Phonics-based instruction emphasizes teaching children the relationships between letters and sounds to develop decoding skills essential for reading fluency. Whole language approaches focus on immersing children in rich, meaningful texts to promote natural language acquisition and comprehension. Combining both methods in preschool can enhance literacy by balancing decoding skills with contextual understanding.
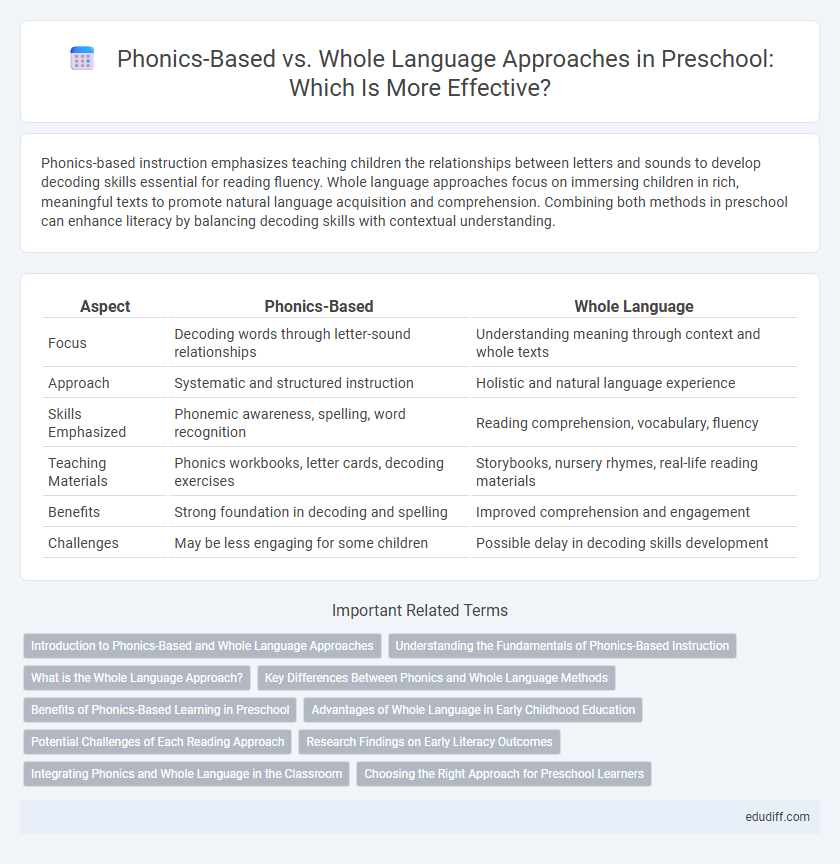
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Phonics-Based | Whole Language |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Decoding words through letter-sound relationships | Understanding meaning through context and whole texts |
| Approach | Systematic and structured instruction | Holistic and natural language experience |
| Skills Emphasized | Phonemic awareness, spelling, word recognition | Reading comprehension, vocabulary, fluency |
| Teaching Materials | Phonics workbooks, letter cards, decoding exercises | Storybooks, nursery rhymes, real-life reading materials |
| Benefits | Strong foundation in decoding and spelling | Improved comprehension and engagement |
| Challenges | May be less engaging for some children | Possible delay in decoding skills development |
Introduction to Phonics-Based and Whole Language Approaches
Phonics-based approach emphasizes systematic teaching of letter-sound relationships to develop decoding skills essential for early reading proficiency. Whole language approach focuses on understanding meaning through exposure to complete texts, promoting natural language learning and comprehension. Both methods serve as foundational strategies in preschool literacy development, balancing decoding mechanics and contextual reading experience.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Phonics-Based Instruction
Phonics-based instruction emphasizes the systematic teaching of letter-sound relationships, enabling preschoolers to decode words and build reading fluency effectively. This method focuses on phonemic awareness, blending sounds, and recognizing patterns, which are essential components in early literacy development. Research shows that mastering phonics skills in preschool significantly enhances vocabulary acquisition and reading comprehension as children progress.
What is the Whole Language Approach?
The Whole Language Approach emphasizes learning to read by recognizing words in context, encouraging children to understand meaning and enjoy stories rather than focusing on individual sounds. It promotes immersion in rich, authentic literature, fostering natural language development through listening, speaking, reading, and writing activities. This approach supports holistic literacy, integrating reading with meaningful communication and comprehension skills in early childhood education.
Key Differences Between Phonics and Whole Language Methods
Phonics-based instruction emphasizes systematic teaching of letter-sound relationships to develop decoding skills essential for early reading proficiency. Whole language methods focus on meaning and context, encouraging children to recognize words as wholes through exposure to rich, authentic texts. Key differences include phonics' structured, skill-focused approach versus whole language's holistic, meaning-centered strategy for literacy development.
Benefits of Phonics-Based Learning in Preschool
Phonics-based learning in preschool enhances early reading skills by emphasizing letter-sound relationships, which strengthens decoding abilities and improves word recognition. This method supports vocabulary development and spelling accuracy by providing a systematic approach to language acquisition. Research shows that children taught with phonics-based strategies demonstrate higher literacy rates and better long-term reading comprehension compared to whole language instruction.
Advantages of Whole Language in Early Childhood Education
Whole Language in early childhood education promotes natural language acquisition by immersing children in meaningful and context-rich reading experiences, fostering better comprehension and a love for reading. This approach supports vocabulary development and critical thinking skills as children engage with authentic texts, encouraging creativity and expression. Research shows that Whole Language methods enhance children's ability to connect reading to real-life communication, boosting motivation and confidence in literacy.
Potential Challenges of Each Reading Approach
Phonics-based reading approaches may present challenges such as difficulties mastering letter-sound relationships and slower comprehension development in some preschoolers. Whole language methods can pose risks with inconsistent decoding skills and reliance on memorization rather than systematic phonemic awareness. Educators must balance structured phonics instruction with rich language exposure to address diverse learner needs effectively.
Research Findings on Early Literacy Outcomes
Research findings consistently demonstrate that phonics-based instruction significantly improves early literacy outcomes by enhancing children's decoding skills and word recognition. Whole language approaches, which emphasize context and meaning, often result in slower gains in phonemic awareness and reading accuracy compared to systematic phonics methods. Studies from the National Reading Panel confirm that explicit phonics instruction fosters stronger foundational reading abilities in preschoolers.
Integrating Phonics and Whole Language in the Classroom
Integrating phonics and whole language in preschool classrooms enhances early literacy by combining systematic letter-sound instruction with meaningful, context-rich reading experiences. This balanced approach supports children's decoding skills while fostering comprehension, vocabulary, and a love of reading through interactive storytelling, shared reading, and guided writing activities. Research from the National Reading Panel highlights that blending phonics with whole language strategies leads to stronger reading outcomes and improved fluency for young learners.
Choosing the Right Approach for Preschool Learners
Phonics-based instruction emphasizes decoding skills, teaching preschool learners the relationship between letters and sounds to build strong foundational reading abilities. Whole language approaches focus on meaning and context, encouraging children to recognize words through exposure to rich, natural texts, fostering literacy through immersive language experiences. Selecting the right approach depends on assessing each child's developmental readiness and learning style to ensure effective early literacy development.
Phonics-Based vs Whole Language Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com