The candidacy exam evaluates a graduate student's comprehensive knowledge in their field to ensure readiness for advanced research, while the proposal defense specifically assesses the feasibility and scholarly merit of the planned research project. Passing the candidacy exam allows the student to advance to doctoral candidacy status, whereas the proposal defense is a crucial step to obtain approval for the dissertation plan. Both milestones are integral to progressing through the graduate program, focusing on knowledge mastery versus project validation.
Table of Comparison
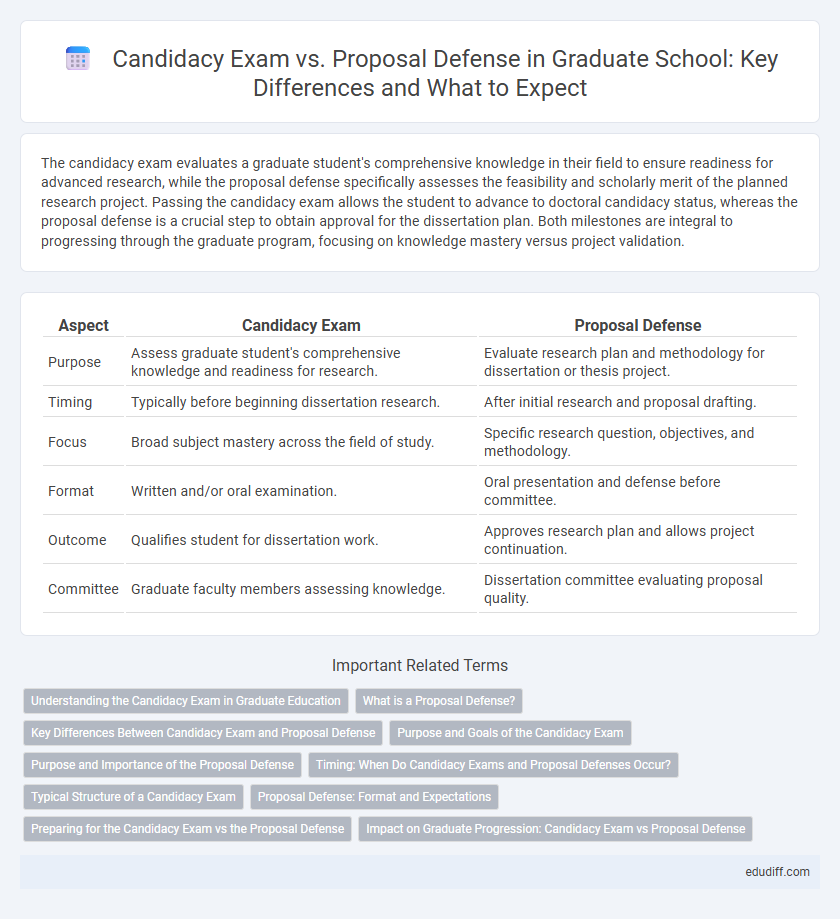
| Aspect | Candidacy Exam | Proposal Defense |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Assess graduate student's comprehensive knowledge and readiness for research. | Evaluate research plan and methodology for dissertation or thesis project. |
| Timing | Typically before beginning dissertation research. | After initial research and proposal drafting. |
| Focus | Broad subject mastery across the field of study. | Specific research question, objectives, and methodology. |
| Format | Written and/or oral examination. | Oral presentation and defense before committee. |
| Outcome | Qualifies student for dissertation work. | Approves research plan and allows project continuation. |
| Committee | Graduate faculty members assessing knowledge. | Dissertation committee evaluating proposal quality. |
Understanding the Candidacy Exam in Graduate Education
The candidacy exam in graduate education serves as a critical assessment to evaluate a student's mastery of core knowledge in their discipline and readiness for independent research. This exam typically tests comprehensive understanding through written and oral formats, ensuring candidates possess the foundational expertise necessary before progressing to their dissertation proposal. Successfully passing the candidacy exam confirms a student's qualification to advance to the proposal defense, where the focus shifts to presenting and refining their specific research plan.
What is a Proposal Defense?
A Proposal Defense is a critical milestone in graduate studies where a student presents and justifies their research plan to a committee of faculty experts. It involves outlining research objectives, methodology, and expected contributions to demonstrate the project's feasibility and academic significance. Successful proposal defense approval allows the student to advance to the dissertation research and writing phase.
Key Differences Between Candidacy Exam and Proposal Defense
The candidacy exam primarily evaluates a graduate student's comprehensive knowledge and readiness to conduct independent research, focusing on core concepts and theoretical understanding within the field. The proposal defense centers on the student's specific research plan, assessing the feasibility, methodology, and significance of the proposed study. Key differences include the candidacy exam's broader scope in testing subject mastery versus the proposal defense's emphasis on detailed research design and objectives.
Purpose and Goals of the Candidacy Exam
The Candidacy Exam primarily evaluates a graduate student's comprehensive knowledge and readiness to undertake specialized research, ensuring mastery of core concepts and methodologies within their field. It serves to confirm the student's qualification to progress from coursework to independent research, acting as a critical milestone for doctoral candidacy status. Unlike the Proposal Defense, which centers on validating the research plan and feasibility, the Candidacy Exam focuses on assessing overall academic competency and foundational expertise.
Purpose and Importance of the Proposal Defense
The proposal defense serves as a critical milestone in a graduate student's research journey, validating the feasibility and significance of the proposed study before substantial resources are committed. Unlike the candidacy exam, which assesses comprehensive knowledge across the discipline, the proposal defense focuses on the specific research plan, methodology, and anticipated contributions. Its importance lies in securing faculty approval and guiding the student toward successful dissertation completion through rigorous feedback and refinement.
Timing: When Do Candidacy Exams and Proposal Defenses Occur?
Candidacy exams typically occur after completing essential coursework, often in the early to mid-stages of a graduate program, serving as a benchmark to assess a student's readiness for independent research. Proposal defenses usually follow successful candidacy exam completion and precede the dissertation research phase, focusing on obtaining approval for the planned research project. Timing varies by institution but generally, candidacy exams mark the transition from coursework to research, while proposal defenses initiate the formal dissertation process.
Typical Structure of a Candidacy Exam
The typical structure of a candidacy exam includes a written component testing comprehensive knowledge across the student's major field and related disciplines, followed by an oral examination where candidates defend their mastery and ability to integrate concepts. This exam often evaluates analytical skills, theoretical understanding, and research readiness essential for advancing to dissertation work. Unlike the proposal defense, which centers on the specific research plan and methodology, the candidacy exam assesses broader academic competence and foundational expertise.
Proposal Defense: Format and Expectations
Proposal Defense in graduate programs typically requires a formal presentation of the research plan, methodology, and significance, followed by a detailed question-and-answer session with the committee. The format emphasizes clarity, feasibility, and scholarly rigor, with candidates expected to demonstrate a thorough understanding of relevant literature and articulate how their research advances the field. Successful Proposal Defense ensures alignment of research objectives and methodology before proceeding to the dissertation phase.
Preparing for the Candidacy Exam vs the Proposal Defense
Preparing for the candidacy exam involves comprehensive review of core coursework, mastering fundamental theories, and synthesizing key research methodologies to demonstrate a broad understanding of the field. In contrast, preparation for the proposal defense requires the development of a clear, detailed research plan, including objectives, hypotheses, and methodology, to convince a committee of the project's feasibility and significance. Effective time management and targeted study resources tailored to each stage maximize success in passing the candidacy exam and gaining approval during the proposal defense.
Impact on Graduate Progression: Candidacy Exam vs Proposal Defense
The Candidacy Exam serves as a critical milestone assessing a graduate student's comprehensive knowledge and readiness to proceed with independent research, directly influencing their eligibility to continue in the program. The Proposal Defense evaluates the feasibility and significance of the planned research project, determining the approval to commence dissertation work and affecting the timeline for degree completion. Both components are essential in graduate progression, with the Candidacy Exam focusing on foundational expertise and the Proposal Defense on research direction and execution.
Candidacy Exam vs Proposal Defense Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com