Dual Enrollment allows high school students to take college courses and earn both high school and college credits simultaneously, offering a practical experience of college-level coursework. AP Credit relies on standardized exams to demonstrate proficiency, with scores potentially earning college credit depending on the institution's policies. Choosing between Dual Enrollment and AP Credit depends on individual goals, the desired college credit transferability, and the learning style suited for in-person college classes versus exam preparation.
Table of Comparison
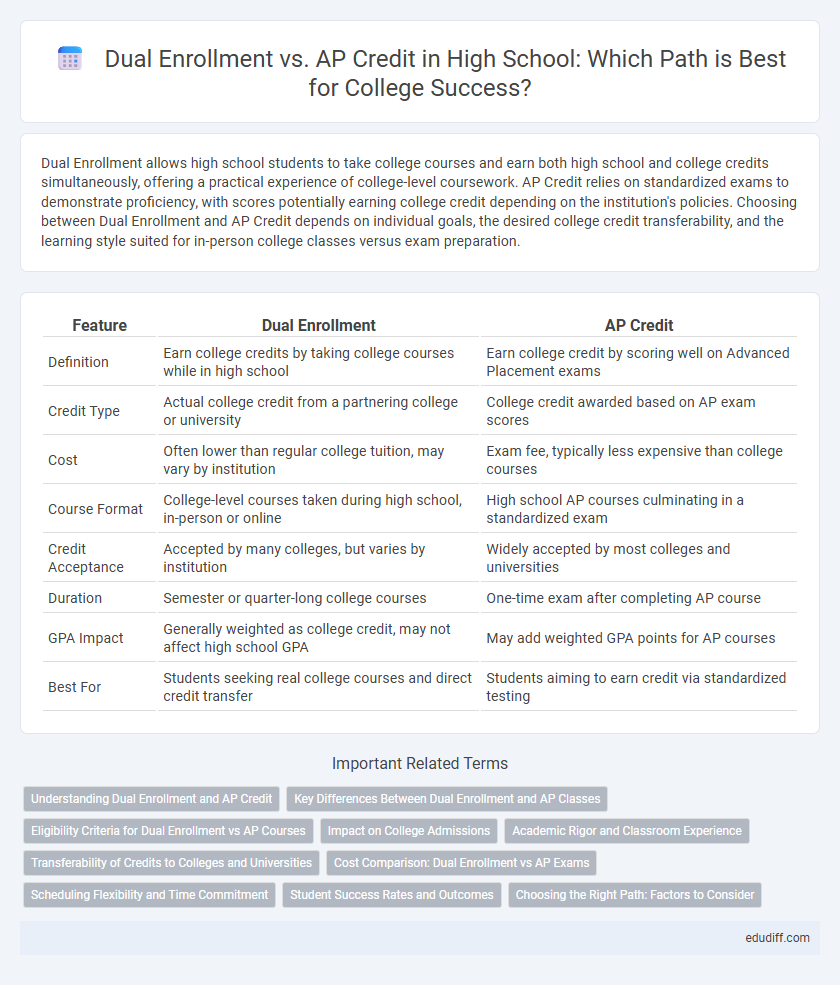
| Feature | Dual Enrollment | AP Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Earn college credits by taking college courses while in high school | Earn college credit by scoring well on Advanced Placement exams |
| Credit Type | Actual college credit from a partnering college or university | College credit awarded based on AP exam scores |
| Cost | Often lower than regular college tuition, may vary by institution | Exam fee, typically less expensive than college courses |
| Course Format | College-level courses taken during high school, in-person or online | High school AP courses culminating in a standardized exam |
| Credit Acceptance | Accepted by many colleges, but varies by institution | Widely accepted by most colleges and universities |
| Duration | Semester or quarter-long college courses | One-time exam after completing AP course |
| GPA Impact | Generally weighted as college credit, may not affect high school GPA | May add weighted GPA points for AP courses |
| Best For | Students seeking real college courses and direct credit transfer | Students aiming to earn credit via standardized testing |
Understanding Dual Enrollment and AP Credit
Dual Enrollment allows high school students to earn both high school and college credits simultaneously by taking actual college courses, providing a direct pathway to college-level learning. AP Credit is earned by scoring well on Advanced Placement exams, which colleges may accept for credit or placement depending on their policies. Understanding the differences helps students choose between enrolling in college classes early or preparing for standardized AP exams to advance their academic progress.
Key Differences Between Dual Enrollment and AP Classes
Dual enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits by taking actual college courses, offering direct exposure to college-level curriculum, while AP classes provide college-level coursework within the high school setting and require passing the AP exam for potential college credit. Dual enrollment courses often result in official college transcripts transferable to many postsecondary institutions, whereas AP credit depends on exam scores meeting individual college policies. Scheduling flexibility and tuition costs also differ, with dual enrollment sometimes involving fees and concurrent college registration, unlike AP classes which are integrated into the high school system.
Eligibility Criteria for Dual Enrollment vs AP Courses
Dual Enrollment eligibility typically requires students to meet specific GPA thresholds, standardized test scores, and counselor recommendations, as well as being enrolled in an accredited high school. AP courses demand enrollment in the designated classes without stringent eligibility besides teacher approval or prerequisite coursework. College credit through AP depends on scoring a minimum score, often 3 or higher, on the AP exam, while Dual Enrollment credits are earned by completing actual college-level courses during high school.
Impact on College Admissions
Dual enrollment courses provide students with college credits by taking actual college classes, demonstrating readiness for college-level work and often impressing admissions officers with real college experience. AP credit requires students to score well on AP exams, granting potential college credit and showcasing mastery of challenging high school coursework. Both options can strengthen college applications, but dual enrollment may offer a clearer indicator of a student's ability to succeed in higher education.
Academic Rigor and Classroom Experience
Dual Enrollment courses offer high school students the opportunity to earn college credits by attending classes at a local college, providing a rigorous academic experience that mirrors actual college coursework and expectations. Advanced Placement (AP) classes follow a high school curriculum with a standardized exam that can earn college credit depending on the score, focusing heavily on test preparation and theoretical knowledge. The classroom experience in Dual Enrollment often involves smaller college-level classes with direct interaction from college professors, while AP courses typically have larger high school classes led by high school teachers specialized in AP curriculum delivery.
Transferability of Credits to Colleges and Universities
Dual Enrollment credits are typically more transferable and widely accepted by colleges and universities, as they are college-level courses taken through accredited postsecondary institutions. AP Credit depends on standardized exam scores and the policies of individual colleges, which can result in variable acceptance and credit recognition. Students should consult specific college transfer policies to maximize credit applicability and avoid redundant coursework.
Cost Comparison: Dual Enrollment vs AP Exams
Dual Enrollment courses often incur tuition fees that can range from $150 to $300 per credit hour, potentially leading to higher upfront costs compared to AP exams, which typically cost around $97 per exam. While AP exams require a one-time payment per subject, Dual Enrollment may involve multiple credit hours, making overall expenses variable based on course load. Evaluating the total cost of earning college credit through Dual Enrollment versus AP exams helps students and families make informed decisions about affordable academic pathways.
Scheduling Flexibility and Time Commitment
Dual enrollment offers greater scheduling flexibility by allowing high school students to take college courses that fit their individual timetables, often outside traditional school hours. AP credit requires a significant upfront time commitment for intensive exam preparation during the school year, typically within a fixed class schedule. Students balancing work, extracurriculars, or family obligations often find dual enrollment more adaptable to their time constraints compared to the rigid structure of AP courses.
Student Success Rates and Outcomes
Dual Enrollment programs typically offer higher student success rates and better college credit transferability compared to AP Credit, as students earn actual college credits upon course completion. Data shows that students participating in Dual Enrollment have increased college retention and graduation rates due to exposure to college-level coursework and support systems. In contrast, AP Credit outcomes depend on exam scores and college policies, which can limit credit recognition and affect academic progression.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Dual Enrollment and AP Credit depends on factors such as college acceptance policies, course rigor, and individual learning preferences. Dual Enrollment offers college-level courses with direct credit applicability and potential cost savings, whereas AP Credit relies on exam scores that may or may not be accepted by every institution. Evaluating the specific college's transfer credit guidelines, the student's readiness for college coursework, and long-term academic goals ensures selecting the path that best aligns with future educational plans.
Dual Enrollment vs AP Credit Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com