3K programs cater to three-year-olds, emphasizing early social skills and sensory play to prepare children for structured learning environments. Pre-K serves four-year-olds with a stronger focus on foundational academics, including basic literacy and numeracy, to ensure readiness for kindergarten. Both programs support developmental milestones but differ in intensity and curriculum depth, tailored to each age group's needs.
Table of Comparison
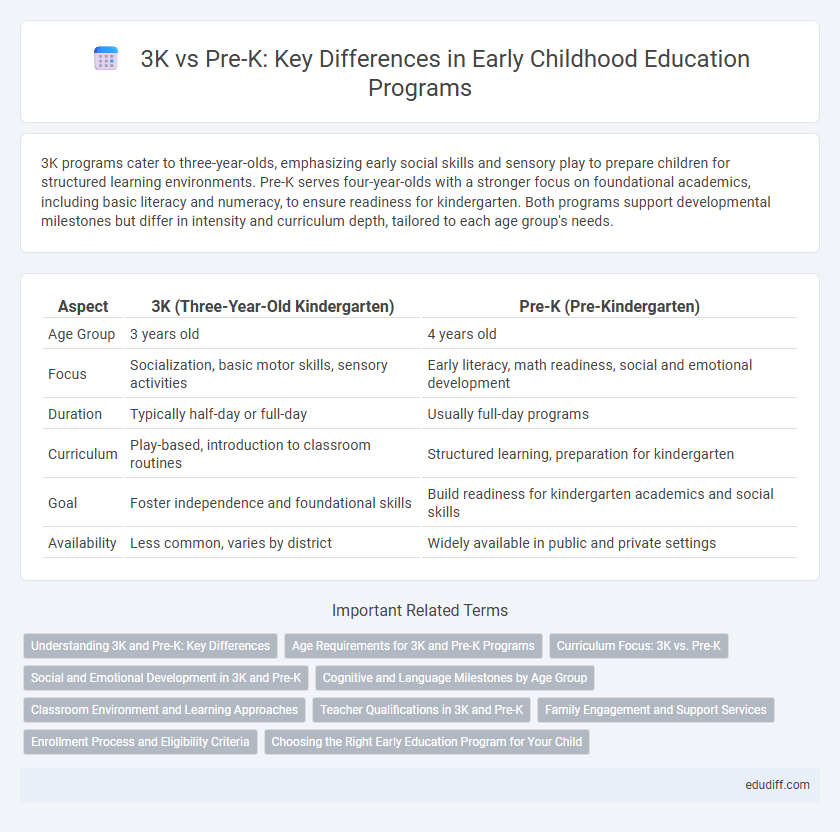
| Aspect | 3K (Three-Year-Old Kindergarten) | Pre-K (Pre-Kindergarten) |
|---|---|---|
| Age Group | 3 years old | 4 years old |
| Focus | Socialization, basic motor skills, sensory activities | Early literacy, math readiness, social and emotional development |
| Duration | Typically half-day or full-day | Usually full-day programs |
| Curriculum | Play-based, introduction to classroom routines | Structured learning, preparation for kindergarten |
| Goal | Foster independence and foundational skills | Build readiness for kindergarten academics and social skills |
| Availability | Less common, varies by district | Widely available in public and private settings |
Understanding 3K and Pre-K: Key Differences
3K programs serve children around age 3, focusing on early socialization and basic motor skills development, while Pre-K typically targets 4-year-olds preparing for kindergarten readiness with early literacy and numeracy skills. 3K emphasizes play-based learning and sensory experiences that promote cognitive and emotional growth suited for toddlers. Pre-K offers more structured activities aimed at fostering early academic skills, social independence, and classroom behavior essential for successful transition into formal schooling.
Age Requirements for 3K and Pre-K Programs
3K programs typically serve children around 3 years old, focusing on early socialization and basic skill development in a play-based environment. Pre-K programs generally enroll 4-year-olds, preparing them for kindergarten by enhancing language, literacy, and cognitive skills. Age requirements for 3K and Pre-K vary by district but generally target children aged 3 and 4, respectively.
Curriculum Focus: 3K vs. Pre-K
3K programs emphasize play-based learning and socialization skills to support early development, while Pre-K focuses more on school readiness with foundational literacy, math, and cognitive skills. The 3K curriculum typically includes activities that promote fine and gross motor development along with early communication, whereas Pre-K integrates structured lessons aimed at preparing children for kindergarten expectations. Both programs support emotional and social growth, but Pre-K places greater emphasis on academic milestones.
Social and Emotional Development in 3K and Pre-K
3K programs emphasize early social skills by fostering interaction through guided play and group activities, promoting emotional regulation and empathy development in young children. Pre-K builds on these foundations by enhancing self-awareness, cooperation, and problem-solving abilities to prepare kids for kindergarten readiness. Both 3K and Pre-K curricula integrate social-emotional learning (SEL) strategies that support confidence, resilience, and positive peer relationships essential for long-term academic success.
Cognitive and Language Milestones by Age Group
3K programs target children around age three, focusing on foundational cognitive skills such as basic problem-solving, early memory retention, and simple language development including vocabulary expansion and simple sentence formation. Pre-K, designed for four-year-olds, emphasizes more advanced cognitive milestones like early literacy, counting, and reasoning abilities, alongside language milestones such as complex sentence structures, storytelling, and improved comprehension. Both age groups benefit from tailored curricula that support developmental readiness for kindergarten, but Pre-K builds on 3K's foundational skills to enhance school readiness through enriched cognitive and language experiences.
Classroom Environment and Learning Approaches
3K classrooms emphasize playful, sensory-rich environments designed to foster social-emotional development and basic motor skills, using hands-on activities and exploratory learning. Pre-K settings adopt a more structured approach with targeted curriculum elements that prepare children for kindergarten by integrating early literacy and numeracy through guided instruction and small-group activities. Both prioritize interaction and engagement, but Pre-K balances play with foundational academic skills to support school readiness.
Teacher Qualifications in 3K and Pre-K
3K teachers typically hold a Child Development Associate (CDA) credential or an associate degree in early childhood education, ensuring foundational skills in child development. Pre-K educators often possess a bachelor's degree in early childhood education or a related field, reflecting a higher level of academic training. This difference in qualifications supports the increasing developmental and instructional needs of Pre-K students compared to 3K learners.
Family Engagement and Support Services
3K programs emphasize family engagement through tailored outreach and personalized support services, fostering strong partnerships between educators and caregivers. Pre-K initiatives often offer comprehensive resources, including health screenings and parent workshops, to address diverse developmental needs. Both settings prioritize collaborative approaches, but 3K centers typically provide more intensive family support due to the younger age group and early intervention goals.
Enrollment Process and Eligibility Criteria
3K programs primarily serve children aged three, requiring proof of age and residency for enrollment, while Pre-K targets four-year-olds, often with additional eligibility criteria such as income limits or developmental assessments. Enrollment processes for both involve submitting an application, providing immunization records, and attending an orientation, but Pre-K programs may require priority enrollment for families meeting specific socioeconomic guidelines. Understanding these distinctions helps families navigate the appropriate early childhood education options efficiently.
Choosing the Right Early Education Program for Your Child
Choosing between 3K and Pre-K programs depends on your child's developmental needs and readiness for structured learning environments. 3K focuses on fostering social skills and basic motor development for three-year-olds, while Pre-K prepares four-year-olds with foundational academic skills like early literacy and numeracy. Assessing your child's individual growth milestones and the curriculum focus of each program ensures a tailored approach to early education that enhances school readiness.
3K vs Pre-K Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com