Story mapping organizes key elements and sequence of events visually, helping students understand plot structure and relationships. Story retelling encourages verbal or written reproduction of the narrative, strengthening comprehension and recall. Both techniques enhance literacy skills but target different cognitive processes: mapping aids in analysis while retelling emphasizes memory and expression.
Table of Comparison
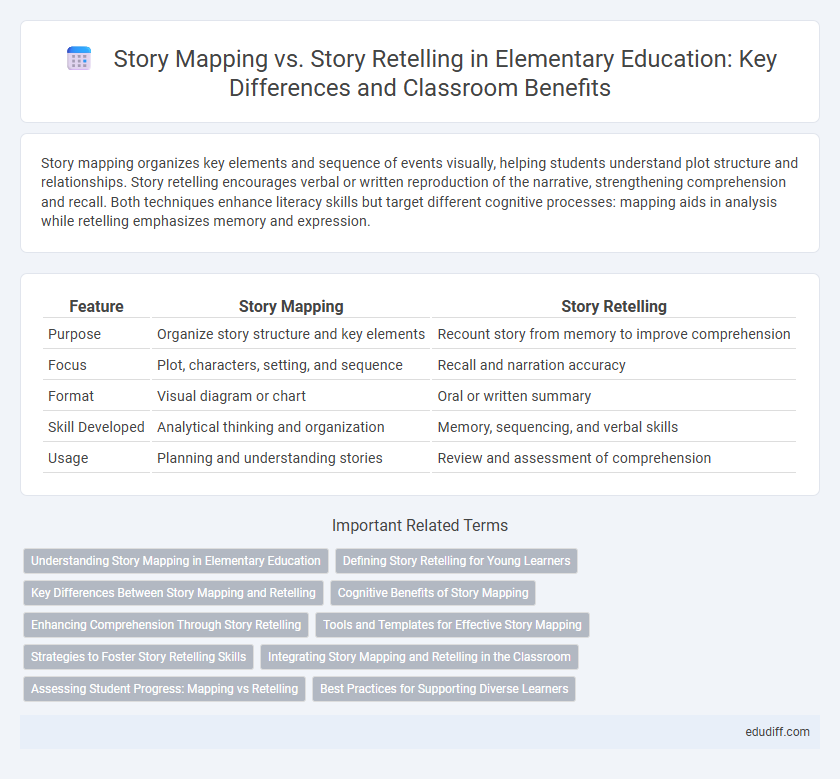
| Feature | Story Mapping | Story Retelling |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Organize story structure and key elements | Recount story from memory to improve comprehension |
| Focus | Plot, characters, setting, and sequence | Recall and narration accuracy |
| Format | Visual diagram or chart | Oral or written summary |
| Skill Developed | Analytical thinking and organization | Memory, sequencing, and verbal skills |
| Usage | Planning and understanding stories | Review and assessment of comprehension |
Understanding Story Mapping in Elementary Education
Story mapping in elementary education enhances comprehension by visually organizing key story elements such as characters, setting, plot, and resolution. This strategy supports students in identifying relationships and sequencing events, which builds a stronger foundation for reading and narrative skills. Unlike story retelling, story mapping provides a structured framework that aids memory retention and critical thinking about the text.
Defining Story Retelling for Young Learners
Story retelling for young learners involves recalling and narrating key events from a story using their own words, which enhances comprehension and memory skills. This process encourages children to focus on the sequence of events, main characters, and important details, fostering narrative understanding. Unlike story mapping, story retelling emphasizes verbal expression and personal interpretation, helping build language development and storytelling confidence.
Key Differences Between Story Mapping and Retelling
Story mapping involves organizing a story's main elements like characters, setting, and plot visually to aid comprehension and retention. Story retelling focuses on verbally recounting the story in one's own words, which enhances memory and expressive skills. Story mapping emphasizes structure and details, while retelling highlights narrative fluency and oral communication.
Cognitive Benefits of Story Mapping
Story mapping enhances comprehension by visually organizing key story elements such as characters, setting, and plot, which supports memory retention and sequencing skills in elementary students. This technique fosters critical thinking and helps children identify cause-and-effect relationships within the narrative. By providing a structured framework, story mapping promotes deeper engagement and improves overall literacy development compared to story retelling alone.
Enhancing Comprehension Through Story Retelling
Story retelling strengthens students' comprehension by encouraging active recall and attention to narrative details, fostering deeper understanding. Unlike story mapping, which visually organizes story elements, retelling emphasizes verbal expression and memory retrieval, helping solidify plot, characters, and sequence. This practice improves language skills and retention, making story retelling a powerful tool for enhancing comprehension in elementary learners.
Tools and Templates for Effective Story Mapping
Story mapping utilizes visual tools like storyboards, sticky notes, and graphic organizers to help students organize and sequence narrative elements effectively. Templates designed for story mapping often include sections for characters, settings, problems, and resolutions, allowing children to break down stories in a structured way. These resources promote comprehension and creativity, contrasting with story retelling, which relies more on verbal recall without such detailed frameworks.
Strategies to Foster Story Retelling Skills
Story mapping develops comprehension by visually organizing plot elements such as characters, setting, and sequence, which supports memory retention. Story retelling emphasizes oral or written narrative reconstruction, encouraging children to verbalize understanding and use expressive language skills. Strategies to foster story retelling include guided prompts, use of graphic organizers, and repeated practice with feedback to enhance detail recollection and narrative coherence.
Integrating Story Mapping and Retelling in the Classroom
Integrating story mapping and retelling in the classroom enhances students' comprehension by visually organizing story elements and reinforcing memory through verbal expression. Story mapping helps elementary learners identify characters, settings, and key events, while retelling encourages active engagement and language development. Combining both strategies supports critical thinking and improves narrative skills essential for literacy growth.
Assessing Student Progress: Mapping vs Retelling
Story mapping helps assess student progress by visually organizing key story elements, allowing teachers to evaluate understanding of plot, characters, and setting. Story retelling measures comprehension through students' verbal recall and narrative sequencing, revealing their grasp of story details and language skills. Both methods provide valuable insights, with mapping emphasizing structural analysis and retelling focusing on expressive language development.
Best Practices for Supporting Diverse Learners
Story mapping offers a visual framework that helps diverse learners organize key story elements such as characters, setting, and plot, enhancing comprehension and retention. Story retelling encourages verbal expression and recall, supporting language development and reinforcing narrative structure through repetition. Combining both strategies provides a balanced approach, meeting the varied needs of elementary students by fostering understanding and communication skills.
Story Mapping vs Story Retelling Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com