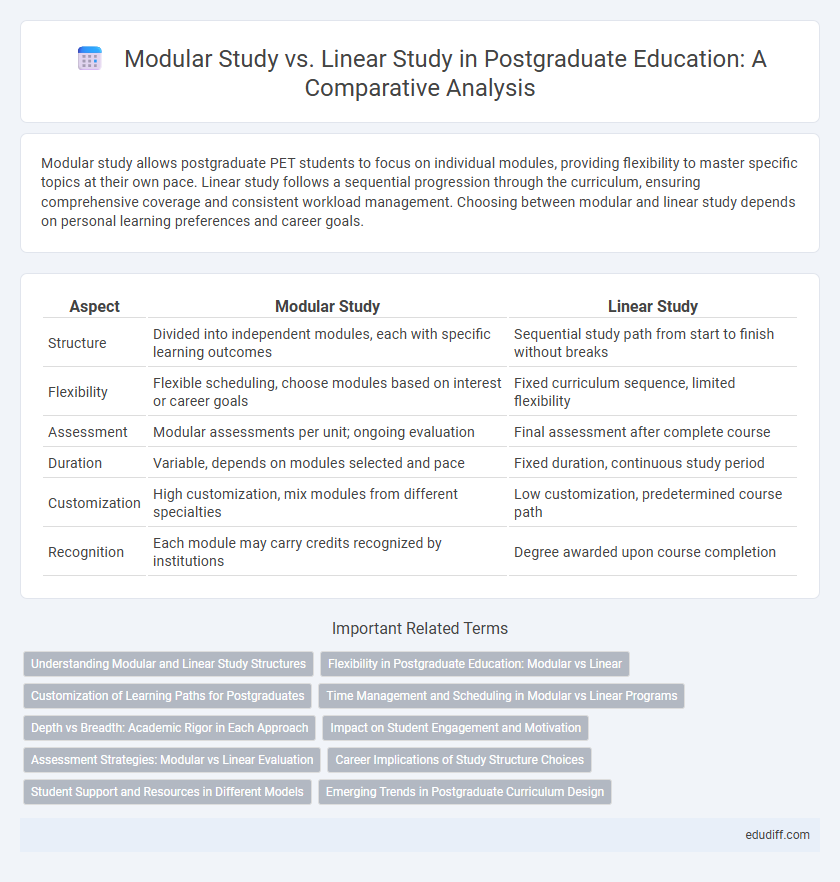
Modular study allows postgraduate PET students to focus on individual modules, providing flexibility to master specific topics at their own pace. Linear study follows a sequential progression through the curriculum, ensuring comprehensive coverage and consistent workload management. Choosing between modular and linear study depends on personal learning preferences and career goals.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Modular Study | Linear Study |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Divided into independent modules, each with specific learning outcomes | Sequential study path from start to finish without breaks |
| Flexibility | Flexible scheduling, choose modules based on interest or career goals | Fixed curriculum sequence, limited flexibility |
| Assessment | Modular assessments per unit; ongoing evaluation | Final assessment after complete course |
| Duration | Variable, depends on modules selected and pace | Fixed duration, continuous study period |
| Customization | High customization, mix modules from different specialties | Low customization, predetermined course path |
| Recognition | Each module may carry credits recognized by institutions | Degree awarded upon course completion |
Understanding Modular and Linear Study Structures
Modular study structures divide postgraduate courses into distinct, self-contained units allowing flexible learning paths and targeted skill development. Linear study structures follow a sequential progression through a fixed curriculum, ensuring comprehensive coverage of foundational and advanced topics. Understanding these models helps students align their study approach with academic goals and time management preferences.
Flexibility in Postgraduate Education: Modular vs Linear
Modular study in postgraduate education offers enhanced flexibility by allowing students to select courses and progress at their own pace, adapting to personal and professional commitments. In contrast, linear study follows a predetermined sequence of courses with fixed timelines, limiting the ability to customize learning paths. This flexibility in modular programs supports diverse student needs and promotes lifelong learning in postgraduate settings.
Customization of Learning Paths for Postgraduates
Modular study offers postgraduates the flexibility to tailor their learning paths by selecting individual modules that align with their research interests and career goals. This customization enables a more interdisciplinary approach, allowing students to combine courses across different fields for a broader skill set. Linear study, in contrast, follows a fixed sequence of courses that can limit personalized academic exploration and adaptability.
Time Management and Scheduling in Modular vs Linear Programs
Modular study programs offer flexibility in time management by allowing postgraduate students to complete discrete course units at their own pace, aligning with personal and professional commitments. Linear study programs follow a fixed, sequential schedule with predetermined deadlines, requiring consistent weekly engagement and stricter adherence to academic calendars. The modular approach often reduces scheduling conflicts and supports part-time study, while linear programs facilitate a structured progression conducive to cohort-based learning.
Depth vs Breadth: Academic Rigor in Each Approach
Modular study offers in-depth exploration of specific subjects through flexible course selections, promoting specialized expertise and academic rigor within chosen fields. Linear study emphasizes breadth by following a structured, sequential curriculum designed to build foundational knowledge across multiple disciplines, ensuring comprehensive understanding. Each approach demands academic discipline, but modular study fosters deeper mastery in targeted areas while linear study secures broad-based intellectual development.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Modular study enhances student engagement by allowing flexible pacing and focused mastery of individual topics, which boosts motivation through increased autonomy and immediate relevance to learners' goals. Linear study offers a structured, sequential progression that may benefit students who prefer clear guidance and cumulative knowledge building but can lead to diminished motivation if perceived as rigid or monotonous. Research indicates that modular formats tend to improve intrinsic motivation and active participation, especially in postgraduate programs where diverse schedules and self-directed learning are common.
Assessment Strategies: Modular vs Linear Evaluation
Modular study assessment strategies emphasize continuous evaluation through assignments, quizzes, and projects tailored to individual modules, enabling targeted feedback and skill refinement. Linear study evaluation relies on terminal examinations or cumulative assessments at the end of a course sequence, focusing on comprehensive knowledge integration over time. Each approach influences learning outcomes, with modular assessments supporting incremental mastery and linear assessments encouraging broad content synthesis.
Career Implications of Study Structure Choices
Modular study programs offer flexibility and the ability to tailor learning to specific career goals, enhancing skills relevant to niche job markets and fostering interdisciplinary expertise. Linear study structures provide a comprehensive and sequential knowledge foundation, building strong theoretical understanding favored in traditional career paths and research roles. Choosing between modular and linear study impacts employability, with modular approaches promoting adaptability and specialized skills, while linear paths emphasize depth and systematic progression valued by employers.
Student Support and Resources in Different Models
Modular study offers tailored student support through flexible, focused resources aligning with individual course modules, enhancing personalized learning experiences. Linear study provides continuous, structured guidance with comprehensive resources that support progressive skill development across a predefined curriculum. Both models prioritize access to academic advising, digital libraries, and peer collaboration, but modular setups emphasize adaptability while linear programs focus on consistency and depth.
Emerging Trends in Postgraduate Curriculum Design
Modular study allows postgraduate students to customize their learning paths by selecting discrete, focused courses, promoting interdisciplinary skill acquisition and flexibility. Linear study follows a fixed sequence of courses, ensuring comprehensive coverage but limiting adaptability to individual interests or emerging fields. Emerging curricular trends emphasize modularity to foster innovation, accommodate diverse learner needs, and rapidly integrate evolving knowledge areas in postgraduate education.
Modular Study vs Linear Study Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com