A Minor Thesis typically requires less extensive research and a shorter word count, making it suitable for students seeking to deepen their knowledge without committing to a full-scale project. A Major Thesis demands comprehensive research, original contribution, and detailed analysis, often serving as a critical component for graduation in postgraduate programs. Choosing between the two depends on the student's academic goals, time availability, and required degree specifications.
Table of Comparison
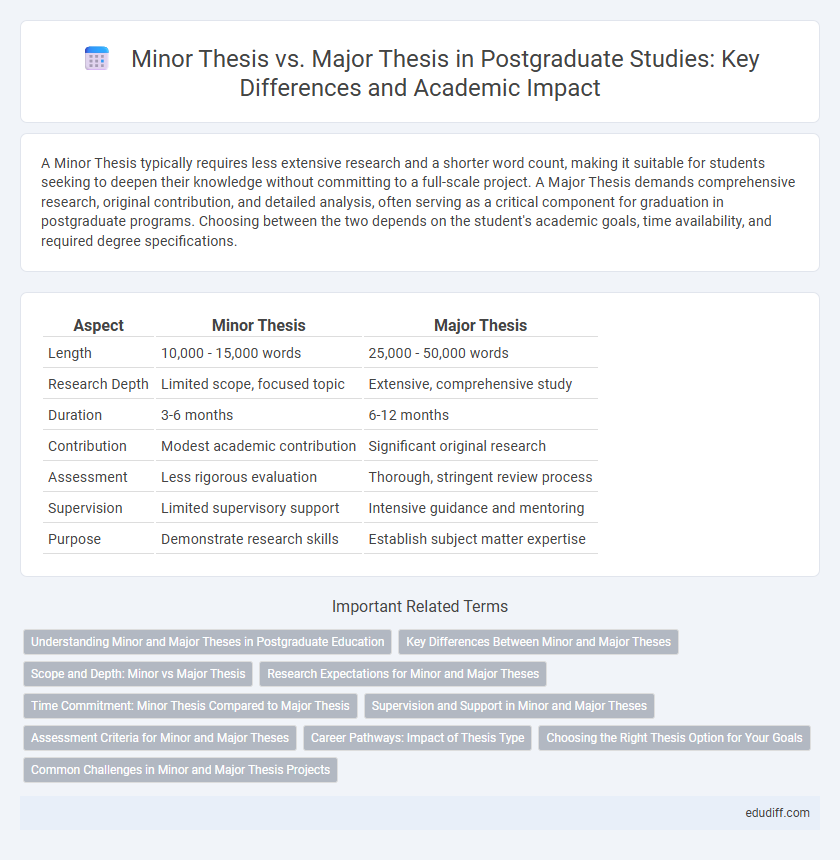
| Aspect | Minor Thesis | Major Thesis |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 10,000 - 15,000 words | 25,000 - 50,000 words |
| Research Depth | Limited scope, focused topic | Extensive, comprehensive study |
| Duration | 3-6 months | 6-12 months |
| Contribution | Modest academic contribution | Significant original research |
| Assessment | Less rigorous evaluation | Thorough, stringent review process |
| Supervision | Limited supervisory support | Intensive guidance and mentoring |
| Purpose | Demonstrate research skills | Establish subject matter expertise |
Understanding Minor and Major Theses in Postgraduate Education
A minor thesis in postgraduate education typically involves a shorter, more focused research project that allows students to explore a specific topic in depth without the extensive scope required by a major thesis. In contrast, a major thesis demands comprehensive research, critical analysis, and a significant original contribution to the field, often serving as a centerpiece for earning a master's or doctoral degree. Understanding the differences in scope, depth, and academic expectations helps postgraduate students select the appropriate thesis type based on their educational goals and available resources.
Key Differences Between Minor and Major Theses
Minor theses typically involve a narrower research scope, shorter length, and less comprehensive literature review compared to major theses. Major theses demand extensive original research, greater methodological rigor, and contribute significantly to the field of study, often requiring a length ranging from 50 to 100+ pages. The assessment criteria for major theses emphasize depth of analysis, theoretical contribution, and originality, while minor theses focus more on demonstrating basic research skills and understanding of the topic.
Scope and Depth: Minor vs Major Thesis
A Minor Thesis typically covers a narrower scope with limited research depth, focusing on a specific aspect of the subject matter, suitable for shorter postgraduate programs. In contrast, a Major Thesis involves extensive investigation and comprehensive analysis, demonstrating advanced understanding and significant contribution to the field, often required for master's or doctoral degrees. The Major Thesis demands rigorous methodology and detailed exploration, reflecting higher academic standards and scholarly impact.
Research Expectations for Minor and Major Theses
Minor theses typically require a focused research question with limited scope, aiming to demonstrate foundational research skills and critical analysis within a shorter timeframe. Major theses demand comprehensive research involving extensive data collection, robust methodology, and significant original contribution to the field, reflecting advanced analytical and synthesis capabilities. Research expectations for minor theses prioritize clarity and coherence, while major theses emphasize depth, rigor, and innovation in scholarly inquiry.
Time Commitment: Minor Thesis Compared to Major Thesis
A minor thesis typically requires a shorter time commitment, often ranging from a few months to one semester, whereas a major thesis demands extensive research and writing, often spanning an entire academic year or longer. The workload for a major thesis involves more comprehensive data collection, in-depth analysis, and a higher volume of literature review compared to a minor thesis. Students undertaking a minor thesis can expect a concise project with defined objectives, while a major thesis entails a substantial commitment to developing and defending a significant research contribution.
Supervision and Support in Minor and Major Theses
Supervision for a major thesis typically involves regular, in-depth meetings with a faculty advisor who provides extensive guidance on research design, methodology, and academic writing. Minor thesis supervision is generally less intensive, with fewer scheduled meetings and more independent work expected from the student. Support services such as research workshops and writing clinics are often available for both types but are more frequently utilized by students undertaking major theses due to the complexity and scope of their projects.
Assessment Criteria for Minor and Major Theses
Assessment criteria for minor theses typically emphasize concise research scope, clarity of argument, and foundational methodology, aiming to demonstrate the student's ability to undertake independent academic work within a limited timeframe. Major theses require comprehensive literature review, rigorous data analysis, and original contribution to the field, reflecting higher expectations for depth, critical thinking, and scholarly innovation. Evaluation of major theses often involves detailed scrutiny of theoretical frameworks, methodological robustness, and the significance of findings in advancing postgraduate research standards.
Career Pathways: Impact of Thesis Type
Choosing a major thesis over a minor thesis often leads to enhanced research skills and deeper subject expertise, which significantly boost opportunities in academic and research-oriented career pathways. A major thesis demonstrates the ability to conduct extensive independent research, making candidates more competitive for doctoral programs, research institutions, and specialized industry roles. Conversely, a minor thesis typically suits professional careers that prioritize practical knowledge and quicker entry into the workforce, offering less intensive research experience but fostering applied skills relevant to various sectors.
Choosing the Right Thesis Option for Your Goals
Choosing between a minor thesis and a major thesis depends on your postgraduate goals, time availability, and desired depth of research. A minor thesis typically requires a shorter, more focused study suitable for those aiming to enhance their research skills without extensive commitment, while a major thesis involves comprehensive investigation ideal for students pursuing academic careers or specialized expertise. Consider your career objectives and program requirements to select the thesis option that aligns with your aspirations and workload capacity.
Common Challenges in Minor and Major Thesis Projects
Common challenges in minor and major thesis projects include time management difficulties, limited access to relevant resources, and struggles with defining clear research objectives. Both thesis types often face issues related to data collection and analysis, which require careful planning and methodological rigor. Additionally, thesis students frequently encounter challenges in maintaining academic writing quality and meeting institutional guidelines.
Minor Thesis vs Major Thesis Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com