistency and deeper relationships by reducing the number of teachers and classroom changes.
Key Differences Between Homeroom and Self-Contained Settings
Homeroom classrooms generally involve students attending multiple subject-specific classes with different teachers throughout the day, promoting varied instructional methods. Self-contained classrooms have one teacher who provides instruction for most or all subjects, offering consistent routines and personalized attention for students with diverse learning needs. The key difference lies in the structure and teacher assignment, where homeroom supports a broader curriculum exposure and self-contained emphasizes individualized support.
Advantages of Homeroom Classrooms in Elementary Education
Homeroom classrooms in elementary education foster strong teacher-student relationships by providing a consistent learning environment with one main educator responsible for multiple subjects. This structure enhances personalized instruction and allows for better monitoring of student progress and social-emotional development. Homeroom settings also encourage collaboration among students, promoting a supportive classroom community.
Benefits of Self-Contained Classrooms for Young Learners
Self-contained classrooms offer young learners a consistent and supportive environment tailored to their developmental needs, promoting stronger teacher-student relationships and individualized instruction. This structure enhances focus and reduces transitions, which helps students grasp foundational skills more effectively. Specialized support in self-contained settings also fosters social-emotional growth and academic confidence among elementary students.
Impact on Student Socialization and Relationships
Homeroom classrooms promote student socialization by allowing interaction with multiple teachers and peers throughout the day, fostering diverse relationships and social skills. Self-contained classrooms provide consistent peer groups and a single teacher, which can strengthen close-knit bonds but may limit broader social exposure. The impact on student relationships depends on the balance between variety in social settings and stability within a consistent classroom environment.
Teacher Roles and Collaboration in Each Model
In homeroom settings, teachers specialize in specific subjects, fostering collaboration through coordinated lesson planning and shared resource development. Self-contained classrooms feature teachers managing all subjects for the same group of students, promoting a holistic approach and continuous monitoring of individual progress. Collaboration in self-contained models often involves integrative strategies with support staff to address diverse student needs comprehensively.
Academic Outcomes: Homeroom vs. Self-Contained
Homeroom classrooms, where students transition to different subject-specific teachers, often promote diverse academic engagement and specialization, enhancing subject mastery. Self-contained classrooms, with one teacher responsible for all subjects, provide consistent instruction and tailored support, which benefits students needing structured learning environments. Research shows students in self-contained settings may experience improved academic outcomes in foundational skills, while homeroom models excel in fostering independent learning and critical thinking.
Special Education Considerations for Classroom Structures
Special education considerations in elementary education require careful evaluation of homeroom versus self-contained classrooms to best support students with diverse learning needs. Homeroom classrooms integrate special education students with general peers, promoting social interaction while providing targeted support, whereas self-contained classrooms offer a specialized, resource-rich environment tailored to intensive intervention and individualized instruction. Educators must assess the child's academic, behavioral, and social requirements to determine the optimal classroom structure that maximizes growth and inclusion.
Choosing the Right Classroom Model for Elementary Schools
Choosing the right classroom model for elementary schools depends on student needs and instructional goals. Homeroom classrooms allow students to remain with one teacher, fostering strong relationships and consistent routines, while self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction tailored to diverse learning styles within a single setting. Evaluating factors such as class size, teacher expertise, and student diversity helps administrators select the optimal structure to enhance academic achievement and social development.
Homeroom vs Self-Contained Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com