PhD programs emphasize original research and theoretical contributions to advance knowledge in specific disciplines, ideal for those pursuing academic or research-intensive careers. EdD programs concentrate on applying research to solve practical problems in educational leadership and administration, making them suitable for professionals aiming to impact policy and practice in educational settings. Both degrees demand rigorous study, but the choice depends on whether the goal is to contribute to theory or to improve practice.
Table of Comparison
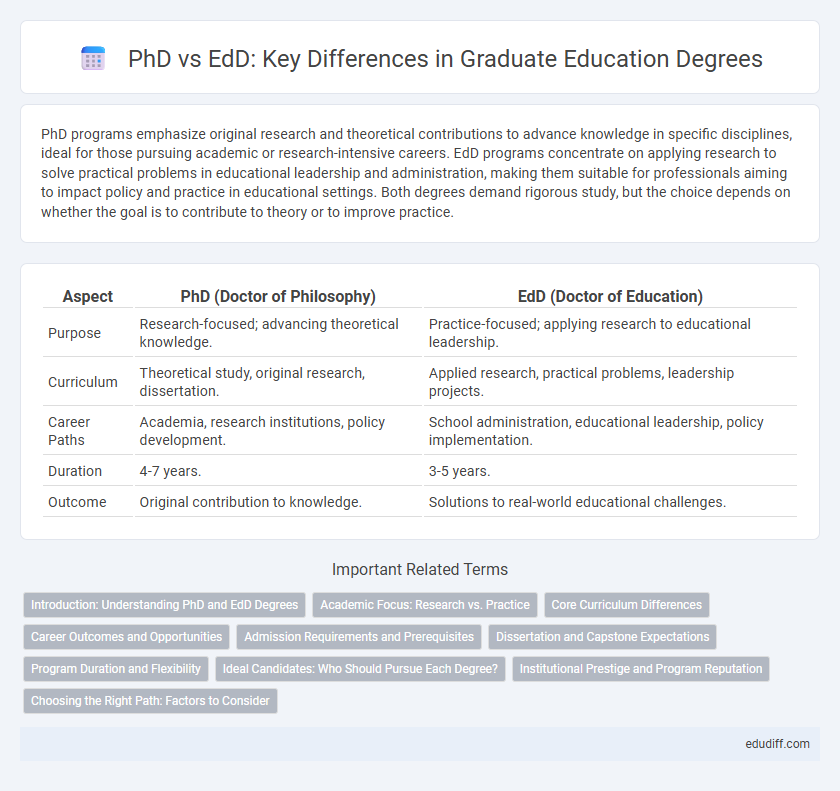
| Aspect | PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) | EdD (Doctor of Education) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Research-focused; advancing theoretical knowledge. | Practice-focused; applying research to educational leadership. |
| Curriculum | Theoretical study, original research, dissertation. | Applied research, practical problems, leadership projects. |
| Career Paths | Academia, research institutions, policy development. | School administration, educational leadership, policy implementation. |
| Duration | 4-7 years. | 3-5 years. |
| Outcome | Original contribution to knowledge. | Solutions to real-world educational challenges. |
Introduction: Understanding PhD and EdD Degrees
PhD and EdD degrees both represent advanced graduate education but serve distinct academic and professional goals. The PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) centers on original research and theoretical contributions to knowledge in a specific discipline, ideal for careers in academia and scholarly research. In contrast, the EdD (Doctor of Education) emphasizes the application of research to practical problems in education, preparing graduates for leadership roles in educational settings and policy development.
Academic Focus: Research vs. Practice
PhD programs emphasize original research and theoretical contributions to advance knowledge within a specific academic discipline. EdD programs prioritize the practical application of existing research to solve real-world problems in educational leadership and organizational settings. This distinction highlights the PhD's focus on creating new knowledge versus the EdD's commitment to applying research for immediate impact in professional practice.
Core Curriculum Differences
The core curriculum of a PhD program emphasizes advanced research methodologies, theoretical frameworks, and original dissertation work aimed at contributing new knowledge to the field. In contrast, an EdD curriculum centers on applying research to practical problems in education leadership, policy, and administration, integrating coursework in organizational theory and change management. PhD candidates often engage heavily in quantitative and qualitative research techniques, whereas EdD students focus on solution-driven projects and evidence-based practice within educational settings.
Career Outcomes and Opportunities
PhD graduates typically pursue careers in academia, research, and specialized fields, benefiting from a strong emphasis on original research and theoretical knowledge. EdD holders often secure leadership roles in educational administration, policy, and practitioner-focused positions, leveraging their expertise in applying research to real-world educational challenges. Both degrees offer distinct career opportunities, with the PhD favoring scholarly and research-intensive paths, while the EdD prioritizes practical leadership and administrative advancement.
Admission Requirements and Prerequisites
PhD programs typically require a strong academic background with a master's degree, high GRE scores, and significant research experience, emphasizing original contributions to knowledge. EdD programs often prioritize professional experience in education, a relevant master's degree, and leadership potential rather than extensive research credentials. Both programs demand letters of recommendation and a statement of purpose, but PhD admission focuses more on academic research capabilities while EdD admission centers on practical educational leadership skills.
Dissertation and Capstone Expectations
PhD dissertations emphasize original research contributing new knowledge to a specific field, requiring rigorous methodology and extensive literature review. EdD capstone projects focus on applying existing research to practical problems in educational settings, often incorporating evidence-based strategies for organizational improvement. Both demand critical analysis and scholarly writing, but the PhD prioritizes theory advancement while the EdD centers on practical impact and professional practice.
Program Duration and Flexibility
PhD programs typically require 4 to 6 years of full-time study, emphasizing extensive research and dissertation completion, while EdD programs often span 3 to 5 years with more flexibility for working professionals through part-time or hybrid formats. PhD candidates pursue theoretical research aiming for academic or research-intensive careers, whereas EdD students focus on applying research to practical issues in educational leadership. This flexibility in EdD programs accommodates career advancement alongside doctoral studies, contrasting with the more rigid timelines of PhD programs.
Ideal Candidates: Who Should Pursue Each Degree?
PhD programs are ideal for candidates aiming for research-intensive careers, academic positions, or contributing to theoretical knowledge in their field. EdD degrees suit professionals seeking leadership roles in educational settings, policy development, or applying research to practical challenges. Both degrees demand advanced expertise, but the PhD emphasizes research innovation, while the EdD focuses on applied educational practice.
Institutional Prestige and Program Reputation
PhD programs are typically associated with higher institutional prestige and emphasize original research contributions, often offered by research-intensive universities with strong academic reputations. EdD programs prioritize applied practice and leadership in educational settings, frequently housed within institutions known for professional development and community engagement rather than pure research prestige. Selecting between a PhD and an EdD should consider the ranking and reputation of the institution's education department, as well as its alignment with the candidate's career goals in academia or educational leadership.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a PhD and an EdD hinges on career goals and research interests; a PhD emphasizes theoretical research and academic scholarship, ideal for those pursuing university faculty roles or extensive research projects. An EdD focuses on the practical application of research in educational leadership and policy, suited for professionals aiming to impact K-12 systems or administrative roles. Consider program curriculum, dissertation requirements, and long-term professional aspirations when selecting the right doctoral path.
PhD vs EdD Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com