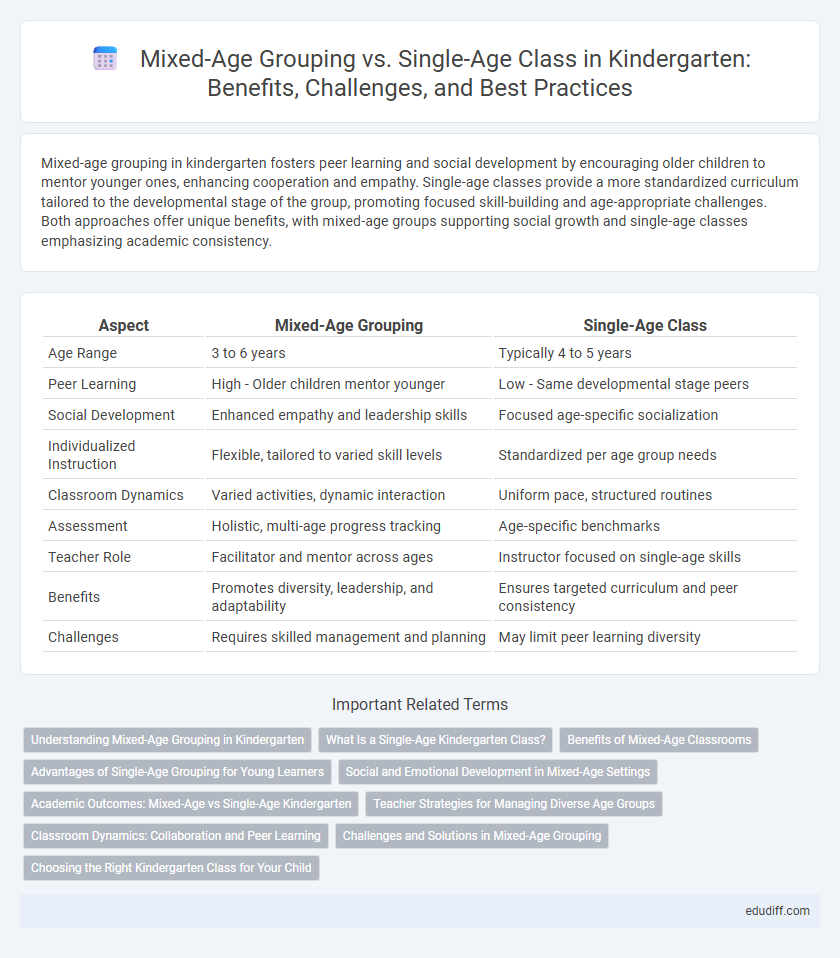
Mixed-age grouping in kindergarten fosters peer learning and social development by encouraging older children to mentor younger ones, enhancing cooperation and empathy. Single-age classes provide a more standardized curriculum tailored to the developmental stage of the group, promoting focused skill-building and age-appropriate challenges. Both approaches offer unique benefits, with mixed-age groups supporting social growth and single-age classes emphasizing academic consistency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mixed-Age Grouping | Single-Age Class |
|---|---|---|
| Age Range | 3 to 6 years | Typically 4 to 5 years |
| Peer Learning | High - Older children mentor younger | Low - Same developmental stage peers |
| Social Development | Enhanced empathy and leadership skills | Focused age-specific socialization |
| Individualized Instruction | Flexible, tailored to varied skill levels | Standardized per age group needs |
| Classroom Dynamics | Varied activities, dynamic interaction | Uniform pace, structured routines |
| Assessment | Holistic, multi-age progress tracking | Age-specific benchmarks |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and mentor across ages | Instructor focused on single-age skills |
| Benefits | Promotes diversity, leadership, and adaptability | Ensures targeted curriculum and peer consistency |
| Challenges | Requires skilled management and planning | May limit peer learning diversity |
Understanding Mixed-Age Grouping in Kindergarten
Mixed-age grouping in kindergarten fosters social development by allowing younger children to learn from older peers while older children reinforce their knowledge through mentorship. This approach supports individualized learning paces and encourages collaboration, enhancing cognitive and emotional growth. Research shows mixed-age classrooms promote adaptability and improved problem-solving skills compared to single-age classes.
What Is a Single-Age Kindergarten Class?
A single-age kindergarten class groups children of the same age, typically five-year-olds, fostering developmentally aligned instruction and social interaction. This model enables educators to tailor curriculum objectives precisely to the typical developmental milestones of that age group. Single-age classes often simplify assessment and curriculum planning while promoting peer bonding among similarly aged children.
Benefits of Mixed-Age Classrooms
Mixed-age classrooms foster peer learning by encouraging older children to mentor younger ones, enhancing social skills and empathy. They support individualized pacing, allowing children to advance based on ability rather than age, which promotes cognitive development. These environments also create a more inclusive community by reducing competition and celebrating diverse abilities.
Advantages of Single-Age Grouping for Young Learners
Single-age grouping in kindergarten allows teachers to tailor instruction precisely to the developmental stage of young learners, promoting more effective skill acquisition and cognitive growth. Consistent peer interactions within the same age range enhance social-emotional learning by providing relatable role models and reducing social comparison stress. This focused environment supports standardized curriculum delivery and better assessment of children's progress in early childhood education.
Social and Emotional Development in Mixed-Age Settings
Mixed-age grouping in kindergarten fosters enhanced social and emotional development by promoting empathy, cooperation, and leadership among children of varying ages. Younger students benefit from modeling behaviors of older peers, while older children gain confidence and responsibility through mentoring roles. Research indicates that mixed-age settings improve communication skills and emotional regulation, contributing to a supportive and inclusive learning environment.
Academic Outcomes: Mixed-Age vs Single-Age Kindergarten
Mixed-age grouping in kindergarten often fosters higher academic outcomes by promoting peer learning and individualized pacing, enabling younger children to benefit from older classmates' skills while older children reinforce their knowledge through mentorship. Research indicates that single-age classes may provide structured curricula tailored to specific developmental stages, but mixed-age classrooms encourage cognitive flexibility and social-emotional growth, which contribute to improved literacy and numeracy skills. Academic performance in mixed-age settings can surpass that of single-age classrooms when teachers effectively differentiate instruction to meet diverse learning needs.
Teacher Strategies for Managing Diverse Age Groups
Effective teacher strategies for managing mixed-age groups in kindergarten emphasize differentiated instruction tailored to varying developmental stages, promoting peer learning where older children support younger classmates. Classroom organization involves flexible seating arrangements and activity centers designed to accommodate diverse abilities, fostering independence and collaboration. Assessment methods are adjusted to track individual progress across age ranges, enabling personalized feedback and goal setting.
Classroom Dynamics: Collaboration and Peer Learning
Mixed-age grouping in kindergarten promotes diverse classroom dynamics by encouraging collaboration and peer learning across developmental stages, enabling older children to reinforce their knowledge through teaching younger peers. Single-age classes often see more uniform skill levels, which can streamline curriculum pacing but limit opportunities for mentorship and varied social interactions. Research indicates that mixed-age settings foster empathy, leadership, and problem-solving skills, enriching the overall learning environment.
Challenges and Solutions in Mixed-Age Grouping
Mixed-age grouping in kindergarten presents challenges such as varied developmental levels, differing learning paces, and increased teacher workload. Effective solutions include differentiated instruction, individualized learning plans, and peer mentoring to address diverse needs and promote collaborative learning. Teachers benefit from professional development in classroom management and adaptive curriculum design tailored to mixed-age environments.
Choosing the Right Kindergarten Class for Your Child
Choosing the right kindergarten class involves evaluating the benefits of mixed-age grouping, which fosters peer learning and social development, against single-age classes that offer age-specific curriculum and targeted skill building. Mixed-age classrooms support individualized learning paces and promote leadership skills among older children, while single-age classes provide structured activities tailored to developmental milestones. Parents should consider their child's social adaptability, learning style, and readiness to thrive in diverse or homogeneous age settings to make an informed decision.
Mixed-age grouping vs Single-age class Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com