Recess time provides essential breaks that improve children's focus and social skills, while extended learning time offers more opportunities for academic enrichment and skill development. Balancing recess with extended learning ensures students benefit from both physical activity and increased instructional time. Prioritizing both aspects supports overall student well-being and academic success.
Table of Comparison
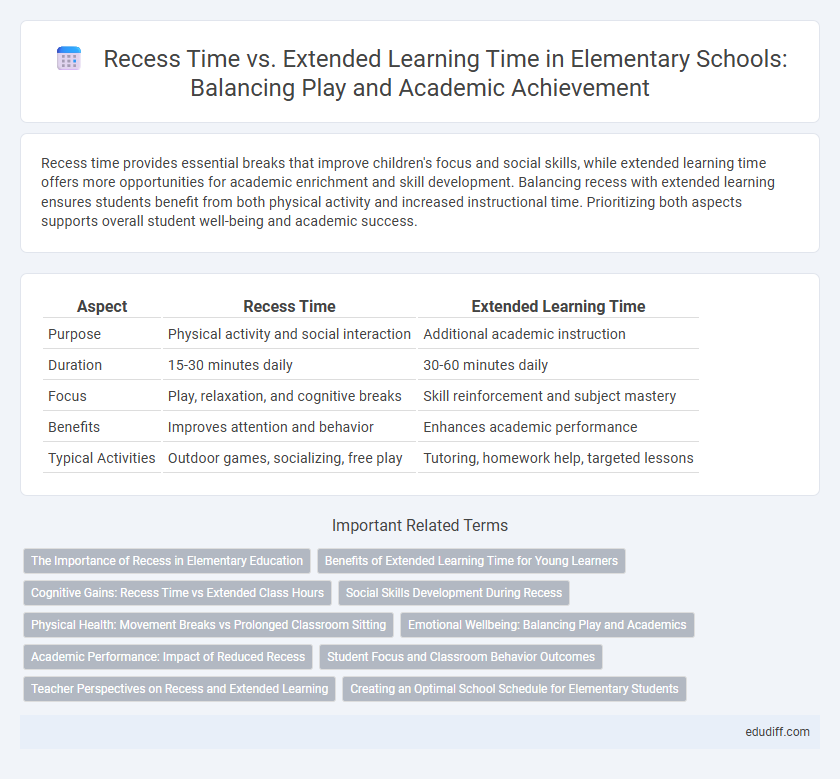
| Aspect | Recess Time | Extended Learning Time |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Physical activity and social interaction | Additional academic instruction |
| Duration | 15-30 minutes daily | 30-60 minutes daily |
| Focus | Play, relaxation, and cognitive breaks | Skill reinforcement and subject mastery |
| Benefits | Improves attention and behavior | Enhances academic performance |
| Typical Activities | Outdoor games, socializing, free play | Tutoring, homework help, targeted lessons |
The Importance of Recess in Elementary Education
Recess time in elementary education is essential for students' physical health, social development, and cognitive function, providing a necessary break that enhances focus and classroom engagement. Research indicates that children benefit from unstructured play as it improves attention span, reduces stress, and fosters creativity, which cannot be replicated during extended learning time. Balancing recess with instructional periods supports overall academic achievement by promoting well-being and active learning.
Benefits of Extended Learning Time for Young Learners
Extended learning time in elementary schools enhances young learners' academic performance by allowing more opportunities for reading, math practice, and hands-on activities. It supports social-emotional development through structured group work and personalized teacher interactions that build stronger relationships. Research shows that extended learning time reduces achievement gaps and promotes long-term educational success for children.
Cognitive Gains: Recess Time vs Extended Class Hours
Recess time enhances cognitive gains by allowing elementary students to engage in physical activity and social interaction, which boost brain function and improve focus in subsequent lessons. Extended learning hours often lead to fatigue, reducing attention span and diminishing the effectiveness of classroom instruction. Research shows balanced recess supports memory retention and problem-solving skills more effectively than prolonged class time.
Social Skills Development During Recess
Recess time provides essential opportunities for elementary students to develop social skills such as cooperation, conflict resolution, and empathy through unstructured play and peer interaction. Extended learning time often prioritizes academic instruction but may limit these spontaneous social experiences that contribute to emotional intelligence and teamwork abilities. Research indicates that regular recess fosters stronger peer relationships and enhances students' abilities to navigate social challenges effectively.
Physical Health: Movement Breaks vs Prolonged Classroom Sitting
Movement breaks during recess significantly boost elementary students' physical health by reducing the risks associated with prolonged classroom sitting, such as obesity and poor posture. Extended learning time often means longer sedentary periods, which can hinder circulation and lead to decreased concentration and energy levels. Incorporating frequent physical activity through recess supports cardiovascular health, muscle development, and overall well-being in young learners.
Emotional Wellbeing: Balancing Play and Academics
Recess time in elementary schools plays a crucial role in supporting emotional wellbeing by providing students with opportunities for unstructured play, social interaction, and stress relief. Extended learning time can improve academic outcomes but risks increasing student burnout and anxiety if not balanced with adequate breaks. Ensuring a harmonious blend of recess and focused study promotes both emotional health and cognitive development in young learners.
Academic Performance: Impact of Reduced Recess
Reduced recess time negatively affects elementary students' academic performance by diminishing opportunities for physical activity essential for cognitive development. Studies indicate that limiting recess correlates with increased behavioral issues and decreased attention spans during classroom instruction. Extended learning time cannot fully compensate for the benefits of unstructured play, which enhances memory retention, creativity, and social skills critical to academic success.
Student Focus and Classroom Behavior Outcomes
Recess time enhances student focus by providing essential physical activity and mental breaks, which reduce restlessness and improve attention during learning. Extended learning time can increase academic exposure but often leads to diminished student engagement and heightened behavioral issues without proper balance. Prioritizing recess supports better classroom behavior outcomes by promoting self-regulation and social skills, critical for effective learning environments.
Teacher Perspectives on Recess and Extended Learning
Elementary teachers often view recess as a critical time for students to develop social skills, improve concentration, and reduce stress, which enhances overall learning outcomes. Many educators emphasize extended learning time as essential for reinforcing academic content and providing individualized support, especially for students needing extra help. Balancing recess with extended learning requires teachers to consider both cognitive development and emotional well-being to optimize student success.
Creating an Optimal School Schedule for Elementary Students
Balancing recess time and extended learning time is critical for creating an optimal school schedule that promotes both academic success and student well-being in elementary schools. Research indicates that frequent, well-timed recess boosts concentration and cognitive function, while structured extended learning time enhances skill mastery and academic achievement. Prioritizing strategic intervals for physical activity alongside targeted instructional periods fosters a holistic learning environment tailored to young learners' developmental needs.
Recess Time vs Extended Learning Time Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com