Social-emotional learning in kindergarten builds a foundation for empathy, self-regulation, and positive interactions, which enhances academic readiness by fostering a supportive learning environment. Children who develop strong social-emotional skills are better equipped to focus, follow instructions, and engage in collaborative activities, essential for early academic success. Prioritizing social-emotional development alongside academic skills leads to well-rounded growth and long-term educational achievement.
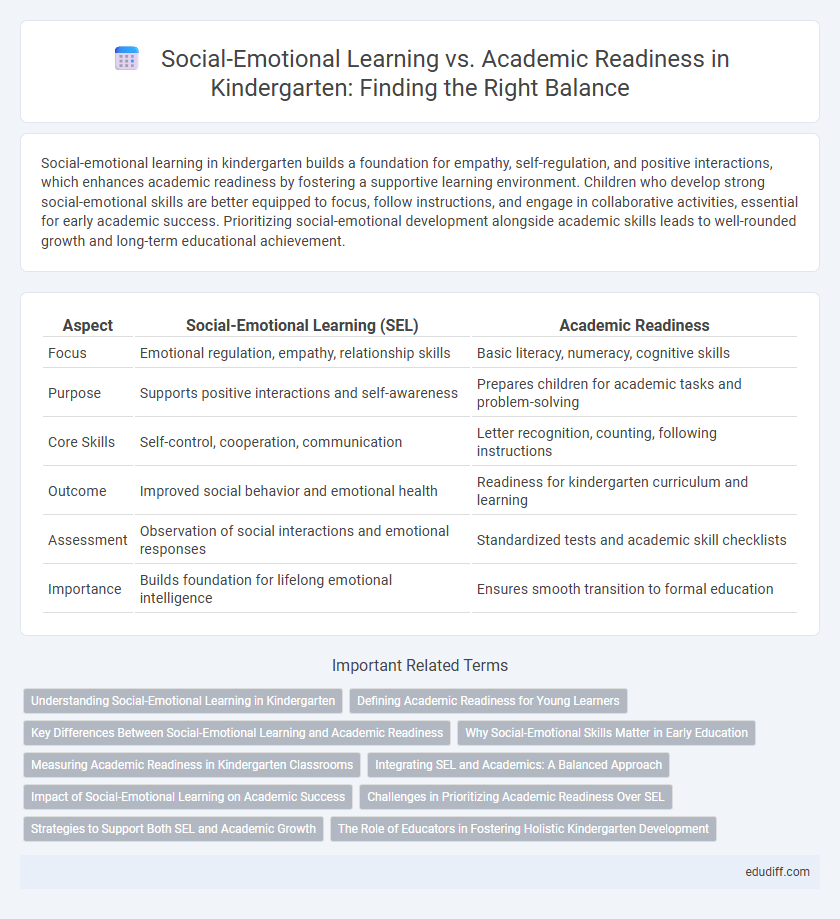
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) | Academic Readiness |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Emotional regulation, empathy, relationship skills | Basic literacy, numeracy, cognitive skills |
| Purpose | Supports positive interactions and self-awareness | Prepares children for academic tasks and problem-solving |
| Core Skills | Self-control, cooperation, communication | Letter recognition, counting, following instructions |
| Outcome | Improved social behavior and emotional health | Readiness for kindergarten curriculum and learning |
| Assessment | Observation of social interactions and emotional responses | Standardized tests and academic skill checklists |
| Importance | Builds foundation for lifelong emotional intelligence | Ensures smooth transition to formal education |
Understanding Social-Emotional Learning in Kindergarten
Understanding social-emotional learning in kindergarten involves developing skills in self-awareness, self-regulation, and interpersonal communication, which are critical for children's overall growth. These competencies build a foundation for academic readiness by promoting focus, resilience, and positive interactions within the classroom environment. Research shows that children with strong social-emotional skills demonstrate improved problem-solving abilities and better adjustment to school routines.
Defining Academic Readiness for Young Learners
Academic readiness for young learners encompasses foundational skills in literacy, numeracy, and cognitive development essential for kindergarten success, including basic letter recognition, counting, and problem-solving abilities. These competencies enable children to engage effectively with classroom activities and curricula, ensuring a smoother transition into formal education. Social-emotional learning complements academic readiness by fostering self-regulation, cooperation, and emotional resilience, which support overall academic achievement.
Key Differences Between Social-Emotional Learning and Academic Readiness
Social-emotional learning in kindergarten cultivates skills like empathy, self-regulation, and cooperation, which are essential for positive peer interactions and emotional resilience. Academic readiness emphasizes foundational knowledge in literacy, numeracy, and cognitive skills to prepare children for formal education. While social-emotional learning supports personal development and classroom behavior, academic readiness focuses on the intellectual abilities required for academic success.
Why Social-Emotional Skills Matter in Early Education
Social-emotional skills in kindergarten, such as self-regulation, empathy, and cooperation, form a critical foundation for academic success and lifelong learning. Research shows children with strong social-emotional development exhibit better focus, improved communication, and higher resilience, directly influencing their readiness to engage with academic content. Fostering these skills early enhances classroom behavior and peer relationships, which contribute significantly to overall educational outcomes.
Measuring Academic Readiness in Kindergarten Classrooms
Measuring academic readiness in kindergarten classrooms involves assessing key skills such as letter recognition, basic numeracy, and following instructions, which provide quantifiable indicators of a child's preparation for formal education. Standardized screening tools and observational checklists are commonly used to evaluate these competencies, ensuring children meet developmental milestones aligned with curriculum standards. While social-emotional learning supports overall development, academic readiness assessments focus specifically on cognitive and foundational academic abilities essential for early learning success.
Integrating SEL and Academics: A Balanced Approach
Integrating social-emotional learning (SEL) with academic readiness in kindergarten fosters a balanced approach that supports both cognitive and emotional development. Research shows that children who engage in SEL experience improved classroom behavior, higher academic achievement, and enhanced interpersonal skills. Educators prioritize strategies that blend SEL competencies such as self-regulation, empathy, and collaboration with foundational literacy and numeracy instruction to create a holistic learning environment.
Impact of Social-Emotional Learning on Academic Success
Social-emotional learning (SEL) in kindergarten fosters essential skills such as emotional regulation, empathy, and collaboration, directly enhancing academic readiness. Research shows that children with strong SEL competencies exhibit higher literacy and math achievement, better classroom behavior, and increased motivation to learn. Integrating SEL into early education creates a foundation for academic success by promoting positive relationships and effective problem-solving skills.
Challenges in Prioritizing Academic Readiness Over SEL
Prioritizing academic readiness over social-emotional learning (SEL) in kindergarten often leads to challenges such as increased student stress, reduced motivation, and difficulty developing critical interpersonal skills. Kindergarteners benefit from SEL programs that foster emotional regulation, empathy, and collaboration, which are foundational for academic success. Ignoring SEL can hinder children's ability to engage fully in learning, impacting long-term educational outcomes and overall well-being.
Strategies to Support Both SEL and Academic Growth
Integrating social-emotional learning (SEL) with academic readiness in kindergarten involves strategies that promote self-regulation, empathy, and cooperative learning alongside literacy and numeracy skills. Techniques such as collaborative group activities, storytelling, and emotion identification games enhance both SEL and cognitive development by fostering communication and critical thinking. Creating a supportive classroom environment with consistent routines and positive reinforcement helps children build confidence and readiness for academic challenges.
The Role of Educators in Fostering Holistic Kindergarten Development
Educators play a crucial role in fostering holistic kindergarten development by balancing social-emotional learning and academic readiness. They implement strategies that nurture self-regulation, empathy, and collaboration alongside foundational skills in literacy and numeracy. Research shows that integrating social-emotional competencies with academic instruction enhances school readiness and long-term student success.
Social-emotional learning vs Academic readiness Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com