Choosing between a single and dual degree in postgraduate PET programs depends on career goals and time commitment. A single degree offers specialized expertise and quicker completion, while a dual degree provides interdisciplinary knowledge and broader career opportunities. Evaluating personal interests and industry demands helps determine the best academic path.
Table of Comparison
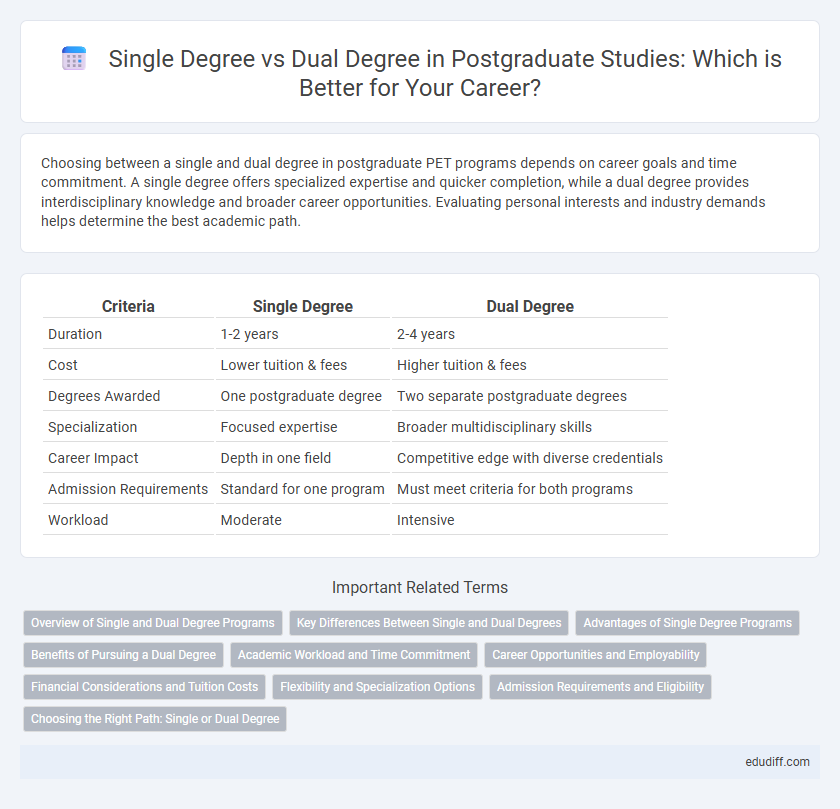
| Criteria | Single Degree | Dual Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 1-2 years | 2-4 years |
| Cost | Lower tuition & fees | Higher tuition & fees |
| Degrees Awarded | One postgraduate degree | Two separate postgraduate degrees |
| Specialization | Focused expertise | Broader multidisciplinary skills |
| Career Impact | Depth in one field | Competitive edge with diverse credentials |
| Admission Requirements | Standard for one program | Must meet criteria for both programs |
| Workload | Moderate | Intensive |
Overview of Single and Dual Degree Programs
Single degree programs offer focused expertise in one discipline, typically requiring 1 to 2 years of graduate-level study, culminating in a master's or doctoral degree. Dual degree programs combine two distinct fields of study, allowing students to earn two separate degrees concurrently, usually in 2 to 4 years, providing interdisciplinary skills and broader career opportunities. These programs are designed to enhance academic versatility and professional marketability by integrating complementary knowledge areas.
Key Differences Between Single and Dual Degrees
Single degree programs concentrate on one specialized field, allowing for deep expertise and a streamlined path to career advancement. Dual degree programs integrate two distinct disciplines, offering interdisciplinary skills and broader professional opportunities but often require more time and financial investment. Key differences include curriculum structure, duration, and the potential for diversified career trajectories.
Advantages of Single Degree Programs
Single degree programs offer focused specialization that enhances expertise in a specific field, making graduates highly competitive for niche career opportunities. These programs often require less time and financial investment compared to dual degrees, allowing for quicker entry into the workforce. Concentrated curricula in single degree courses support deeper academic engagement and mastery, facilitating stronger research outputs and professional development.
Benefits of Pursuing a Dual Degree
Pursuing a dual degree in postgraduate studies offers the advantage of acquiring comprehensive expertise across two distinct but complementary fields, enhancing career flexibility and marketability. Dual degree programs often provide interdisciplinary knowledge, fostering innovative problem-solving skills and expanding professional networks through diverse academic communities. Graduates from dual degree programs typically experience increased employment opportunities and higher earning potential due to their specialized, multifaceted qualifications.
Academic Workload and Time Commitment
Single degree programs typically involve a focused academic workload, allowing students to complete their studies within a standard timeframe of one to two years. Dual degree programs require managing the combined curriculum of two disciplines, leading to a higher academic workload and an extended time commitment, often ranging from three to four years. Balancing dual degrees demands effective time management and increased dedication to coursework, research, and examinations compared to single degree studies.
Career Opportunities and Employability
Single degree postgraduate programs often provide specialized expertise, making candidates highly attractive for niche roles within specific industries. Dual degree programs combine complementary disciplines, broadening professional networks and enhancing versatility, which increases employability across diverse sectors. Employers increasingly value dual degree graduates for their multidisciplinary skills and adaptability in dynamic job markets.
Financial Considerations and Tuition Costs
Choosing between a single and dual degree program significantly impacts financial planning, as dual degrees often incur higher tuition costs due to extended study duration and additional coursework. Single degree programs typically present a more affordable option with lower total tuition and reduced ancillary fees, making them suitable for budget-conscious postgraduate students. Scholarships, employer funding, and loan repayment options can vary substantially between single and dual degrees, influencing the overall financial burden.
Flexibility and Specialization Options
Single degree programs offer focused specialization in one discipline, allowing deeper expertise and research opportunities tailored to specific career goals. Dual degree programs provide enhanced flexibility by combining complementary fields, enabling graduates to diversify their skill sets and improve interdisciplinary knowledge for broader career prospects. Choosing between single and dual degrees depends on the desired balance between specialization depth and educational versatility in postgraduate studies.
Admission Requirements and Eligibility
Single degree postgraduate programs typically require a focused academic background relevant to the chosen field, a bachelor's degree with a minimum GPA of 3.0, and standardized test scores such as the GRE or GMAT, depending on the discipline. Dual degree programs demand meeting admission requirements for both participating institutions or departments, often necessitating higher academic credentials, including a stronger GPA (3.5 or above), multiple standardized tests, and prerequisite coursework relevant to both degrees. Eligibility for dual degrees may also include demonstrated ability to manage a rigorous academic workload and compliance with additional application components like interviews, personal statements, and letters of recommendation tailored to each program's standards.
Choosing the Right Path: Single or Dual Degree
Choosing between a single and dual postgraduate degree depends on your career goals, time commitment, and financial resources. A single degree offers focused expertise and quicker completion, while a dual degree provides interdisciplinary skills and broader professional opportunities but requires more time and investment. Evaluating future job market demands and personal growth priorities helps determine the most suitable academic path.
Single vs Dual Degree Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com