Letter recognition and number recognition are foundational skills in early childhood education that support literacy and numeracy development. Letters help children understand sounds and word formation, while numbers introduce concepts of quantity and basic math operations. Mastering both skills simultaneously enhances cognitive growth and prepares children for academic success.
Table of Comparison
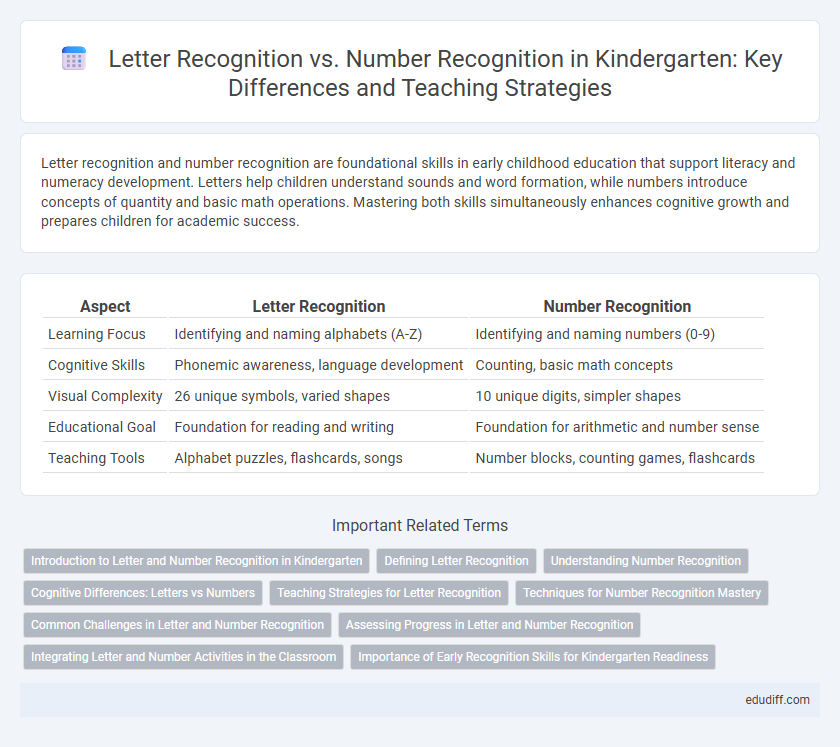
| Aspect | Letter Recognition | Number Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Focus | Identifying and naming alphabets (A-Z) | Identifying and naming numbers (0-9) |
| Cognitive Skills | Phonemic awareness, language development | Counting, basic math concepts |
| Visual Complexity | 26 unique symbols, varied shapes | 10 unique digits, simpler shapes |
| Educational Goal | Foundation for reading and writing | Foundation for arithmetic and number sense |
| Teaching Tools | Alphabet puzzles, flashcards, songs | Number blocks, counting games, flashcards |
Introduction to Letter and Number Recognition in Kindergarten
Kindergarten curriculum introduces letter recognition by focusing on uppercase and lowercase letters through engaging activities and phonics-based learning, enhancing early literacy skills. Number recognition emphasizes identifying numerals 0-20, counting objects, and understanding basic quantity concepts to build foundational math abilities. Integrating multisensory approaches in both areas supports cognitive development and prepares children for reading and arithmetic proficiency.
Defining Letter Recognition
Letter recognition involves identifying and naming the letters of the alphabet, which is a fundamental skill in early literacy development. This process helps children associate letters with their corresponding sounds, enabling reading and writing proficiency. Unlike number recognition, which focuses on understanding numerical symbols and quantities, letter recognition lays the foundation for language acquisition and communication.
Understanding Number Recognition
Understanding number recognition in kindergarten involves identifying and naming numerals, which is foundational for early math skills like counting and simple addition. Children who master number recognition gain the ability to link numbers with quantities, enabling better problem-solving and logical thinking. This skill is crucial for developing numerical fluency and preparing students for more complex mathematical concepts.
Cognitive Differences: Letters vs Numbers
Letter recognition in kindergarten involves identifying unique shapes and associating them with sounds, engaging language processing areas in the brain, whereas number recognition primarily activates numerical cognition regions responsible for quantity and order understanding. Letters require phonemic awareness and are processed through symbolic decoding linked to reading skills, while numbers necessitate grasping abstract concepts like magnitude and sequencing. These cognitive differences influence how educators tailor teaching strategies to develop literacy and numeracy foundations effectively.
Teaching Strategies for Letter Recognition
Effective teaching strategies for letter recognition in kindergarten include using multisensory approaches such as tactile tracing, visual flashcards, and phonetic songs to reinforce letter shapes and sounds. Incorporating interactive activities like alphabet games, storytelling, and letter hunts enhances engagement and helps solidify memory connections. Consistent practice with positive reinforcement promotes retention, differentiating letter recognition techniques from number recognition methods that often emphasize counting and numerical concepts.
Techniques for Number Recognition Mastery
Hands-on activities like counting objects and using number puzzles enhance number recognition skills in kindergarten. Incorporating visual aids such as number charts and flashcards helps children associate numerals with quantities effectively. Regular practice through games and interactive storytelling solidifies understanding and supports mastery of number concepts.
Common Challenges in Letter and Number Recognition
Kindergarten children often face challenges in letter recognition due to similar letter shapes like b, d, p, and q, which can cause confusion. Number recognition difficulties commonly arise with numerals such as 6 and 9 or 3 and 8, which share visual similarities that hinder accurate identification. Both letter and number recognition struggles impact early literacy and numeracy development, requiring targeted interventions to support mastery.
Assessing Progress in Letter and Number Recognition
Assessing progress in letter and number recognition involves tracking a child's ability to identify, name, and differentiate between letters and numerals. Effective methods include observational checklists, flashcard exercises, and interactive games that capture recognition speed and accuracy. Regular assessment helps tailor instruction to support literacy and numeracy development in kindergarten students.
Integrating Letter and Number Activities in the Classroom
Integrating letter and number recognition activities in kindergarten enhances cognitive development by promoting literacy and numeracy skills simultaneously. Activities like alphabet-number matching games and interactive story problems help children make connections between symbols and their meanings. This integrated approach supports early learning goals by fostering pattern recognition and critical thinking in a cohesive, engaging environment.
Importance of Early Recognition Skills for Kindergarten Readiness
Early recognition of letters enhances phonemic awareness and lays the foundation for reading and writing proficiency, crucial for kindergarten readiness. Simultaneously, number recognition supports the development of basic math skills such as counting and pattern identification, essential for early numeracy. Prioritizing both letter and number recognition fosters comprehensive cognitive development and prepares children for academic success in kindergarten.
Letter recognition vs Number recognition Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com