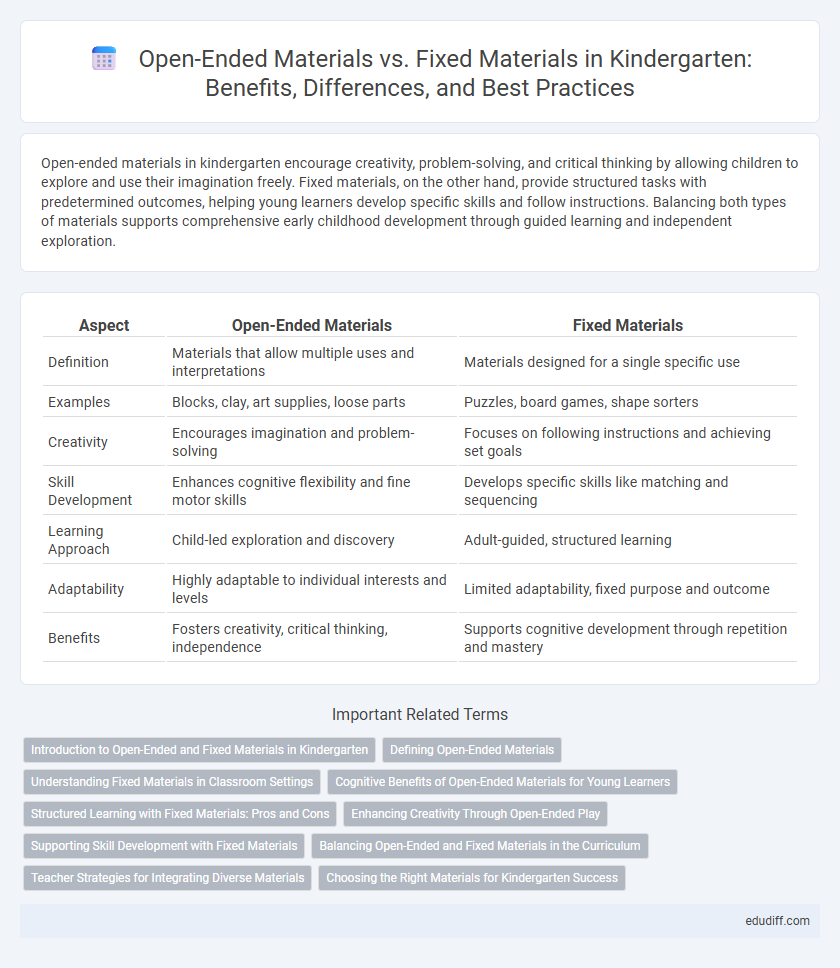
Open-ended materials in kindergarten encourage creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking by allowing children to explore and use their imagination freely. Fixed materials, on the other hand, provide structured tasks with predetermined outcomes, helping young learners develop specific skills and follow instructions. Balancing both types of materials supports comprehensive early childhood development through guided learning and independent exploration.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Open-Ended Materials | Fixed Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Materials that allow multiple uses and interpretations | Materials designed for a single specific use |
| Examples | Blocks, clay, art supplies, loose parts | Puzzles, board games, shape sorters |
| Creativity | Encourages imagination and problem-solving | Focuses on following instructions and achieving set goals |
| Skill Development | Enhances cognitive flexibility and fine motor skills | Develops specific skills like matching and sequencing |
| Learning Approach | Child-led exploration and discovery | Adult-guided, structured learning |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable to individual interests and levels | Limited adaptability, fixed purpose and outcome |
| Benefits | Fosters creativity, critical thinking, independence | Supports cognitive development through repetition and mastery |
Introduction to Open-Ended and Fixed Materials in Kindergarten
Open-ended materials in kindergarten, such as blocks, clay, and art supplies, encourage creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking by allowing multiple uses and interpretations. Fixed materials, like puzzles and matching sets, provide structured learning with specific outcomes, promoting skills such as pattern recognition and fine motor development. Integrating both types supports balanced cognitive growth, fostering both imaginative exploration and focused skill mastery in early childhood education.
Defining Open-Ended Materials
Open-ended materials in kindergarten are versatile resources that encourage creativity, exploration, and problem-solving without predetermined outcomes, such as blocks, art supplies, or natural objects. These materials foster divergent thinking by allowing children to interpret and use them in multiple ways, enhancing cognitive and fine motor skills. Unlike fixed materials that have specific functions or rules, open-ended materials promote autonomy and social interaction in early childhood learning environments.
Understanding Fixed Materials in Classroom Settings
Fixed materials in kindergarten classrooms offer structured, purpose-driven activities that help children develop specific skills such as fine motor coordination, number recognition, and letter formation. These materials often include puzzles, shape sorters, and counting blocks, which provide clear objectives and measurable outcomes to support targeted learning goals. Understanding how to integrate fixed materials effectively enables teachers to balance creativity with foundational skill-building in early childhood education.
Cognitive Benefits of Open-Ended Materials for Young Learners
Open-ended materials in kindergarten foster creativity and critical thinking by allowing children to explore multiple solutions and interpretations. These materials promote problem-solving skills and cognitive flexibility, essential for brain development in early childhood. In contrast to fixed materials, open-ended resources adapt to varied learning styles and encourage independent decision-making, enhancing cognitive growth and engagement.
Structured Learning with Fixed Materials: Pros and Cons
Structured learning with fixed materials in kindergarten provides clear guidelines and predictable outcomes, which support skill mastery and reinforce specific concepts efficiently. Fixed materials, such as puzzles with defined pieces or worksheets, help children develop focused cognitive skills and follow instructions, promoting discipline and concentration. However, these materials may limit creativity and exploration, restricting opportunities for open-ended problem-solving and individual expression.
Enhancing Creativity Through Open-Ended Play
Open-ended materials in kindergarten, such as blocks, clay, and loose parts, significantly boost children's creativity by encouraging imagination, problem-solving, and independent thinking. Unlike fixed materials with predetermined outcomes, these open-ended resources allow for multiple interpretations and solutions, fostering innovation and cognitive flexibility. Studies show that early exposure to open-ended play correlates with enhanced divergent thinking and greater adaptability in learning environments.
Supporting Skill Development with Fixed Materials
Fixed materials provide structured opportunities for children to develop fine motor skills, pattern recognition, and problem-solving abilities through consistent and predictable use. These materials, such as puzzles, blocks with specific shapes, and matching games, reinforce cognitive skills by offering clear goals and immediate feedback. Utilizing fixed materials in kindergarten settings supports skill acquisition by promoting focused practice and mastery of fundamental concepts.
Balancing Open-Ended and Fixed Materials in the Curriculum
Balancing open-ended and fixed materials in a kindergarten curriculum fosters creativity alongside skill mastery, allowing children to explore imaginative play with flexible resources while also developing specific competencies through structured tools. Open-ended materials like blocks and art supplies encourage problem-solving and innovation, whereas fixed materials such as puzzles and counting beads support cognitive development and fine motor skills. Integrating both types ensures a well-rounded learning environment that adapts to diverse developmental needs and promotes holistic growth in early childhood education.
Teacher Strategies for Integrating Diverse Materials
Teachers enhance cognitive development by integrating open-ended materials, such as blocks and art supplies, which foster creativity and problem-solving skills in kindergarten students. Fixed materials, like puzzles and pre-assembled kits, support rule-following and fine motor skills but require balanced use to prevent limiting exploration. Effective strategies include blending both material types to address diverse learning styles and scaffold individualized instruction.
Choosing the Right Materials for Kindergarten Success
Open-ended materials such as blocks, art supplies, and loose parts encourage creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking in kindergarteners by allowing multiple outcomes and uses. Fixed materials like puzzles and predefined toys support skill-building, structure, and goal-oriented play, which help develop fine motor skills and cognitive abilities. Balancing open-ended and fixed materials in the classroom creates an enriching environment that fosters independent exploration while guiding developmental milestones for kindergarten success.
Open-ended materials vs Fixed materials Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com