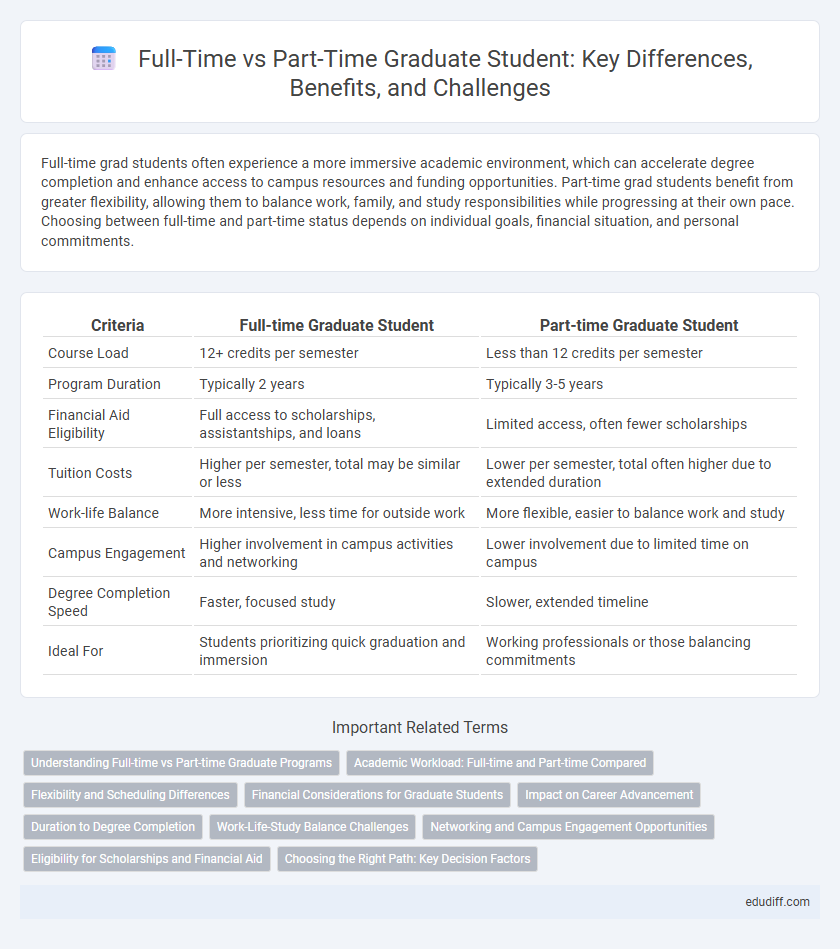
Full-time grad students often experience a more immersive academic environment, which can accelerate degree completion and enhance access to campus resources and funding opportunities. Part-time grad students benefit from greater flexibility, allowing them to balance work, family, and study responsibilities while progressing at their own pace. Choosing between full-time and part-time status depends on individual goals, financial situation, and personal commitments.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Full-time Graduate Student | Part-time Graduate Student |
|---|---|---|
| Course Load | 12+ credits per semester | Less than 12 credits per semester |
| Program Duration | Typically 2 years | Typically 3-5 years |
| Financial Aid Eligibility | Full access to scholarships, assistantships, and loans | Limited access, often fewer scholarships |
| Tuition Costs | Higher per semester, total may be similar or less | Lower per semester, total often higher due to extended duration |
| Work-life Balance | More intensive, less time for outside work | More flexible, easier to balance work and study |
| Campus Engagement | Higher involvement in campus activities and networking | Lower involvement due to limited time on campus |
| Degree Completion Speed | Faster, focused study | Slower, extended timeline |
| Ideal For | Students prioritizing quick graduation and immersion | Working professionals or those balancing commitments |
Understanding Full-time vs Part-time Graduate Programs
Full-time graduate programs typically require 9 to 12 credit hours per semester, enabling students to complete their degrees faster and access more campus resources and financial aid. Part-time graduate students usually enroll in fewer than 9 credits per semester, allowing flexibility to balance work or personal commitments but extending the time to degree completion. Understanding these differences helps prospective graduates choose a path aligned with their career goals, financial situation, and lifestyle preferences.
Academic Workload: Full-time and Part-time Compared
Full-time graduate students typically enroll in 9 to 12 credit hours per semester, balancing a heavy academic workload that includes coursework, research, and often teaching responsibilities. Part-time graduate students usually take fewer than 9 credit hours, allowing more flexibility but extending the duration required to complete their degree. The intensity of academic commitments differs significantly, with full-time students experiencing a more immersive and fast-paced educational environment compared to the gradual progression of part-time students.
Flexibility and Scheduling Differences
Full-time graduate students often follow a structured schedule with a heavier course load, enabling faster program completion but less flexibility for work or personal commitments. Part-time graduate students benefit from greater scheduling flexibility, allowing them to balance studies with professional responsibilities or family life, although this extends the program duration. The choice between full-time and part-time status impacts workload intensity, time management, and overall academic timeline.
Financial Considerations for Graduate Students
Full-time graduate students often face higher tuition fees and increased living expenses but may access more substantial financial aid packages, including scholarships and assistantships, compared to part-time students. Part-time graduate students typically benefit from lower per-semester tuition costs and the flexibility to maintain employment income, mitigating overall financial strain. Evaluating the balance between tuition expenses, potential earnings, and available financial support is crucial for graduate students when choosing full-time or part-time enrollment.
Impact on Career Advancement
Full-time graduate students often benefit from accelerated career advancement due to concentrated study and more opportunities for networking, internships, and research collaborations. Part-time graduate students may experience slower career progression as balancing work and study can limit availability for career-building activities and professional development. Employers frequently value the intensive commitment demonstrated by full-time students, which can lead to faster promotions and leadership roles in competitive fields.
Duration to Degree Completion
Full-time grad students typically complete their degrees in 2 to 3 years due to their intensive course loads and continuous enrollment. Part-time grad students often extend their duration to 4 to 6 years or more, balancing coursework with professional or personal commitments. The extended timeline for part-time learners allows greater flexibility but may impact the overall time to degree completion.
Work-Life-Study Balance Challenges
Full-time graduate students often face intense academic demands that limit time for personal activities and increase stress, complicating work-life-study balance. Part-time graduate students juggle employment and studies simultaneously, leading to prolonged program duration but offering more flexibility in managing finances and personal obligations. Both paths require strategic time management and prioritization to maintain mental health and academic performance.
Networking and Campus Engagement Opportunities
Full-time graduate students benefit from increased networking and campus engagement opportunities due to their consistent presence in academic and social settings, fostering stronger connections with peers, faculty, and industry professionals. Part-time graduate students often face limited access to these opportunities as their schedules may restrict participation in on-campus events and collaborative projects. Engaging fully on campus builds critical relationships that enhance academic success and career prospects for full-time students.
Eligibility for Scholarships and Financial Aid
Full-time graduate students typically qualify for a wider range of scholarships and financial aid opportunities due to enrollment requirements set by most funding programs, which often mandate a minimum of 9 to 12 credit hours per semester. Part-time graduate students may face limited eligibility for certain merit-based and need-based scholarships, as many institutions prioritize full-time enrollment for financial aid awards. Understanding the specific scholarship criteria and institutional financial aid policies is crucial for both full-time and part-time graduate students to maximize funding opportunities.
Choosing the Right Path: Key Decision Factors
Choosing between full-time and part-time graduate studies depends on factors such as financial stability, career goals, and time commitment. Full-time students often complete programs faster and engage more deeply in research opportunities, while part-time students benefit from maintaining employment and managing personal responsibilities. Evaluating workload flexibility, funding options, and long-term professional objectives ensures an informed decision aligned with individual circumstances.
Full-time Grad Student vs Part-time Grad Student Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com