Kindergarten readiness evaluates a child's overall development, including social, emotional, cognitive, and physical skills, to ensure they are prepared for school success. Universal screening systematically assesses all children within a population to identify those needing additional support before entering kindergarten. Both practices play a crucial role in early childhood education by targeting readiness and early intervention.
Table of Comparison
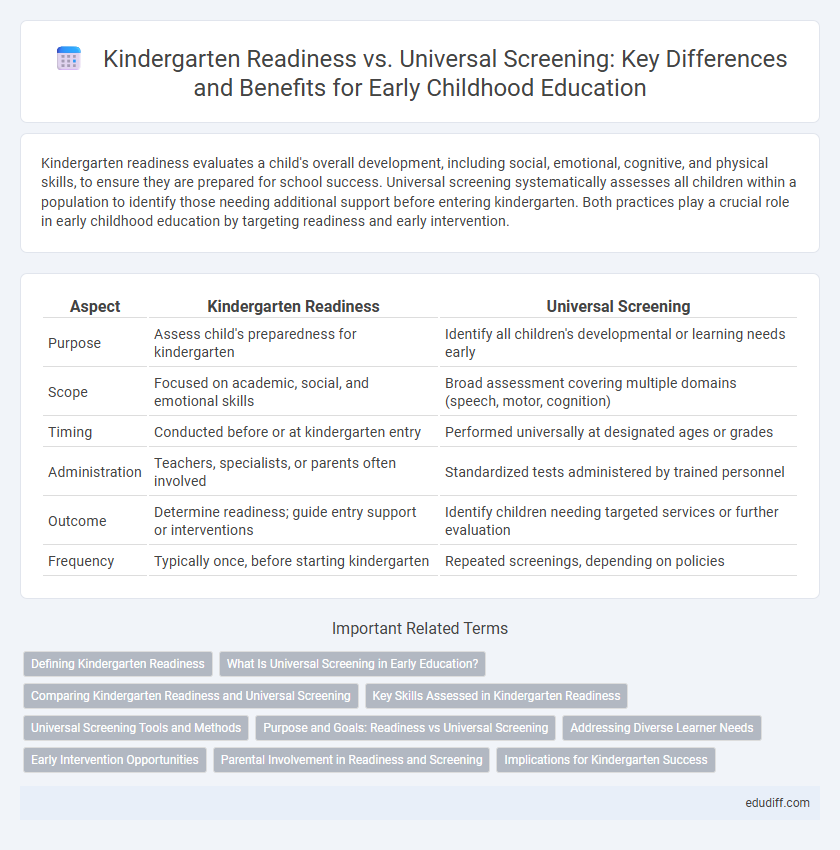
| Aspect | Kindergarten Readiness | Universal Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Assess child's preparedness for kindergarten | Identify all children's developmental or learning needs early |
| Scope | Focused on academic, social, and emotional skills | Broad assessment covering multiple domains (speech, motor, cognition) |
| Timing | Conducted before or at kindergarten entry | Performed universally at designated ages or grades |
| Administration | Teachers, specialists, or parents often involved | Standardized tests administered by trained personnel |
| Outcome | Determine readiness; guide entry support or interventions | Identify children needing targeted services or further evaluation |
| Frequency | Typically once, before starting kindergarten | Repeated screenings, depending on policies |
Defining Kindergarten Readiness
Kindergarten readiness encompasses a child's cognitive, social-emotional, and physical development necessary for success in school, assessed through observational skills and developmental milestones. Universal screening refers to standardized assessments administered to all children to identify those who may need additional support before entering kindergarten. Defining kindergarten readiness involves evaluating key areas such as language proficiency, motor skills, and social behavior to ensure children are prepared for the academic and social demands of kindergarten.
What Is Universal Screening in Early Education?
Universal screening in early education involves systematically assessing all kindergarten children to identify developmental delays or learning challenges before they impact academic progress. This process uses standardized tools to evaluate key domains such as language, motor skills, and social-emotional development, ensuring early identification and intervention. Unlike kindergarten readiness assessments that focus on suitability for school entry, universal screening emphasizes early detection to support individualized learning plans.
Comparing Kindergarten Readiness and Universal Screening
Kindergarten readiness assesses a child's developmental, social, and cognitive skills to determine their preparedness for school, while universal screening involves systematically evaluating all children at a specific age to identify potential learning or developmental challenges. Readiness assessments provide individualized insights to tailor early education, whereas universal screenings aim to detect risks early for intervention across entire populations. Both approaches complement each other by addressing readiness through personalized evaluation and broad identification of support needs.
Key Skills Assessed in Kindergarten Readiness
Kindergarten readiness assessments evaluate key skills such as language and communication, motor abilities, social-emotional development, and early literacy and numeracy to determine a child's preparedness for school. Universal screening, in contrast, provides a broad evaluation of all children to identify potential learning delays or disabilities early, ensuring timely support. Focusing on kindergarten readiness emphasizes developmental milestones essential for successful adjustment and learning in the school environment.
Universal Screening Tools and Methods
Universal screening tools in kindergarten readiness assess all children universally to identify those who may need additional support before starting school. Common methods include standardized assessments, observational checklists, and developmental milestone screenings that evaluate cognitive, language, motor, and social-emotional skills. These tools provide objective data to guide early interventions and ensure equitable opportunities for academic success.
Purpose and Goals: Readiness vs Universal Screening
Kindergarten readiness assessments evaluate a child's developmental milestones, social-emotional skills, and cognitive abilities to determine preparedness for school entry and to tailor early learning experiences accordingly. Universal screening, in contrast, is a broad, systematic process aimed at identifying all children who may need additional support or intervention by assessing key domains such as language, motor skills, and behavior. The primary goal of readiness assessments is to support classroom integration and individualized learning plans, whereas universal screening seeks early identification of developmental delays or learning challenges to prompt timely interventions.
Addressing Diverse Learner Needs
Kindergarten readiness assessments evaluate children's developmental skills to tailor early learning strategies, while universal screening systematically identifies all students' needs, including those with disabilities or language barriers. Addressing diverse learner needs requires integrating both methods to ensure timely support and inclusive instruction. Combining targeted readiness evaluations with broad universal screenings improves educational outcomes by recognizing individual differences and promoting equitable access to resources.
Early Intervention Opportunities
Kindergarten readiness assessments provide targeted insights into a child's developmental strengths and areas for growth, enabling tailored early intervention opportunities to support school success. Universal screening systematically evaluates all children, identifying those who may benefit from early support services before academic difficulties arise. Combining both approaches enhances early detection and maximizes the impact of interventions during critical developmental periods.
Parental Involvement in Readiness and Screening
Parental involvement plays a critical role in both kindergarten readiness and universal screening by providing valuable insights into a child's development that standardized assessments might overlook. Engaged parents contribute to more accurate screenings and readiness evaluations through sharing observations of social, emotional, and cognitive skills demonstrated at home. Research shows that collaboration between educators and families enhances early identification of learning needs and supports tailored interventions for successful kindergarten entry.
Implications for Kindergarten Success
Kindergarten readiness assesses a child's development across cognitive, social, emotional, and physical domains to predict their ability to succeed in school, while universal screening identifies specific learning or developmental delays early. Early identification through universal screening enables timely interventions that support readiness, reducing achievement gaps and improving long-term academic outcomes. Integrating both approaches ensures targeted support that fosters a smoother transition and sustained success throughout kindergarten.
Kindergarten readiness vs Universal screening Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com