The Comprehensive Exam evaluates a postgraduate student's overall knowledge and mastery of their field, serving as a critical milestone before advancing. The Candidacy Exam typically focuses on the student's proposed research, assessing their readiness to undertake independent study and contribute original findings. Understanding the distinctions between these exams helps students strategically prepare for their academic progression in postgraduate studies.
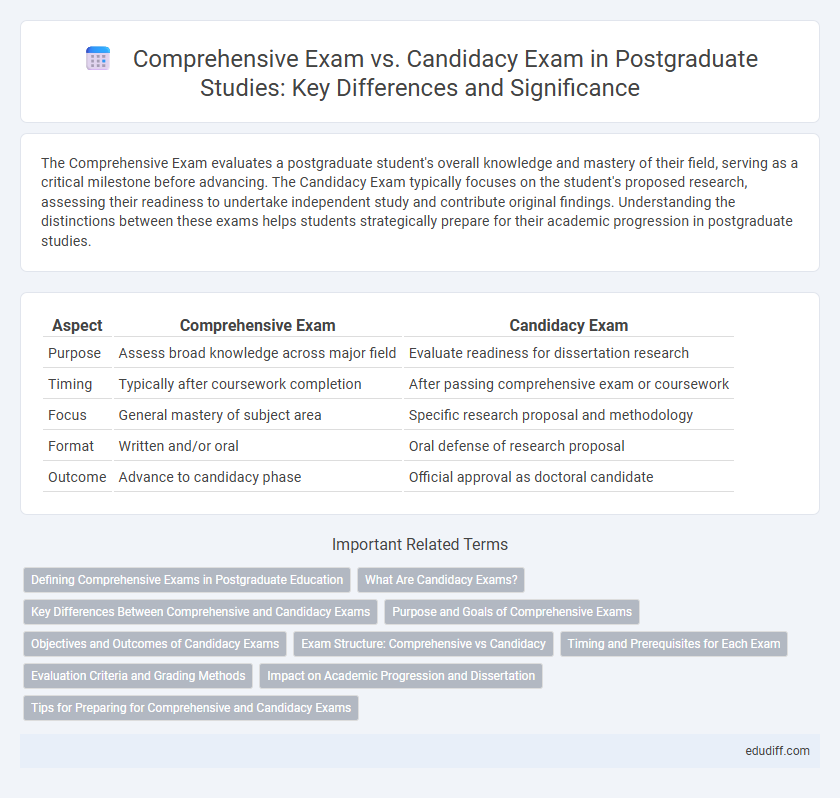
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Comprehensive Exam | Candidacy Exam |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Assess broad knowledge across major field | Evaluate readiness for dissertation research |
| Timing | Typically after coursework completion | After passing comprehensive exam or coursework |
| Focus | General mastery of subject area | Specific research proposal and methodology |
| Format | Written and/or oral | Oral defense of research proposal |
| Outcome | Advance to candidacy phase | Official approval as doctoral candidate |
Defining Comprehensive Exams in Postgraduate Education
Comprehensive exams in postgraduate education are rigorous assessments designed to evaluate a student's mastery of core knowledge and critical concepts within their discipline. These exams ensure readiness for advanced research by testing broad theoretical understanding and analytical skills across multiple subject areas. Successful completion signifies a key milestone, allowing progression to candidacy status and dissertation work.
What Are Candidacy Exams?
Candidacy exams are rigorous assessments designed to evaluate a postgraduate student's mastery of their field and readiness to undertake independent research leading to a dissertation. These exams typically assess both theoretical knowledge and practical research skills, ensuring candidates have a deep understanding of core concepts and can formulate original research questions. Passing candidacy exams often marks the transition from coursework to dissertation phase, signifying a key milestone in postgraduate education.
Key Differences Between Comprehensive and Candidacy Exams
Comprehensive exams assess a broad understanding of core coursework and foundational knowledge across the discipline, while candidacy exams focus specifically on a student's proposed research area and readiness for dissertation work. Comprehensive exams are typically taken early in a graduate program to ensure mastery of essential concepts, whereas candidacy exams are more advanced, serving as a gateway to official PhD candidacy status. The scope, timing, and evaluation criteria distinguish these exams, with comprehensive assessments emphasizing breadth and candidacy exams emphasizing depth and research potential.
Purpose and Goals of Comprehensive Exams
Comprehensive exams assess a postgraduate student's mastery of core knowledge within their field, ensuring readiness for advanced research and academic challenges. These exams evaluate critical thinking, integration of key concepts, and the ability to synthesize information across multiple subject areas. Successfully passing comprehensive exams is a prerequisite for candidacy status, indicating the student is prepared to undertake dissertation research.
Objectives and Outcomes of Candidacy Exams
Candidacy exams in postgraduate studies primarily assess a student's mastery of core knowledge and readiness to conduct independent research essential for dissertation work. These exams evaluate critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a deep understanding of the field to ensure the candidate's capability to contribute original research. Successful completion results in formal advancement to doctoral candidacy, signifying eligibility to focus fully on dissertation development and fulfillment of degree requirements.
Exam Structure: Comprehensive vs Candidacy
The Comprehensive Exam typically assesses a broad knowledge base across multiple subjects within a postgraduate program and often includes written components covering core areas. In contrast, the Candidacy Exam is more specialized, focusing on a specific research area or dissertation proposal, with both written and oral components designed to evaluate the candidate's readiness for independent research. Exam structures differ by institution but generally, the Comprehensive Exam serves as a qualifying step, while the Candidacy Exam confirms the student's suitability for dissertation work.
Timing and Prerequisites for Each Exam
The Comprehensive Exam is typically taken after completing core coursework, serving as a benchmark to assess mastery of foundational knowledge within the first year or two of a postgraduate program. The Candidacy Exam usually follows the successful completion of the Comprehensive Exam and any required research proposals, marking the transition to dissertation research phase. Timing for the Comprehensive Exam is earlier with coursework prerequisites, whereas the Candidacy Exam demands comprehensive exam clearance and research plan approval before proceeding.
Evaluation Criteria and Grading Methods
Comprehensive exams evaluate a student's mastery of foundational knowledge across their discipline, typically graded with pass/fail or scaled criteria emphasizing breadth of understanding. Candidacy exams assess the readiness for dissertation research by focusing on critical thinking, research proposal quality, and subject matter expertise, often graded through detailed rubrics or committee consensus. Both exams use evaluative criteria tailored to measure readiness at different postgraduate milestones, ensuring students meet academic standards for progression.
Impact on Academic Progression and Dissertation
Comprehensive exams serve as a critical milestone evaluating a postgraduate student's broad knowledge across their field, ensuring readiness to specialize further in dissertation research. Candidacy exams specifically assess the student's proficiency in their chosen research area, acting as a gateway to advancing into dissertation proposal development and completion. Success in both exams directly impacts academic progression by confirming the student's capability to undertake independent research, thus determining eligibility for doctoral candidacy and subsequent dissertation work.
Tips for Preparing for Comprehensive and Candidacy Exams
Effective preparation for comprehensive and candidacy exams in postgraduate studies involves thorough review of course materials, focusing on core concepts and research methodologies relevant to one's field. Creating detailed study plans that allocate time to practice essay questions, research proposals, and oral presentations enhances understanding and recall. Engaging with faculty mentors and participating in study groups can provide critical feedback and diverse perspectives, ultimately boosting confidence and performance on exam day.
Comprehensive Exam vs Candidacy Exam Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com