Emergent curriculum in kindergarten adapts to children's interests and promotes creativity by allowing flexible, child-driven learning experiences. In contrast, a preset curriculum follows a fixed plan with specific goals and activities designed by educators to ensure consistent coverage of developmental milestones. Balancing both approaches can support holistic growth by combining structured learning with opportunities for exploration and discovery.
Table of Comparison
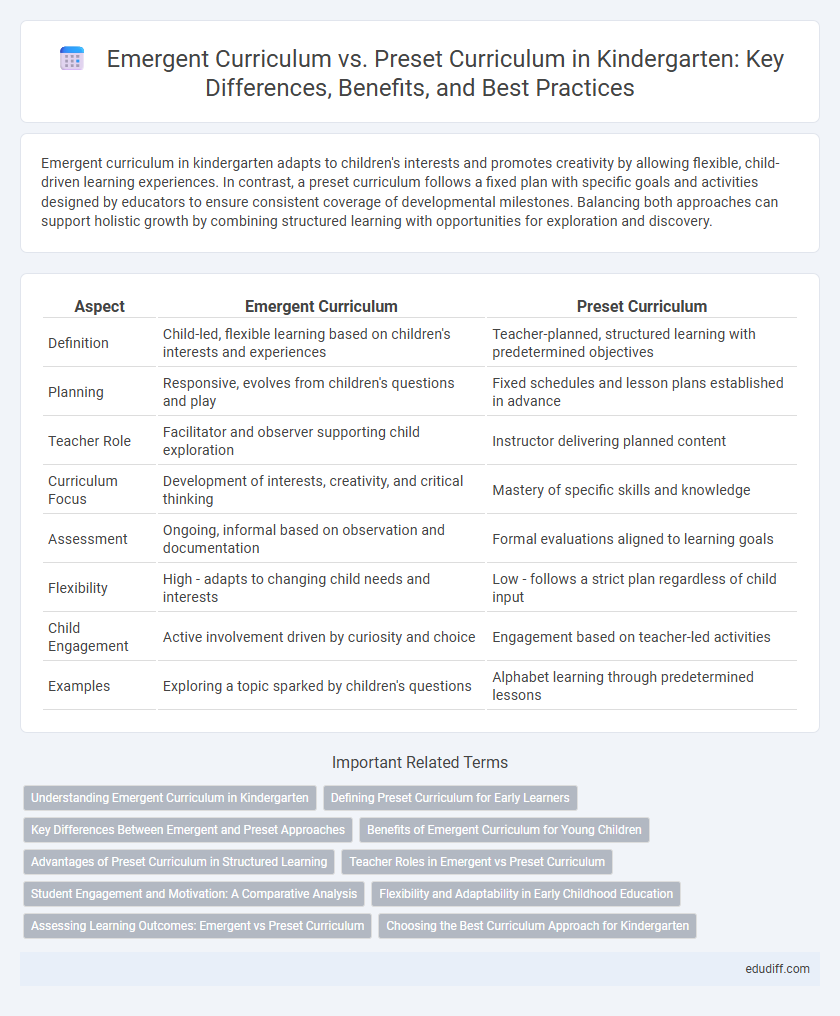
| Aspect | Emergent Curriculum | Preset Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child-led, flexible learning based on children's interests and experiences | Teacher-planned, structured learning with predetermined objectives |
| Planning | Responsive, evolves from children's questions and play | Fixed schedules and lesson plans established in advance |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and observer supporting child exploration | Instructor delivering planned content |
| Curriculum Focus | Development of interests, creativity, and critical thinking | Mastery of specific skills and knowledge |
| Assessment | Ongoing, informal based on observation and documentation | Formal evaluations aligned to learning goals |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to changing child needs and interests | Low - follows a strict plan regardless of child input |
| Child Engagement | Active involvement driven by curiosity and choice | Engagement based on teacher-led activities |
| Examples | Exploring a topic sparked by children's questions | Alphabet learning through predetermined lessons |
Understanding Emergent Curriculum in Kindergarten
Emergent curriculum in kindergarten centers on child-led learning, where teachers observe children's interests and integrate those themes into educational activities, promoting engagement and creativity. This approach contrasts with preset curriculum, which follows a fixed syllabus with predetermined lessons and outcomes. Understanding emergent curriculum highlights the importance of flexibility, responsiveness, and fostering development through exploration and discovery in early childhood education.
Defining Preset Curriculum for Early Learners
Preset curriculum for early learners refers to a structured educational framework with predefined goals, lessons, and activities designed to guide kindergarten instruction. It emphasizes consistency, measurable outcomes, and adherence to standards, ensuring all students receive uniform content regardless of their individual interests. This approach contrasts with emergent curriculum by prioritizing teacher-led planning and predetermined learning objectives.
Key Differences Between Emergent and Preset Approaches
Emergent curriculum in kindergarten emphasizes child-led exploration where learning themes arise from students' interests and experiences, promoting creativity and adaptability. Preset curriculum follows a structured plan with predetermined goals and activities designed to meet specific educational standards and benchmarks. Key differences include the flexibility of emergent approaches versus the consistency and predictability of preset models, impacting teacher roles and responsiveness to individual learning needs.
Benefits of Emergent Curriculum for Young Children
Emergent curriculum in kindergarten fosters creativity and critical thinking by adapting to children's interests and developmental stages, promoting active engagement and deeper learning. It enhances social-emotional skills by encouraging collaboration and communication through child-led activities. This flexible approach supports individualized learning, making it more inclusive and responsive to diverse needs compared to a preset curriculum.
Advantages of Preset Curriculum in Structured Learning
Preset curriculum in kindergarten offers a structured learning environment that ensures comprehensive coverage of essential developmental milestones and academic skills. Its consistent framework helps teachers systematically track progress and tailor interventions effectively. The predictability of preset curricula supports classroom management and aligns learning outcomes with educational standards.
Teacher Roles in Emergent vs Preset Curriculum
In emergent curriculum, teachers act as facilitators and observers, adapting lesson plans based on children's interests and developmental needs to foster a child-centered learning environment. In contrast, preset curriculum requires teachers to follow a fixed syllabus with predetermined objectives and activities, emphasizing structure and consistency. The emergent approach empowers teachers to be responsive and flexible, while the preset model positions them as implementers of established educational goals.
Student Engagement and Motivation: A Comparative Analysis
Emergent curriculum fosters higher student engagement and motivation in kindergarten by adapting to children's interests and promoting active exploration, leading to deeper learning experiences. In contrast, preset curriculum often limits student motivation due to its structured and uniform approach, which may not align with individual children's curiosities and developmental needs. Research indicates that emergent curricula enhance intrinsic motivation and participation, which are critical for early childhood cognitive and social development.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Early Childhood Education
Emergent curriculum in early childhood education emphasizes flexibility, allowing educators to adapt lessons based on children's interests, developmental stages, and spontaneous learning opportunities. In contrast, preset curriculum follows a structured plan with predetermined objectives and activities, limiting the ability to respond dynamically to individual needs. This adaptability in emergent curriculum supports personalized learning, fostering creativity and deeper engagement among kindergarten students.
Assessing Learning Outcomes: Emergent vs Preset Curriculum
Assessing learning outcomes in an emergent curriculum involves ongoing documentation, observation, and reflective practices that capture children's interests and developmental progress in real-time. In contrast, preset curriculum assessment relies on standardized benchmarks and predetermined objectives to measure skill acquisition and knowledge retention. The emergent approach promotes individualized understanding of learning trajectories, while preset assessment emphasizes comparability and structured evaluation.
Choosing the Best Curriculum Approach for Kindergarten
Emergent curriculum in kindergarten prioritizes children's interests and developmental readiness, fostering creativity and engagement through responsive, flexible learning experiences. Preset curriculum offers structured, predefined lessons aligned with educational standards, ensuring consistency and measurable outcomes for early childhood education. Selecting the best curriculum approach depends on balancing individualized child development with curriculum standards to promote holistic growth in kindergarten settings.
Emergent curriculum vs Preset curriculum Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com