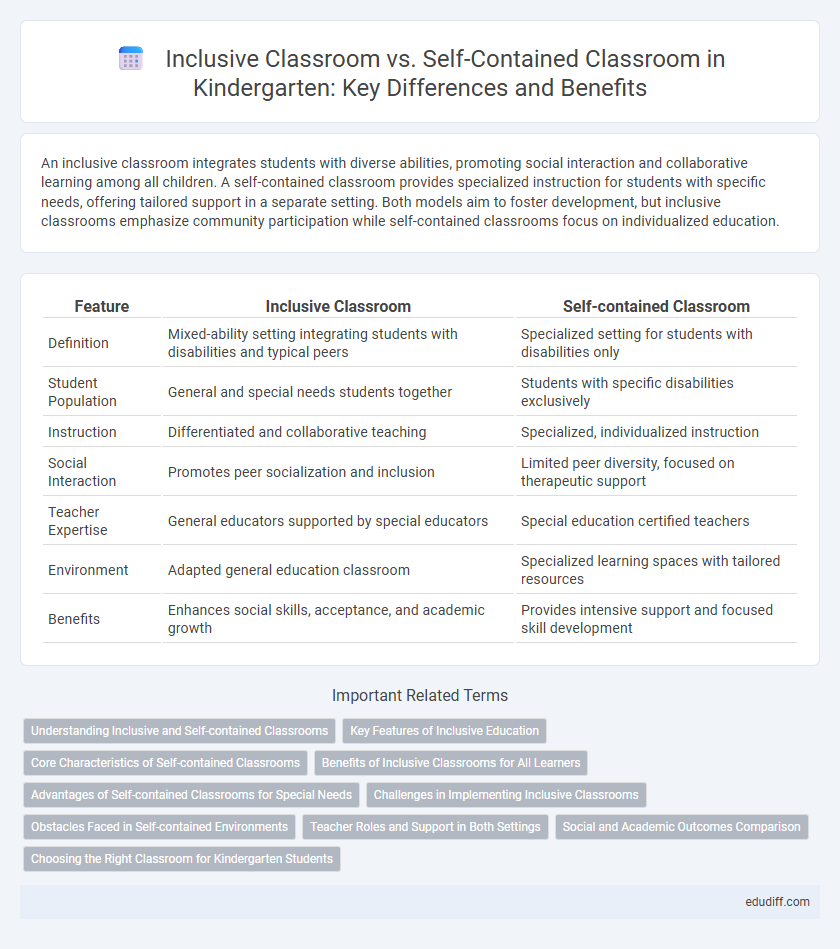
An inclusive classroom integrates students with diverse abilities, promoting social interaction and collaborative learning among all children. A self-contained classroom provides specialized instruction for students with specific needs, offering tailored support in a separate setting. Both models aim to foster development, but inclusive classrooms emphasize community participation while self-contained classrooms focus on individualized education.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inclusive Classroom | Self-contained Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mixed-ability setting integrating students with disabilities and typical peers | Specialized setting for students with disabilities only |
| Student Population | General and special needs students together | Students with specific disabilities exclusively |
| Instruction | Differentiated and collaborative teaching | Specialized, individualized instruction |
| Social Interaction | Promotes peer socialization and inclusion | Limited peer diversity, focused on therapeutic support |
| Teacher Expertise | General educators supported by special educators | Special education certified teachers |
| Environment | Adapted general education classroom | Specialized learning spaces with tailored resources |
| Benefits | Enhances social skills, acceptance, and academic growth | Provides intensive support and focused skill development |
Understanding Inclusive and Self-contained Classrooms
Inclusive classrooms integrate children with diverse learning needs into general education settings, promoting social interaction and peer support, which enhances developmental outcomes for all students. Self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction within a separate environment tailored to children with significant individual needs, offering focused support and resources to address specific challenges. Both classroom types aim to optimize educational experiences but differ in structure, instructional approach, and level of integration with typically developing peers.
Key Features of Inclusive Education
Inclusive classrooms integrate children with diverse learning needs in the same environment, promoting social interaction and peer learning while utilizing differentiated instruction tailored to individual abilities. Key features include collaborative teaching strategies, ongoing assessment, and accessibility accommodations that support all students. Emphasis on fostering a sense of community and encouraging participation ensures equitable opportunities for growth and development.
Core Characteristics of Self-contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms in kindergarten feature a dedicated teacher responsible for all academic and behavioral instruction within a single classroom environment, providing tailored support to students with specific learning needs. These classrooms typically have smaller class sizes to ensure individualized attention and foster a structured, consistent routine that helps children build confidence and mastery in essential skills. Emphasizing personalized interventions, self-contained classrooms create a supportive setting designed to address diverse developmental challenges and promote social-emotional growth.
Benefits of Inclusive Classrooms for All Learners
Inclusive classrooms foster social-emotional development by encouraging interaction among diverse learners, promoting empathy and collaboration skills. Exposure to varied learning styles and abilities enhances cognitive growth, increasing adaptability and problem-solving skills for all children. Inclusive settings provide equitable access to resources and individualized support, benefiting both students with special needs and their typically developing peers.
Advantages of Self-contained Classrooms for Special Needs
Self-contained classrooms provide specialized support tailored to the unique learning needs of students with disabilities, allowing for individualized instruction and targeted intervention. These environments often feature smaller class sizes, enabling educators to foster stronger relationships and closely monitor student progress. Access to specialized resources and therapists within the classroom setting enhances skill development and promotes a supportive learning atmosphere for special needs children.
Challenges in Implementing Inclusive Classrooms
Implementing inclusive classrooms in kindergarten often faces challenges such as limited teacher training in differentiated instruction and insufficient classroom resources to support diverse learning needs. Managing varied behavioral and developmental levels within a single inclusive setting can strain educators, impacting individualized attention and student engagement. Classroom size and inadequate support staff further complicate maintaining an effective inclusive environment compared to self-contained classrooms.
Obstacles Faced in Self-contained Environments
Self-contained classrooms for kindergarteners often present obstacles such as limited social interaction opportunities with neurotypical peers, which can hinder the development of essential communication and social skills. These environments may lack the diversity of learning styles found in inclusive classrooms, reducing exposure to varied teaching methods and collaborative experiences. Furthermore, self-contained settings sometimes struggle with inadequate resources and support tailored to individual needs, impacting the overall efficacy of specialized education.
Teacher Roles and Support in Both Settings
In an inclusive classroom, teachers adapt lessons to accommodate diverse learning needs, promoting collaboration with special education staff to support all students. Self-contained classroom teachers specialize in individualized instruction for students with significant disabilities, providing targeted interventions within a smaller, controlled setting. Both roles require ongoing assessment and tailored strategies to enhance student engagement and academic growth.
Social and Academic Outcomes Comparison
Inclusive classrooms in kindergarten promote social integration by allowing diverse learners to interact and develop empathy, resulting in improved communication and collaboration skills. Academic outcomes tend to be positive in inclusive settings, as differentiated instruction supports individualized learning, enhancing overall achievement for students with and without disabilities. In contrast, self-contained classrooms offer tailored instruction for students with specific needs but may limit social interaction and exposure to typical peer modeling, potentially affecting social development and integration.
Choosing the Right Classroom for Kindergarten Students
Selecting the right classroom setting for kindergarten students depends on their individual learning needs and social development goals. Inclusive classrooms promote interaction with diverse peers, fostering social skills and adaptability, while self-contained classrooms provide tailored instruction for students requiring specialized support. Evaluating a child's academic abilities, behavioral needs, and individualized education program (IEP) helps determine the most effective environment to enhance early learning outcomes.
Inclusive Classroom vs Self-contained Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com