Magnet schools offer specialized curricula focused on areas like science, arts, or technology, attracting students with specific academic interests and talents. Charter schools operate independently from traditional public school systems, providing flexible teaching methods and innovative educational approaches to meet diverse student needs. Both options emphasize tailored learning experiences but differ in structure, governance, and program specialization.
Table of Comparison
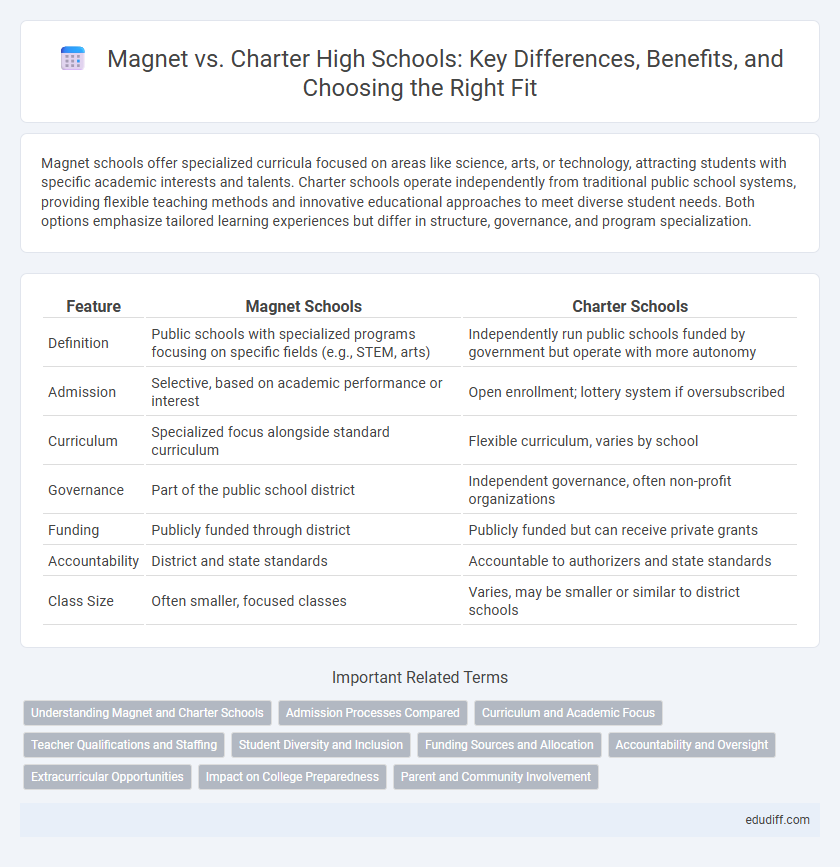
| Feature | Magnet Schools | Charter Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Public schools with specialized programs focusing on specific fields (e.g., STEM, arts) | Independently run public schools funded by government but operate with more autonomy |
| Admission | Selective, based on academic performance or interest | Open enrollment; lottery system if oversubscribed |
| Curriculum | Specialized focus alongside standard curriculum | Flexible curriculum, varies by school |
| Governance | Part of the public school district | Independent governance, often non-profit organizations |
| Funding | Publicly funded through district | Publicly funded but can receive private grants |
| Accountability | District and state standards | Accountable to authorizers and state standards |
| Class Size | Often smaller, focused classes | Varies, may be smaller or similar to district schools |
Understanding Magnet and Charter Schools
Magnet schools offer specialized curricula designed to attract diverse students from across traditional school boundaries, often focusing on themes like STEM, arts, or language immersion. Charter schools operate independently from district regulations, providing flexible educational approaches and accountability based on performance contracts. Both school types aim to enhance academic opportunities but differ in governance, enrollment policies, and funding sources.
Admission Processes Compared
Magnet schools often require a selective admission process focused on academic performance, entrance exams, and demonstrated interest in specialized programs, ensuring students meet specific criteria related to the school's theme. Charter schools typically use a lottery-based admission system open to all students within a district, promoting equal access without stringent academic requirements. Both systems aim to provide unique educational experiences, but magnet admissions prioritize merit and specialized skills, while charter admissions emphasize inclusivity and chance.
Curriculum and Academic Focus
Magnet schools emphasize specialized curricula such as STEM, performing arts, or international studies, designed to attract students with specific academic interests and talents. Charter schools often offer more flexible and innovative academic programs tailored to meet local community needs, frequently incorporating project-based learning and personalized instruction. Both school types prioritize high academic standards but differ in curricular structure, with magnets offering concentrated disciplines and charters promoting adaptive, student-centered approaches.
Teacher Qualifications and Staffing
Magnet schools typically employ teachers with specialized certifications and advanced degrees tailored to their focused curricula, ensuring expertise in niche subjects. Charter schools often have more flexibility in hiring, sometimes employing educators without traditional certification but with relevant experience or unique skills. This difference in teacher qualifications and staffing approaches impacts instructional quality and program delivery in each school type.
Student Diversity and Inclusion
Magnet schools often emphasize specialized curricula that attract students from diverse racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic backgrounds, fostering an inclusive environment through targeted recruitment. Charter schools vary widely in diversity, with some implementing inclusive admission policies while others show less demographic variety due to neighborhood-based enrollment. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics highlights that magnet schools generally maintain higher levels of racial and socioeconomic diversity compared to many charter schools.
Funding Sources and Allocation
Magnet schools primarily receive funding from local school districts, state education budgets, and federal grants, often allocating resources toward specialized programs like STEM or the arts. Charter schools rely heavily on public funding based on enrollment but have greater flexibility in budget allocation, allowing them to prioritize innovative curricula and operational costs. Differences in funding sources and allocation strategies impact the availability of resources, teacher recruitment, and student support services in both school types.
Accountability and Oversight
Magnet schools maintain rigorous accountability through district oversight and adherence to state education standards, ensuring consistent academic performance and equity. Charter schools operate under independent authorizers, such as school districts or charter boards, subjecting them to periodic performance reviews and renewal processes based on student achievement and financial management. Both models emphasize transparency but differ in governance structures impacting their oversight mechanisms.
Extracurricular Opportunities
Magnet schools often provide specialized extracurricular programs aligned with their focused academic themes, such as STEM clubs, performing arts, and competitive robotics, enhancing students' practical learning experiences. Charter schools, while diverse in offerings, may have limited extracurricular options due to funding constraints and smaller student bodies, potentially reducing access to a wide range of activities like varsity sports or advanced music programs. Students at magnet schools frequently benefit from partnerships with local universities and organizations, resulting in expanded opportunities for internships, leadership roles, and community engagement beyond typical charter school offerings.
Impact on College Preparedness
Magnet schools often provide rigorous, specialized curricula with advanced placement and STEM programs that enhance college readiness. Charter schools offer flexible, innovative teaching methods aimed at improving critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for higher education success. Both school types contribute uniquely to college preparedness by fostering academic excellence and personalized learning environments tailored to student needs.
Parent and Community Involvement
Magnet schools often foster higher parent and community involvement through specialized programs and strong partnerships with local organizations, enhancing student engagement and resources. Charter schools provide flexible structures that encourage parents to take active roles in governance and decision-making, promoting a collaborative school environment. Both school types significantly benefit from robust family participation, which contributes to improved academic outcomes and community support.
Magnet vs Charter Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com