Postgraduate PET programs often balance residency requirements with remote learning options to accommodate diverse student needs. Residency mandates ensure hands-on clinical experience critical for skill development, while remote learning provides flexibility and access to theoretical coursework. This combination enhances the overall educational experience by integrating practical exposure with academic rigor.
Table of Comparison
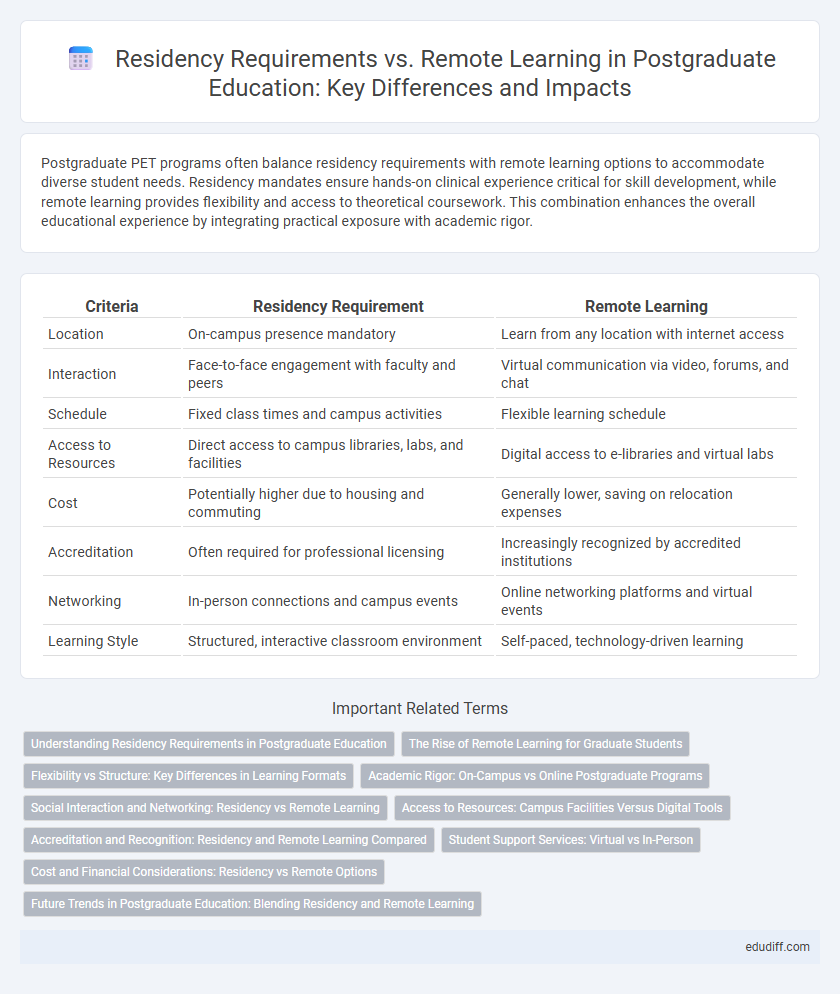
| Criteria | Residency Requirement | Remote Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Location | On-campus presence mandatory | Learn from any location with internet access |
| Interaction | Face-to-face engagement with faculty and peers | Virtual communication via video, forums, and chat |
| Schedule | Fixed class times and campus activities | Flexible learning schedule |
| Access to Resources | Direct access to campus libraries, labs, and facilities | Digital access to e-libraries and virtual labs |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to housing and commuting | Generally lower, saving on relocation expenses |
| Accreditation | Often required for professional licensing | Increasingly recognized by accredited institutions |
| Networking | In-person connections and campus events | Online networking platforms and virtual events |
| Learning Style | Structured, interactive classroom environment | Self-paced, technology-driven learning |
Understanding Residency Requirements in Postgraduate Education
Residency requirements in postgraduate education mandate that students complete a specified portion of their coursework or practical training on campus or at designated facilities to ensure hands-on experience and direct interaction with faculty. Remote learning options often complement but do not fully replace these requirements, particularly in clinical, laboratory, or research-intensive programs where in-person participation is crucial. Understanding these residency mandates is essential for postgraduate students to plan their schedules, meet accreditation standards, and fulfill graduation criteria effectively.
The Rise of Remote Learning for Graduate Students
Postgraduate programs increasingly incorporate remote learning to offer flexibility and accessibility for diverse student populations. Residency requirements, traditionally mandating in-person attendance, are now balanced with virtual coursework to accommodate working professionals and international students. This shift enhances educational inclusivity while maintaining rigorous academic standards through hybrid and fully online modalities.
Flexibility vs Structure: Key Differences in Learning Formats
Residency requirements in postgraduate programs demand on-campus attendance, providing structured schedules and direct faculty interaction that enhance discipline and networking opportunities. Remote learning offers greater flexibility, allowing students to balance studies with personal and professional commitments through asynchronous course materials and virtual collaboration. The key difference lies in the balance between flexibility in time management versus the structured environment conducive to immersive, hands-on learning experiences.
Academic Rigor: On-Campus vs Online Postgraduate Programs
Residency requirements in postgraduate programs ensure immersive academic rigor through face-to-face interactions, access to campus facilities, and real-time collaborative learning, which are often limited in remote learning environments. On-campus programs offer structured schedules and direct faculty mentorship that enhance discipline and immediate feedback, critical for mastering complex postgraduate material. Remote learning postgraduate programs rely heavily on self-motivation and digital resources, which may challenge consistent academic engagement but provide flexibility for diverse student needs.
Social Interaction and Networking: Residency vs Remote Learning
Residency requirements in postgraduate programs foster rich social interaction and networking opportunities through in-person collaboration, seminars, and campus events, essential for building professional relationships and mentorships. Remote learning limits these spontaneous engagements, relying heavily on virtual platforms that may hinder organic connection and reduce access to peer support and informal academic discussions. Effective postgraduate networking in remote settings demands proactive participation in online communities and scheduled video interactions to compensate for the lack of physical presence.
Access to Resources: Campus Facilities Versus Digital Tools
Residency requirements for postgraduate programs offer direct access to campus facilities such as libraries, laboratories, and study spaces, which support hands-on learning and research activities. Remote learning relies on digital tools, including virtual libraries, online databases, and collaborative platforms, providing flexibility but sometimes limiting experiential resources. The choice between residency and remote learning impacts the availability and nature of academic resources essential for postgraduate success.
Accreditation and Recognition: Residency and Remote Learning Compared
Accreditation and recognition standards for postgraduate programs vary significantly between residency and remote learning formats, with many accrediting bodies emphasizing on-site presence for clinical or practical disciplines to ensure quality and competency. Remote learning programs must demonstrate robust virtual engagement, rigorous assessment methods, and adherence to accreditation criteria to gain equal recognition, especially in fields requiring hands-on experience. Understanding these distinctions is critical for students when selecting accredited postgraduate programs that align with professional licensure and career advancement requirements.
Student Support Services: Virtual vs In-Person
Student support services for postgraduate residency requirements typically include in-person academic advising, career counseling, and mental health resources to provide direct interaction and personalized assistance, enhancing student engagement and success. Remote learning platforms offer virtual support services such as online tutoring, digital library access, and telecounseling, facilitating flexible access but often with less immediate personal contact. Comparing both, in-person support is traditionally favored for comprehensive postgraduate guidance, while virtual services are evolving to bridge gaps for remote learners needing timely and accessible assistance.
Cost and Financial Considerations: Residency vs Remote Options
Residency requirement in postgraduate programs often involves higher costs due to on-campus housing, commuting, and campus facility fees, which can significantly increase the overall financial burden. Remote learning options tend to reduce expenses by eliminating travel and accommodation costs, allowing students to maintain employment or personal responsibilities while studying. However, some remote programs may have technology fees or require investment in reliable internet and hardware, which should be factored into the total cost comparison.
Future Trends in Postgraduate Education: Blending Residency and Remote Learning
Future trends in postgraduate education emphasize a hybrid model blending residency requirements with remote learning to maximize flexibility and accessibility. Institutions are increasingly adopting technology-enhanced platforms to deliver synchronous and asynchronous coursework, supporting diverse learner needs while maintaining essential in-person experiences for clinical or laboratory work. This integrated approach fosters collaboration, skill development, and adaptability, preparing graduates for dynamic professional environments.
Residency Requirement vs Remote Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com