Research universities prioritize advancing knowledge through extensive research projects and often offer a wide range of graduate programs, attracting faculty who are leaders in their fields. Teaching colleges focus primarily on undergraduate education, emphasizing smaller class sizes and personalized instruction to foster close student-faculty relationships. Choosing between the two depends on whether a student values cutting-edge research opportunities or a more intimate, teaching-focused academic environment.
Table of Comparison
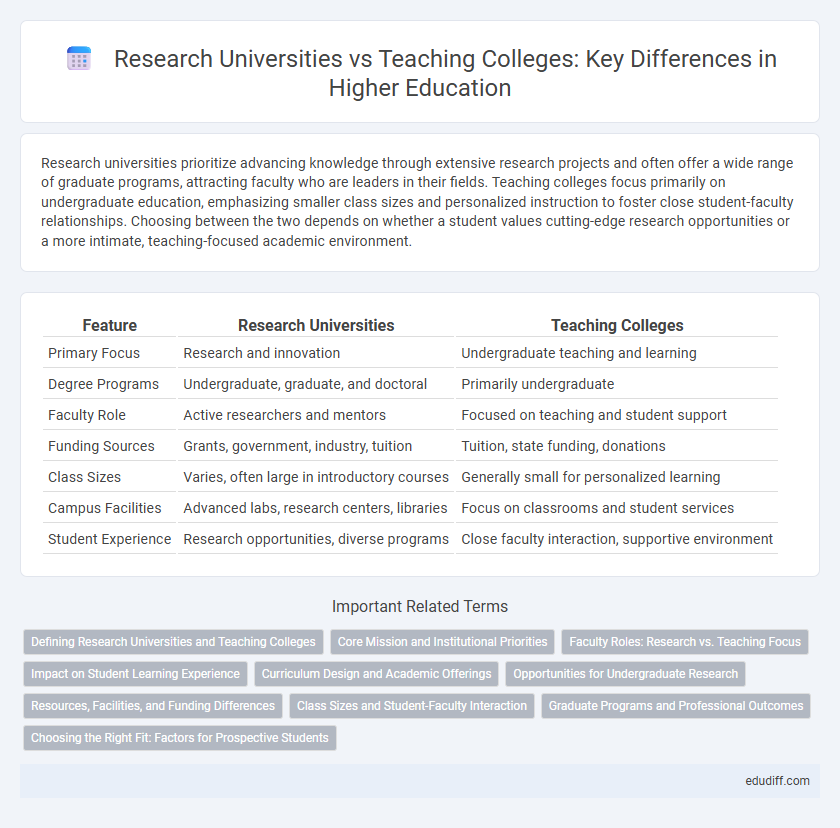
| Feature | Research Universities | Teaching Colleges |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Research and innovation | Undergraduate teaching and learning |
| Degree Programs | Undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral | Primarily undergraduate |
| Faculty Role | Active researchers and mentors | Focused on teaching and student support |
| Funding Sources | Grants, government, industry, tuition | Tuition, state funding, donations |
| Class Sizes | Varies, often large in introductory courses | Generally small for personalized learning |
| Campus Facilities | Advanced labs, research centers, libraries | Focus on classrooms and student services |
| Student Experience | Research opportunities, diverse programs | Close faculty interaction, supportive environment |
Defining Research Universities and Teaching Colleges
Research universities prioritize the creation and dissemination of new knowledge through extensive research activities, often supported by significant funding and graduate programs. Teaching colleges emphasize personalized instruction and student-centered learning, focusing primarily on undergraduate education with limited research obligations. Both types of institutions play distinct roles in higher education, balancing scholarship and pedagogy.
Core Mission and Institutional Priorities
Research universities prioritize knowledge creation and innovation through extensive research programs, often attracting significant funding and renowned faculty. Teaching colleges focus on delivering high-quality education and personalized learning experiences, emphasizing student engagement and curriculum development. Institutional priorities at research universities center on advancing scholarship and graduate education, while teaching colleges prioritize undergraduate success and community involvement.
Faculty Roles: Research vs. Teaching Focus
Research universities prioritize faculty roles centered on conducting original research, securing grants, and publishing in peer-reviewed journals to advance academic knowledge and innovation. Teaching colleges emphasize faculty responsibilities in delivering high-quality instruction, mentoring students, and fostering a supportive learning environment, often with smaller class sizes and focused student engagement. The balance between research and teaching duties significantly shapes faculty workload, evaluation criteria, and institutional mission in each type of institution.
Impact on Student Learning Experience
Research universities offer students access to cutting-edge knowledge and resources, fostering critical thinking and innovation through involvement in faculty-led research projects. Teaching colleges emphasize personalized instruction and smaller class sizes, enhancing engagement and immediate feedback to support individual learning needs. The combination of research opportunities and tailored teaching methods directly contributes to a richer, more dynamic student learning experience.
Curriculum Design and Academic Offerings
Research universities prioritize curriculum design that emphasizes advanced disciplinary knowledge, interdisciplinary research opportunities, and specialized graduate programs. Teaching colleges focus on curriculum offerings that enhance foundational skills, promote small class sizes, and integrate experiential learning to support undergraduate student engagement. Both institutions tailor academic offerings to meet their distinct educational missions and student demographics.
Opportunities for Undergraduate Research
Research universities offer extensive opportunities for undergraduate research through well-funded labs, dedicated faculty mentors, and access to cutting-edge technology, fostering hands-on experience in diverse academic fields. Teaching colleges typically provide more personalized guidance but may have limited research infrastructure and fewer large-scale projects, emphasizing master's or smaller-scale student-led studies instead. Undergraduates at research-intensive institutions benefit from collaborative networks and potential co-authorship on publications, enhancing their academic resumes and graduate school prospects.
Resources, Facilities, and Funding Differences
Research universities typically receive substantially higher funding from government grants, private sector partnerships, and endowments, enabling extensive resources and state-of-the-art facilities. Teaching colleges prioritize instructional quality but operate with more limited financial support, resulting in fewer specialized research labs and less advanced infrastructure. These funding disparities significantly influence the scope of academic programs, research opportunities, and technological advancements available to students and faculty.
Class Sizes and Student-Faculty Interaction
Research universities typically feature larger class sizes, which can limit direct student-faculty interaction and create a more impersonal learning environment. Teaching colleges prioritize smaller class sizes, fostering closer relationships between students and professors and enhancing personalized academic support. Smaller student-faculty ratios at teaching colleges contribute to increased mentorship opportunities and more engaging classroom discussions.
Graduate Programs and Professional Outcomes
Research universities offer extensive graduate programs with cutting-edge facilities and opportunities for interdisciplinary collaboration, enhancing academic rigor and innovation. Teaching colleges prioritize smaller class sizes and personalized instruction, which can foster deeper mentorship and stronger professional networks for students. Graduates from research universities often pursue advanced careers in academia and research-intensive industries, while those from teaching colleges frequently excel in applied professions and community-focused roles.
Choosing the Right Fit: Factors for Prospective Students
Research universities offer extensive resources, cutting-edge facilities, and opportunities for undergraduate involvement in advanced projects, ideal for students seeking in-depth expertise and career-oriented research experience. Teaching colleges prioritize smaller class sizes and personalized instruction, fostering close faculty-student relationships and a supportive learning environment suited for those valuing mentorship and foundational knowledge. Prospective students should assess their career goals, preferred learning style, and desired campus culture to determine the optimal institution for academic growth and personal development.
Research Universities vs Teaching Colleges Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com