Magnet schools specialize in specific academic disciplines or themes, offering students unique programs that foster advanced learning and creativity, which attracts a diverse student body through a competitive admission process. Charter schools operate independently of traditional public school systems, providing flexible curricula and innovative teaching methods tailored to community needs while maintaining accountability for academic performance. Both school types aim to enhance educational opportunities but differ in governance, admission policies, and program focus.
Table of Comparison
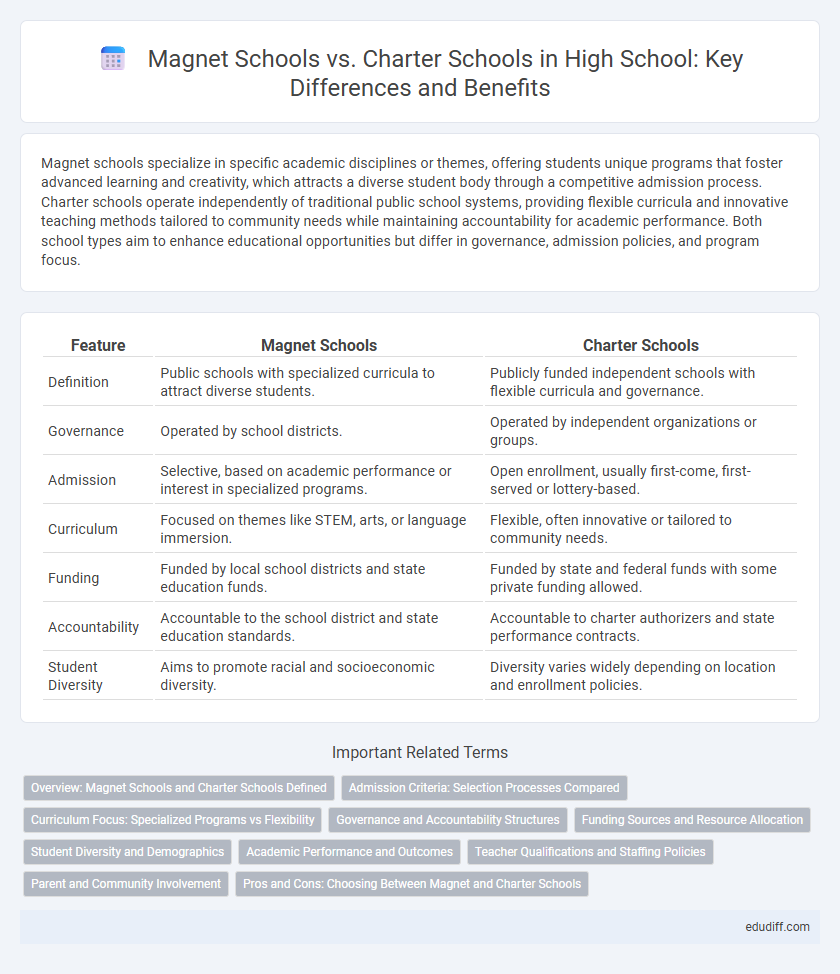
| Feature | Magnet Schools | Charter Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Public schools with specialized curricula to attract diverse students. | Publicly funded independent schools with flexible curricula and governance. |
| Governance | Operated by school districts. | Operated by independent organizations or groups. |
| Admission | Selective, based on academic performance or interest in specialized programs. | Open enrollment, usually first-come, first-served or lottery-based. |
| Curriculum | Focused on themes like STEM, arts, or language immersion. | Flexible, often innovative or tailored to community needs. |
| Funding | Funded by local school districts and state education funds. | Funded by state and federal funds with some private funding allowed. |
| Accountability | Accountable to the school district and state education standards. | Accountable to charter authorizers and state performance contracts. |
| Student Diversity | Aims to promote racial and socioeconomic diversity. | Diversity varies widely depending on location and enrollment policies. |
Overview: Magnet Schools and Charter Schools Defined
Magnet schools are public schools with specialized curricula designed to attract a diverse student body from across traditional school zones, often emphasizing themes like science, technology, or the arts. Charter schools operate independently of traditional public school districts, receiving public funding but functioning under a charter that grants greater flexibility in curriculum design, staffing, and governance. Both types aim to improve academic outcomes and offer unique educational opportunities distinct from standard public high schools.
Admission Criteria: Selection Processes Compared
Magnet schools typically use a selective admission process based on academic performance, talents, and entrance exams, aiming to attract students with specific interests or aptitudes. Charter schools often have open enrollment policies with lottery systems when applications exceed available spots, promoting broader access regardless of academic achievements. The contrast lies in magnet schools' focus on specialized criteria versus charter schools' emphasis on equitable opportunity through randomized selection.
Curriculum Focus: Specialized Programs vs Flexibility
Magnet schools offer specialized programs tailored to specific fields such as STEM, performing arts, or international studies, providing students with focused academic experiences and advanced resources. Charter schools emphasize curricular flexibility, allowing educators to design innovative teaching approaches and adapt programs to meet diverse student needs. This distinction impacts student choice by aligning magnet schools with targeted career pathways while charter schools cater to personalized learning styles and community preferences.
Governance and Accountability Structures
Magnet schools operate under traditional public school district governance with strict adherence to district policies and oversight by the local school board, ensuring established accountability through standardized evaluations and state regulations. Charter schools function under independent governance through a charter or contract often granted by state or local authorizers, allowing for greater operational flexibility but requiring periodic performance reviews to maintain their charter status. Both models emphasize accountability; magnet schools align with district goals, while charter schools are held accountable primarily through academic results and financial transparency outlined in their charters.
Funding Sources and Resource Allocation
Magnet schools primarily receive funding from public school districts and federal grants aimed at promoting specialized programs, allowing for targeted resource allocation in areas like science, technology, and the arts. Charter schools receive funding based on student enrollment from state and local governments but often supplement their budgets with private donations and grants, leading to varied resource availability. The difference in funding sources influences how each type of school allocates resources, with magnet schools generally benefiting from consistent public funding and charter schools experiencing fluctuating financial support.
Student Diversity and Demographics
Magnet schools often promote student diversity by offering specialized programs that attract a wide range of students from various socioeconomic and racial backgrounds across school districts. Charter schools, while publicly funded, tend to reflect the demographics of their immediate neighborhoods, which can result in less diversity compared to magnet schools. Data shows magnet schools usually achieve higher enrollment of underrepresented minorities due to targeted admission strategies and emphasis on inclusivity.
Academic Performance and Outcomes
Magnet schools consistently demonstrate higher academic performance due to specialized curricula and selective admissions processes that attract motivated students. Charter schools show varied outcomes, with some outperforming traditional public schools while others struggle due to differences in management and resource allocation. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics indicate magnet schools have a 10% higher graduation rate on average compared to charter schools.
Teacher Qualifications and Staffing Policies
Magnet schools often prioritize hiring teachers with specialized certifications and advanced degrees aligned with their focus areas, such as STEM or the arts, ensuring high instructional quality. Charter schools typically have more flexible staffing policies, allowing for a mix of certified and non-certified educators, which can lead to varied teaching qualifications. These differences in teacher qualifications and staffing policies directly impact curriculum delivery and student outcomes in high school settings.
Parent and Community Involvement
Magnet schools prioritize specialized curricula that often attract families actively seeking targeted educational programs, resulting in strong parent and community engagement through organized events and volunteer opportunities. Charter schools emphasize flexible, innovative teaching methods and frequently encourage parental input in decision-making processes, fostering a collaborative environment between educators and families. Both school types rely on active parent and community participation to enhance student outcomes and support school initiatives.
Pros and Cons: Choosing Between Magnet and Charter Schools
Magnet schools offer specialized curriculums in areas like STEM or the arts, attracting students with specific academic interests and often providing advanced resources and experienced instructors, but they can be highly competitive and may require entrance exams. Charter schools provide flexible, innovative teaching methods and often emphasize community involvement, fostering a personalized learning environment, yet their quality and resources can vary significantly due to differing management and funding structures. Choosing between magnet and charter schools depends on a student's academic goals, learning style, and the availability of programs that best align with their educational needs.
Magnet schools vs Charter schools Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com