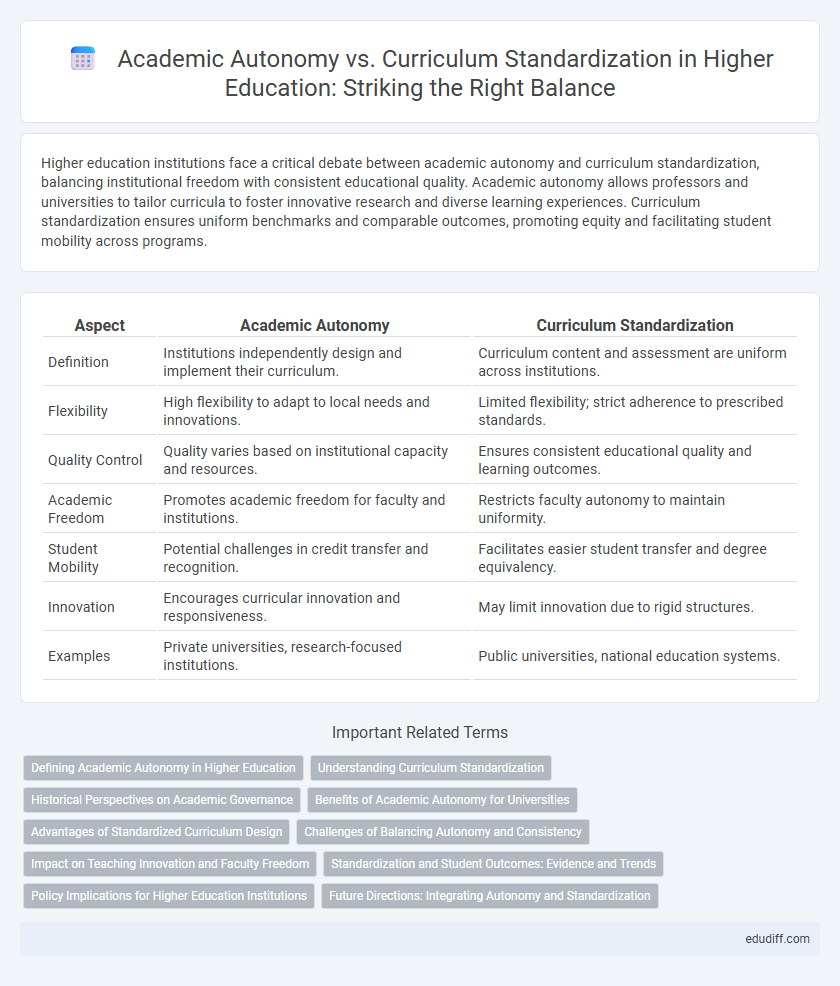
Higher education institutions face a critical debate between academic autonomy and curriculum standardization, balancing institutional freedom with consistent educational quality. Academic autonomy allows professors and universities to tailor curricula to foster innovative research and diverse learning experiences. Curriculum standardization ensures uniform benchmarks and comparable outcomes, promoting equity and facilitating student mobility across programs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Academic Autonomy | Curriculum Standardization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Institutions independently design and implement their curriculum. | Curriculum content and assessment are uniform across institutions. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to adapt to local needs and innovations. | Limited flexibility; strict adherence to prescribed standards. |
| Quality Control | Quality varies based on institutional capacity and resources. | Ensures consistent educational quality and learning outcomes. |
| Academic Freedom | Promotes academic freedom for faculty and institutions. | Restricts faculty autonomy to maintain uniformity. |
| Student Mobility | Potential challenges in credit transfer and recognition. | Facilitates easier student transfer and degree equivalency. |
| Innovation | Encourages curricular innovation and responsiveness. | May limit innovation due to rigid structures. |
| Examples | Private universities, research-focused institutions. | Public universities, national education systems. |
Defining Academic Autonomy in Higher Education
Academic autonomy in higher education refers to the institution's ability to govern its academic affairs independently, including decisions on curriculum design, teaching methods, and research priorities. This autonomy ensures universities can tailor programs to foster innovation, critical thinking, and address local or global challenges without external constraints. Defining academic autonomy highlights the balance between institutional freedom and accountability, crucial for maintaining educational quality and relevance in diverse academic environments.
Understanding Curriculum Standardization
Curriculum standardization establishes uniform educational goals, content, and assessment criteria across institutions to ensure consistency and comparability in academic programs. This approach facilitates quality assurance and equitable learning outcomes by aligning curricula with national or international benchmarks. Standardized curricula enable effective resource allocation and streamline accreditation processes within higher education systems.
Historical Perspectives on Academic Governance
Historical perspectives on academic governance reveal a complex balance between academic autonomy and curriculum standardization, rooted in the evolution of universities since the medieval period. The rise of state involvement in education during the 19th and 20th centuries prompted increased curriculum standardization to ensure uniform quality and accountability across institutions. Key events such as the University of Bologna's early self-governance model and the Morrill Act's establishment of standardized land-grant universities demonstrate ongoing tensions between institutional independence and centralized control in shaping higher education policies.
Benefits of Academic Autonomy for Universities
Academic autonomy in universities fosters innovative research and teaching methods, enabling institutions to tailor curricula to evolving industry demands and student needs. It enhances faculty motivation and intellectual freedom, driving higher quality education and academic excellence. This flexibility supports diverse learning approaches that improve critical thinking and adaptability among graduates.
Advantages of Standardized Curriculum Design
Standardized curriculum design in higher education ensures consistent learning outcomes across institutions, facilitating equitable assessment and transferability of credits. It streamlines curriculum development by providing a clear framework aligned with industry standards and accreditation requirements. This uniformity supports collaborative research and benchmarking, enhancing overall academic quality and institutional accountability.
Challenges of Balancing Autonomy and Consistency
Balancing academic autonomy with curriculum standardization presents challenges such as maintaining institutional freedom while ensuring consistency in educational quality across programs. Higher education institutions struggle to align diverse academic interests and innovative teaching methods with standardized learning outcomes and accreditation requirements. This tension affects curriculum design, assessment practices, and ultimately influences student preparedness and employability in a competitive global market.
Impact on Teaching Innovation and Faculty Freedom
Academic autonomy fosters teaching innovation by empowering faculty to design and implement curricula that reflect cutting-edge research and diverse pedagogical approaches. In contrast, curriculum standardization often restricts faculty freedom, limiting opportunities for creative course development and adaptation to student needs. Balancing autonomy with standardization is critical to promoting both educational consistency and dynamic teaching practices in higher education institutions.
Standardization and Student Outcomes: Evidence and Trends
Curriculum standardization in higher education has been shown to promote consistent student outcomes by establishing clear benchmarks and learning objectives across institutions. Studies indicate that standardized curricula can reduce disparities in academic achievement, facilitating equitable assessments of student performance. Trends reveal that integration of standardized frameworks correlates with improved graduation rates and competency acquisition, supporting policy shifts towards unified academic standards.
Policy Implications for Higher Education Institutions
Academic autonomy enables higher education institutions to tailor curricula to regional needs and innovative research, increasing adaptability and student engagement. Curriculum standardization promotes consistent quality and comparability across institutions, facilitating national accreditation and mobility of students within higher education systems. Policymakers must balance these approaches, ensuring frameworks support institutional independence while maintaining rigorous academic standards to enhance both global competitiveness and local relevance.
Future Directions: Integrating Autonomy and Standardization
Future directions in higher education emphasize integrating academic autonomy with curriculum standardization to foster innovation while ensuring quality. Institutions can adopt flexible frameworks that allow faculty to tailor content to local needs within standardized learning outcomes. Leveraging technology and data analytics supports personalized learning paths, aligning autonomy with accountability and continuous improvement.
Academic Autonomy vs Curriculum Standardization Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com