Blended learning in postgraduate PET programs integrates online digital media with traditional face-to-face classroom methods, offering flexibility and personalized pacing for students. On-campus learning fosters direct interaction and immediate feedback through physical presence, enhancing collaboration and hands-on experiences vital for practical skills. Both approaches cater to diverse learning preferences, but blended learning often provides greater accessibility for working professionals seeking advanced certification.
Table of Comparison
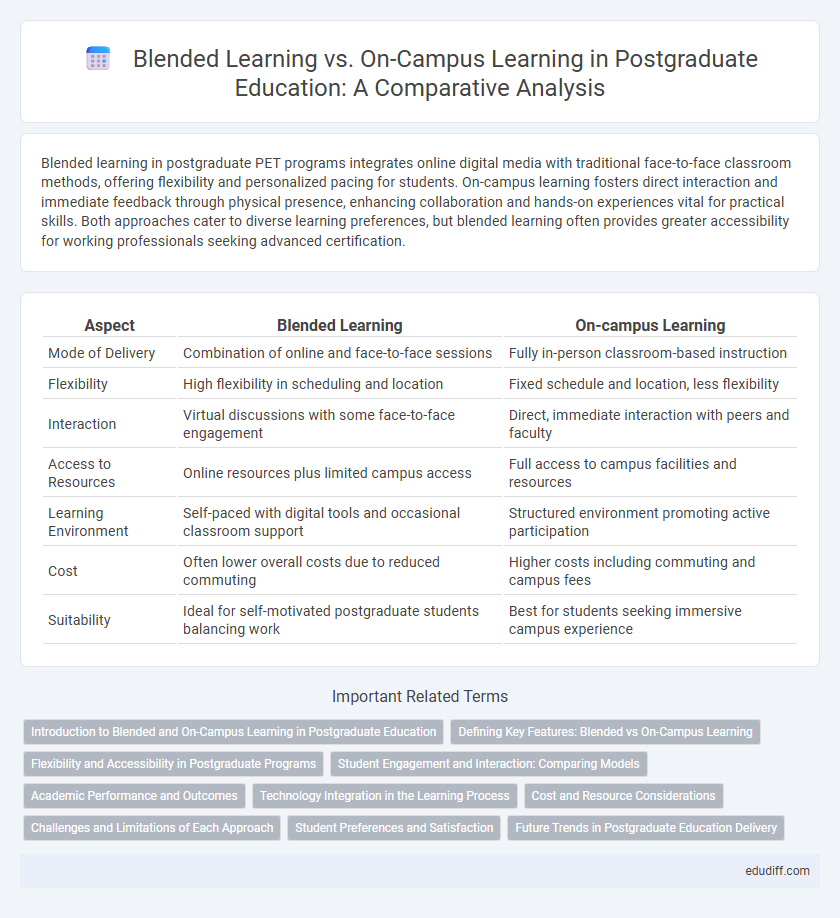
| Aspect | Blended Learning | On-campus Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Mode of Delivery | Combination of online and face-to-face sessions | Fully in-person classroom-based instruction |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in scheduling and location | Fixed schedule and location, less flexibility |
| Interaction | Virtual discussions with some face-to-face engagement | Direct, immediate interaction with peers and faculty |
| Access to Resources | Online resources plus limited campus access | Full access to campus facilities and resources |
| Learning Environment | Self-paced with digital tools and occasional classroom support | Structured environment promoting active participation |
| Cost | Often lower overall costs due to reduced commuting | Higher costs including commuting and campus fees |
| Suitability | Ideal for self-motivated postgraduate students balancing work | Best for students seeking immersive campus experience |
Introduction to Blended and On-Campus Learning in Postgraduate Education
Blended learning in postgraduate education combines online digital resources with traditional face-to-face instruction, enhancing flexibility and accessibility for graduate students. On-campus learning emphasizes direct interaction with faculty and peers, fostering immersive academic experiences and immediate access to campus facilities. Both modalities aim to accommodate diverse learning styles and optimize educational outcomes in advanced academic programs.
Defining Key Features: Blended vs On-Campus Learning
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face classroom methods, allowing postgraduate students flexibility in scheduling and access to diverse resources. On-campus learning emphasizes direct interaction within a structured environment, promoting immediate feedback, hands-on experiences, and peer collaboration. Understanding these key features helps postgraduate students choose the most effective educational approach based on their learning preferences and professional commitments.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Postgraduate Programs
Blended learning in postgraduate programs offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling students to balance studies with professional and personal commitments through a combination of online and face-to-face instruction. Accessibility improves as learners from diverse geographical locations can engage with high-quality education without relocating or interrupting careers. On-campus learning, while providing immersive campus experiences and direct access to faculty and peers, often restricts flexibility due to fixed schedules and commuting demands.
Student Engagement and Interaction: Comparing Models
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face classroom methods, enhancing student engagement through diverse interaction formats such as discussion forums, real-time video sessions, and collaborative projects. On-campus learning fosters immediate personal connections, spontaneous discussions, and hands-on experiences that often lead to higher levels of interpersonal interaction and motivation. Research shows blended models can increase flexibility and access, while on-campus environments typically provide richer social engagement and direct feedback opportunities critical for postgraduate success.
Academic Performance and Outcomes
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, enhancing flexibility and often resulting in improved academic performance and higher retention rates among postgraduate students. On-campus learning fosters direct interaction and immediate feedback, which can strengthen critical thinking and practical skills crucial for advanced studies. Studies indicate postgraduate learners engaging in blended formats tend to achieve comparable or superior outcomes relative to exclusively on-campus cohorts, due to personalized pacing and diverse instructional resources.
Technology Integration in the Learning Process
Blended learning integrates advanced digital tools such as interactive software, virtual simulations, and Learning Management Systems (LMS) to enhance postgraduate education, offering flexibility and personalized learning paths that on-campus learning alone may not provide. On-campus learning benefits from face-to-face interaction, but often lacks the seamless technology integration that supports real-time data analytics and adaptive learning techniques found in blended environments. Effective use of technology in blended learning fosters greater student engagement, improves access to diverse resources, and enables continuous assessment, making it a powerful complement to traditional on-campus methods.
Cost and Resource Considerations
Blended learning reduces overall expenses by minimizing commuting and accommodation costs, making it more affordable for postgraduate students compared to traditional on-campus learning. On-campus programs often require higher investment in physical infrastructure and maintenance, increasing institutional costs that are typically passed on to students. Resource allocation in blended learning leverages digital platforms, optimizing faculty time and educational materials while expanding access to diverse learning tools.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Blended learning in postgraduate education often faces challenges such as technological accessibility issues, inconsistent student engagement, and difficulties in replicating hands-on experiences. On-campus learning limitations include rigid scheduling, higher costs, and limited flexibility for students balancing professional and personal commitments. Both approaches demand tailored solutions to address the unique barriers in postgraduate studies and optimize learning outcomes.
Student Preferences and Satisfaction
Postgraduate students exhibit diverse preferences between blended learning and on-campus learning, influenced by flexibility, access to resources, and social interaction. Research indicates higher satisfaction levels in blended learning environments due to personalized pacing and integrated digital tools, while on-campus learning benefits those prioritizing face-to-face engagement and immediate academic support. Data from recent surveys reveals approximately 65% of postgraduate students favor blended learning for balancing academic and professional commitments, highlighting its growing prominence in higher education.
Future Trends in Postgraduate Education Delivery
Blended learning in postgraduate education is rapidly evolving, integrating digital platforms with traditional on-campus methods to enhance flexibility and accessibility for diverse learners. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven personalized learning and immersive virtual reality environments are shaping future education delivery models, enabling more interactive and adaptive postgraduate experiences. Institutions adopting hybrid frameworks are better positioned to meet the demands of remote and on-site learners, reflecting a growing trend toward customized and technology-enhanced postgraduate programs.
Blended Learning vs On-campus Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com