Public schools offer diverse student populations and are funded primarily through government sources, providing free education to all enrolled. Private schools rely on tuition fees and private funding, often featuring smaller class sizes and specialized curricula. The choice between public and private schooling depends on factors such as budget, educational goals, and available resources.
Table of Comparison
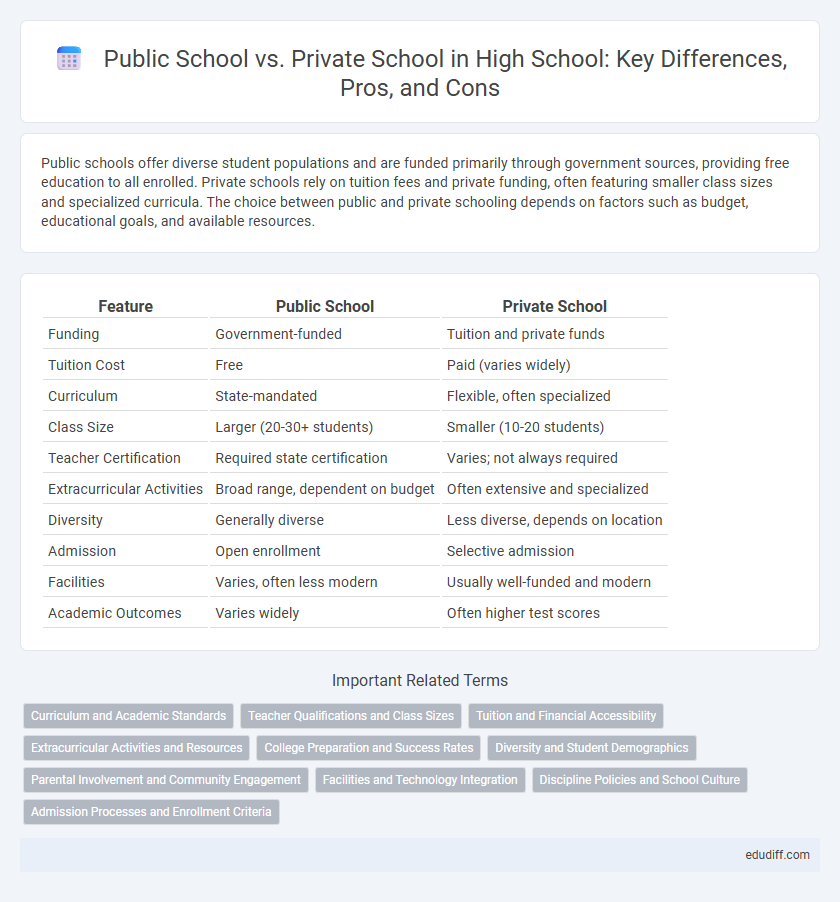
| Feature | Public School | Private School |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Government-funded | Tuition and private funds |
| Tuition Cost | Free | Paid (varies widely) |
| Curriculum | State-mandated | Flexible, often specialized |
| Class Size | Larger (20-30+ students) | Smaller (10-20 students) |
| Teacher Certification | Required state certification | Varies; not always required |
| Extracurricular Activities | Broad range, dependent on budget | Often extensive and specialized |
| Diversity | Generally diverse | Less diverse, depends on location |
| Admission | Open enrollment | Selective admission |
| Facilities | Varies, often less modern | Usually well-funded and modern |
| Academic Outcomes | Varies widely | Often higher test scores |
Curriculum and Academic Standards
Public schools follow state-mandated curricula aligned with standardized testing and educational benchmarks, ensuring consistency across diverse student populations. Private schools often implement specialized or advanced curricula, such as International Baccalaureate (IB) or Advanced Placement (AP) programs, providing enhanced academic rigor and flexibility. Academic standards in private schools tend to be higher due to selective admissions and smaller class sizes, promoting personalized instruction and accelerated learning paths.
Teacher Qualifications and Class Sizes
Private schools typically employ teachers with advanced degrees and specialized certifications, ensuring high instructional quality. Smaller class sizes in private schools allow for personalized attention, enhancing student engagement and learning outcomes. Public schools often face larger class sizes and a more diverse range of teacher qualifications, impacting individualized support.
Tuition and Financial Accessibility
Public schools offer significantly lower tuition fees compared to private schools, making them a more financially accessible option for many families. Private school tuition can range from $10,000 to over $50,000 annually, whereas public schools are funded by taxes and usually have no tuition costs. Financial aid and scholarships are often available at private institutions, but the overall expense remains a barrier for many students seeking quality education.
Extracurricular Activities and Resources
Public schools typically offer a wide range of extracurricular activities funded by local taxes, ensuring accessibility for all students, while private schools often provide specialized clubs and resources with investment from tuition fees. Resources such as advanced technology, arts programs, and athletic facilities tend to be more abundant in private schools due to higher funding levels. The diversity and scope of extracurricular options in private schools can enhance student development, though public schools often excel in community engagement and inclusivity.
College Preparation and Success Rates
Private schools often provide more rigorous college preparation programs, smaller class sizes, and personalized counseling, resulting in higher college acceptance and graduation rates. Public schools vary widely in resources and support, but many have implemented Advanced Placement (AP) courses and dual-enrollment programs to improve college readiness. Data shows private school students typically outperform public school peers in standardized tests and college retention, though some public schools in affluent areas match or exceed these outcomes.
Diversity and Student Demographics
Public schools generally offer greater diversity in student demographics, reflecting the local community's socioeconomic and cultural variety. Private schools tend to have more homogeneous student populations, often influenced by tuition costs and selective admission processes. Research indicates that exposure to diverse peers in public schools enhances social development and cross-cultural understanding among high school students.
Parental Involvement and Community Engagement
Parental involvement in public schools is often encouraged through organized school events, parent-teacher associations, and community volunteer programs that foster strong connections between families and educators. Private schools typically offer more personalized communication channels and structured opportunities for parents to participate in decision-making processes and extracurricular activities. Community engagement in public schools benefits from diverse partnerships with local organizations and government agencies, while private schools tend to leverage exclusive networks and resources to enhance student experiences.
Facilities and Technology Integration
Public schools often provide a broad range of facilities but may face budget constraints limiting advanced technology integration. Private schools typically offer state-of-the-art facilities, including smart classrooms and specialized labs, enhancing learning experiences through cutting-edge technology. The difference in resource allocation directly impacts students' access to digital tools and hands-on educational opportunities.
Discipline Policies and School Culture
Public schools often implement standardized discipline policies guided by state regulations, fostering a structured environment with clear consequences for misconduct. Private schools tend to establish discipline policies that reflect their specific educational philosophies and values, which can create a closely-knit school culture emphasizing respect and personal responsibility. The cultural climate in private schools typically promotes a strong sense of community and collaboration, while public schools accommodate a more diverse student body, influencing varied social dynamics and disciplinary approaches.
Admission Processes and Enrollment Criteria
Public schools typically admit students based on geographic zoning and residency requirements, ensuring access for local families without selective criteria. Private schools implement competitive admission processes, including entrance exams, interviews, and evaluation of academic records to maintain specific enrollment standards. Understanding these distinctions clarifies the enrollment pathways and eligibility differences influencing the choice between public and private education.
Public school vs Private school Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com