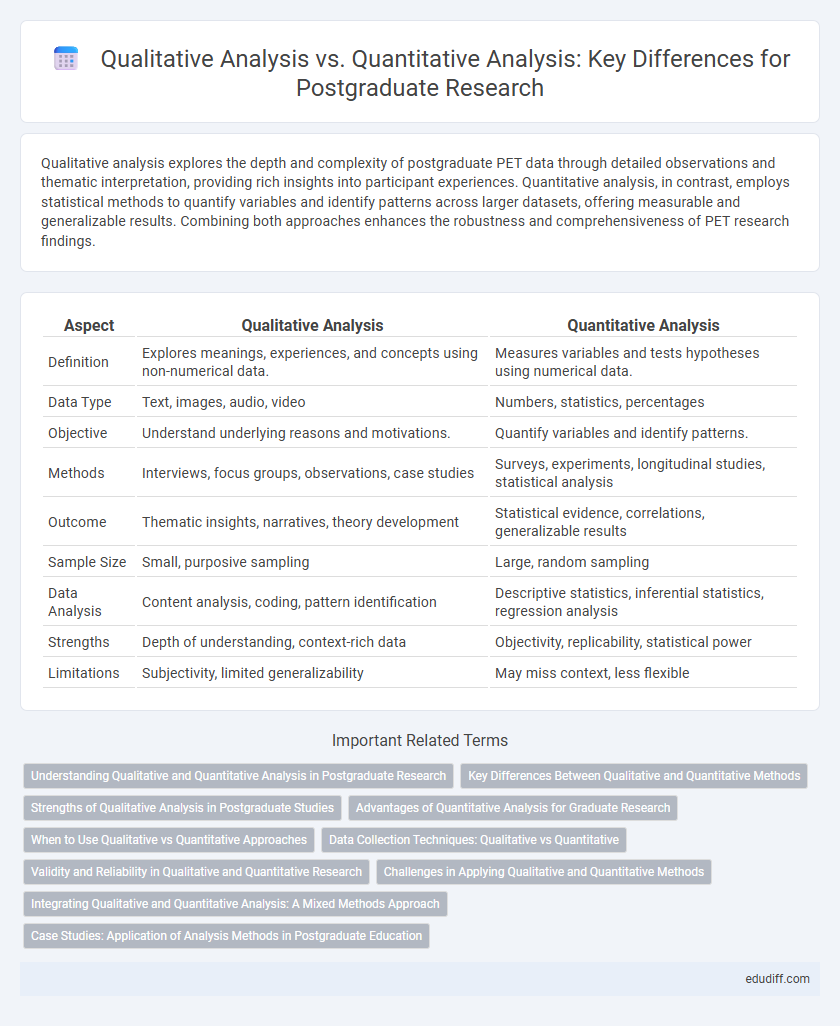
Qualitative analysis explores the depth and complexity of postgraduate PET data through detailed observations and thematic interpretation, providing rich insights into participant experiences. Quantitative analysis, in contrast, employs statistical methods to quantify variables and identify patterns across larger datasets, offering measurable and generalizable results. Combining both approaches enhances the robustness and comprehensiveness of PET research findings.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Qualitative Analysis | Quantitative Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explores meanings, experiences, and concepts using non-numerical data. | Measures variables and tests hypotheses using numerical data. |
| Data Type | Text, images, audio, video | Numbers, statistics, percentages |
| Objective | Understand underlying reasons and motivations. | Quantify variables and identify patterns. |
| Methods | Interviews, focus groups, observations, case studies | Surveys, experiments, longitudinal studies, statistical analysis |
| Outcome | Thematic insights, narratives, theory development | Statistical evidence, correlations, generalizable results |
| Sample Size | Small, purposive sampling | Large, random sampling |
| Data Analysis | Content analysis, coding, pattern identification | Descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, regression analysis |
| Strengths | Depth of understanding, context-rich data | Objectivity, replicability, statistical power |
| Limitations | Subjectivity, limited generalizability | May miss context, less flexible |
Understanding Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis in Postgraduate Research
Qualitative analysis in postgraduate research explores complex phenomena through thematic investigation, emphasizing depth and context via interviews, focus groups, and content analysis. Quantitative analysis relies on statistical methods and numerical data to test hypotheses, measure variables, and establish generalizable findings using tools like surveys and experiments. Integrating qualitative and quantitative approaches enhances the comprehensiveness and rigor of postgraduate research outcomes.
Key Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
Qualitative analysis explores phenomena through non-numerical data, emphasizing depth, context, and participant perspectives to uncover underlying meanings and patterns. Quantitative analysis relies on numerical data, statistical techniques, and measurable variables to test hypotheses and identify correlations with generalizable results. Key differences include data type, methodological approach, analysis process, and the nature of insights, where qualitative methods offer rich, detailed understanding, while quantitative methods provide structured, objective evidence.
Strengths of Qualitative Analysis in Postgraduate Studies
Qualitative analysis in postgraduate studies excels at providing in-depth understanding of complex phenomena, capturing participants' perspectives and contextual nuances often missed by quantitative methods. It enables the exploration of meanings, motivations, and experiences, fostering rich, detailed data critical for developing theories and frameworks. This approach is especially valuable in fields such as social sciences, education, and health studies, where subjective insights directly inform policy and practice.
Advantages of Quantitative Analysis for Graduate Research
Quantitative analysis in graduate research offers precise, numerical data that facilitates statistical validation and generalizability of results across larger populations. Graduate students benefit from its structured methodologies, which enable efficient hypothesis testing and objective measurement of variables to support evidence-based conclusions. The scalability and replicability of quantitative methods enhance the reliability and academic rigor essential for postgraduate-level research.
When to Use Qualitative vs Quantitative Approaches
Qualitative analysis is best suited for exploring complex phenomena where understanding meanings, experiences, and motivations is crucial, such as in case studies, interviews, and ethnographic research. Quantitative analysis is ideal for testing hypotheses, measuring variables, and generalizing findings using structured data from surveys, experiments, or statistical models. Selecting between qualitative and quantitative approaches depends on research objectives, data availability, and the need for depth versus breadth in postgraduate studies.
Data Collection Techniques: Qualitative vs Quantitative
Qualitative data collection techniques include in-depth interviews, focus groups, and participant observations, which aim to explore complex phenomena through open-ended responses and contextual understanding. Quantitative data collection relies on structured methods such as surveys, questionnaires, and experiments to gather numerical data that can be statistically analyzed for patterns and correlations. Choosing between qualitative and quantitative techniques depends on the research objectives, with qualitative methods providing rich, detailed insights and quantitative methods offering generalizable and measurable results.
Validity and Reliability in Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative analysis emphasizes validity through in-depth understanding and contextual accuracy, ensuring findings genuinely reflect participants' experiences, while quantitative analysis prioritizes reliability by employing standardized measurements and statistical techniques to produce consistent, replicable results. Validity in qualitative research is often achieved via triangulation and rich, detailed data, contrasting with quantitative validity that relies on instrument reliability and controlled variables. Both approaches address validity and reliability differently, highlighting qualitative's focus on meaning and quantitative's emphasis on numerical precision.
Challenges in Applying Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
Qualitative analysis in postgraduate research faces challenges such as subjectivity in data interpretation, difficulty in ensuring validity, and time-intensive data collection processes like interviews and focus groups. Quantitative analysis encounters obstacles including the need for large sample sizes, potential biases in survey design, and complexities in statistical modeling to ensure accurate results. Both methods demand rigorous methodological frameworks to address issues of reliability and generalizability in research findings.
Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis: A Mixed Methods Approach
Integrating qualitative and quantitative analysis in postgraduate research enhances data robustness by combining narrative depth with statistical rigor. Mixed methods approaches leverage qualitative insights to contextualize numerical trends, offering comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. This synergy improves validity and enriches interpretations by addressing research questions from multiple dimensions.
Case Studies: Application of Analysis Methods in Postgraduate Education
Case studies in postgraduate education predominantly utilize qualitative analysis to explore complex phenomena through thematic coding and narrative synthesis, allowing deep contextual understanding. Quantitative analysis, by contrast, applies statistical techniques to measure variables and test hypotheses across larger samples, providing generalizable results. Combining both methods enhances research rigor and offers comprehensive insights into educational practices and outcomes.
Qualitative Analysis vs Quantitative Analysis Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com