Extracurricular activities in high school offer students opportunities to explore interests outside the academic curriculum, such as sports, clubs, and arts, enhancing social and leadership skills. Co-curricular activities complement classroom learning by integrating educational content, like science fairs or debate teams, reinforcing theoretical knowledge through practical application. Both types play crucial roles in student development by promoting a balanced education that nurtures diverse talents and prepares students for future challenges.
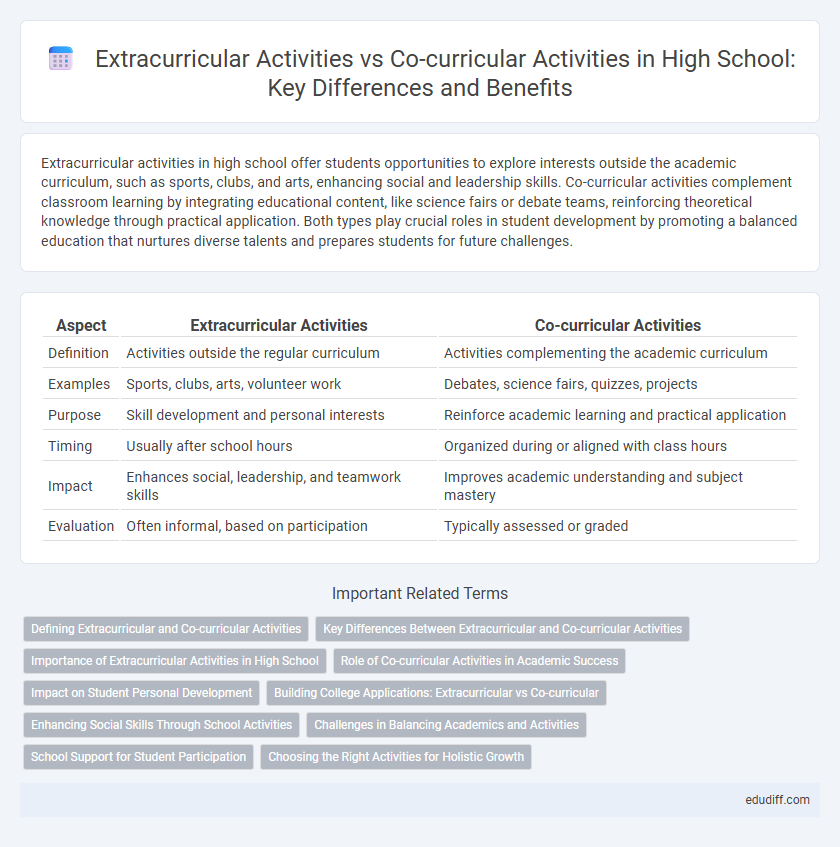
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Extracurricular Activities | Co-curricular Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Activities outside the regular curriculum | Activities complementing the academic curriculum |
| Examples | Sports, clubs, arts, volunteer work | Debates, science fairs, quizzes, projects |
| Purpose | Skill development and personal interests | Reinforce academic learning and practical application |
| Timing | Usually after school hours | Organized during or aligned with class hours |
| Impact | Enhances social, leadership, and teamwork skills | Improves academic understanding and subject mastery |
| Evaluation | Often informal, based on participation | Typically assessed or graded |
Defining Extracurricular and Co-curricular Activities
Extracurricular activities refer to voluntary, non-academic pursuits such as sports, clubs, and arts that take place outside the formal curriculum, fostering personal interests and skills. Co-curricular activities are structured programs integrated with the academic syllabus, like debates, science fairs, and group projects, enhancing classroom learning through practical application. Both types of activities contribute to holistic development but differ in their connection to the school's educational framework.
Key Differences Between Extracurricular and Co-curricular Activities
Extracurricular activities are voluntary, non-academic pursuits such as sports, music clubs, and drama that enhance students' personal skills and interests beyond the classroom. Co-curricular activities complement the academic curriculum by integrating practical experiences like science fairs, debates, and group projects that reinforce classroom learning. The key difference lies in their direct connection to academic content, with co-curricular activities supporting educational outcomes while extracurricular activities focus on holistic development.
Importance of Extracurricular Activities in High School
Extracurricular activities in high school play a crucial role in fostering social skills, leadership qualities, and personal interests beyond the academic curriculum. Participation in sports teams, clubs, and volunteer work enhances time management and teamwork abilities, directly contributing to college applications and future career opportunities. These activities also support mental health and personal growth by providing a balanced and engaging environment for students.
Role of Co-curricular Activities in Academic Success
Co-curricular activities, integrated with the academic curriculum, enhance students' learning experiences by developing critical thinking, teamwork, and time management skills vital for academic success. Participation in activities such as debate clubs, science fairs, and school projects reinforces classroom knowledge and promotes practical application of concepts. Research indicates students engaged in co-curricular programs consistently achieve higher grades and demonstrate improved cognitive and social development compared to those involved solely in extracurricular activities.
Impact on Student Personal Development
Extracurricular activities such as sports, clubs, and volunteer work enhance leadership skills, teamwork, and social interaction outside the academic curriculum. Co-curricular activities like debates, science fairs, and school plays integrate with academic learning, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and time management. Both types of activities significantly contribute to a student's personal development by promoting self-discipline, confidence, and emotional intelligence.
Building College Applications: Extracurricular vs Co-curricular
Extracurricular activities such as sports, clubs, and volunteer work showcase a student's initiative, leadership skills, and diverse interests, making college applications stand out. Co-curricular activities, including academic competitions and school projects, complement classroom learning and demonstrate intellectual engagement and subject mastery. Balancing both types enriches a college application by highlighting a well-rounded student profile with practical skills and academic commitment.
Enhancing Social Skills Through School Activities
Extracurricular activities such as sports clubs, drama, and debate teams foster teamwork, leadership, and communication skills by encouraging interaction beyond the classroom. Co-curricular activities, integrated with academic curricula like science fairs and student councils, reinforce collaborative learning and social responsibility tied directly to educational goals. Both types of school activities enhance social skills by providing diverse opportunities for peer engagement, conflict resolution, and empathy development.
Challenges in Balancing Academics and Activities
Balancing academics with extracurricular and co-curricular activities presents significant challenges for high school students, often leading to time management conflicts and increased stress levels. Extracurricular activities, which occur outside of standard curriculum hours, can interfere with study time, while co-curricular activities directly tie into academic requirements, necessitating careful prioritization to avoid academic decline. Effective planning and support are essential to help students maintain high performance across both academic and activity commitments.
School Support for Student Participation
Schools increasingly invest resources in extracurricular activities such as sports, clubs, and arts programs to enhance student engagement beyond academics, promoting skills like leadership and teamwork. Co-curricular activities, directly linked to the curriculum, receive structured support through scheduled class time and integration with academic goals, ensuring complementary learning experiences. Institutional support includes funding, dedicated staff, and facilities, which are crucial for maximizing student participation and balancing academic and personal growth.
Choosing the Right Activities for Holistic Growth
Selecting the right mix of extracurricular and co-curricular activities enhances holistic growth by balancing academic learning with personal development. Extracurricular activities like sports, clubs, and arts build social skills, leadership, and creativity, while co-curricular activities integrated with academics, such as science fairs and debates, reinforce knowledge application and critical thinking. High school students who engage in both types of activities develop well-rounded abilities that support academic success and emotional intelligence.
Extracurricular Activities vs Co-curricular Activities Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com