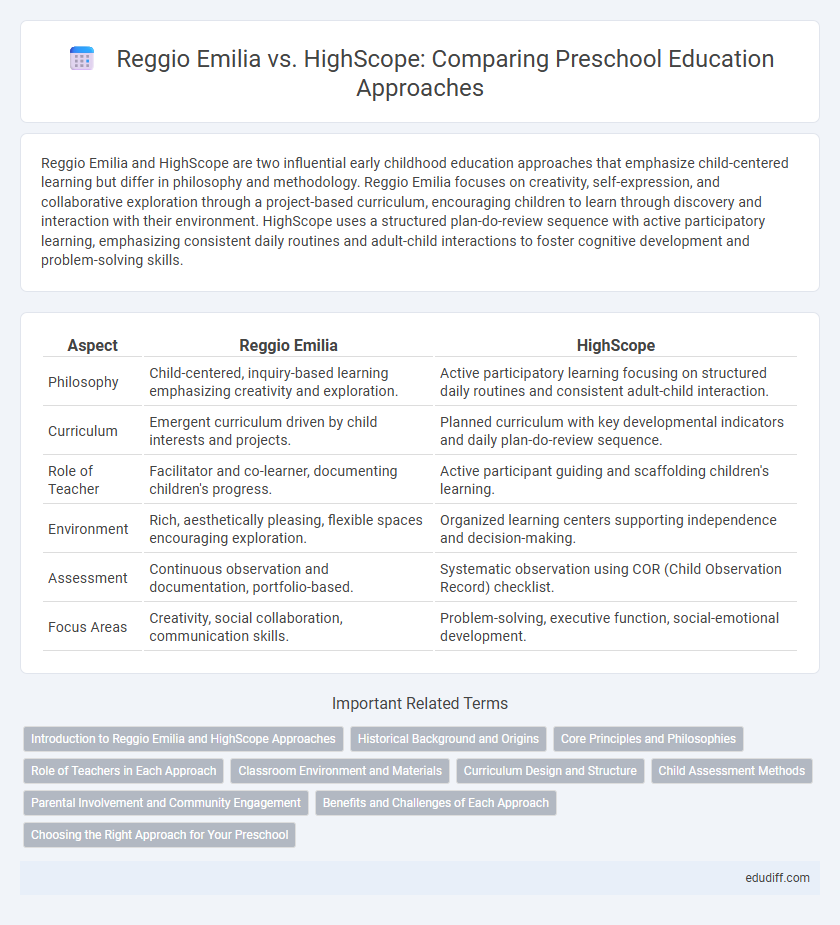
Reggio Emilia and HighScope are two influential early childhood education approaches that emphasize child-centered learning but differ in philosophy and methodology. Reggio Emilia focuses on creativity, self-expression, and collaborative exploration through a project-based curriculum, encouraging children to learn through discovery and interaction with their environment. HighScope uses a structured plan-do-review sequence with active participatory learning, emphasizing consistent daily routines and adult-child interactions to foster cognitive development and problem-solving skills.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reggio Emilia | HighScope |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Child-centered, inquiry-based learning emphasizing creativity and exploration. | Active participatory learning focusing on structured daily routines and consistent adult-child interaction. |
| Curriculum | Emergent curriculum driven by child interests and projects. | Planned curriculum with key developmental indicators and daily plan-do-review sequence. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and co-learner, documenting children's progress. | Active participant guiding and scaffolding children's learning. |
| Environment | Rich, aesthetically pleasing, flexible spaces encouraging exploration. | Organized learning centers supporting independence and decision-making. |
| Assessment | Continuous observation and documentation, portfolio-based. | Systematic observation using COR (Child Observation Record) checklist. |
| Focus Areas | Creativity, social collaboration, communication skills. | Problem-solving, executive function, social-emotional development. |
Introduction to Reggio Emilia and HighScope Approaches
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes child-led learning through exploration and expressive arts, fostering creativity and collaboration in a carefully designed environment. HighScope uses a structured curriculum based on active participatory learning, where children make choices and engage in hands-on experiences guided by adult scaffolding. Both approaches prioritize developmentally appropriate practices, yet Reggio Emilia focuses on emergent curriculum and documentation, while HighScope relies on consistent daily routines and assessment tools like the Child Observation Record (COR).
Historical Background and Origins
Reggio Emilia originated in post-World War II Italy, inspired by founder Loris Malaguzzi's vision of child-centered education emphasizing community involvement and expressive arts. HighScope emerged in the 1960s in the United States, developed by David Weikart through research focused on active participatory learning and cognitive development in young children. Both approaches revolutionized early childhood education by integrating developmental psychology with practical classroom strategies, yet they reflect distinct cultural and philosophical roots.
Core Principles and Philosophies
Reggio Emilia emphasizes child-led exploration, viewing children as competent individuals who learn through social interaction and environmental discovery, with a strong focus on creativity and collaboration. HighScope centers on active participatory learning, structured routines, and adult-guided scaffolding, prioritizing cognitive development through planned activities and consistent assessment. Both approaches value play but differ in the balance between child autonomy and adult guidance in early childhood education.
Role of Teachers in Each Approach
In the Reggio Emilia approach, teachers act as co-learners and collaborators, guiding children through inquiry-based projects that emphasize exploration and creativity. HighScope teachers follow a structured curriculum, supporting active learning with planned interactions and consistent daily routines to foster cognitive development. Both approaches value teacher responsiveness but differ in balance between child-led discovery and adult-guided instruction.
Classroom Environment and Materials
Reggio Emilia classrooms emphasize natural light, open spaces, and accessible materials that encourage creativity and exploration, fostering a child-centered learning environment. HighScope classrooms are organized into well-defined learning areas with a variety of hands-on materials designed to support active participatory learning and promote independence. Both approaches prioritize safe, engaging environments but differ in structure and the role of materials in shaping children's experiences.
Curriculum Design and Structure
Reggio Emilia curriculum emphasizes child-led exploration and creativity, fostering collaborative projects within a flexible environment that adapts to children's interests and developmental stages. HighScope curriculum uses a structured plan-do-review approach with clearly defined daily routines and adult-guided learning experiences to promote active participation and cognitive growth. Both methodologies prioritize experiential learning but differ in balancing teacher direction and child autonomy in curriculum design.
Child Assessment Methods
Reggio Emilia emphasizes observational documentation and portfolio assessment to capture children's creativity and learning processes, fostering individualized development plans. HighScope employs the Child Observation Record (COR), a structured tool that assesses key developmental indicators across cognitive, social, and physical domains. Both methods prioritize formative assessment but differ in data collection scope and interpretative frameworks, with Reggio Emilia favoring qualitative narratives and HighScope using standardized metrics.
Parental Involvement and Community Engagement
Reggio Emilia emphasizes parental involvement as a collaborative partnership, encouraging parents to actively participate in classroom activities and decision-making, fostering a strong sense of community connection. HighScope also values parental involvement but focuses on structured communication through daily reports and parent-teacher conferences to enhance child development consistency between home and school. Both approaches integrate community resources, with Reggio Emilia leveraging local cultural assets to enrich learning experiences while HighScope incorporates community-based activities to support practical skill development.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Reggio Emilia emphasizes child-led exploration and creativity, fostering deep cognitive and social development through project-based learning, though it requires highly trained educators and flexible environments that can be resource-intensive. HighScope focuses on active participatory learning with a consistent daily routine, promoting independence and academic skills, while its structured format may limit spontaneous creativity and requires strict adherence to curriculum guidelines. Both approaches support child development but demand different levels of educator involvement and resource allocation to effectively implement their respective benefits.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Preschool
Choosing the right preschool approach involves understanding the core principles of Reggio Emilia and HighScope. Reggio Emilia emphasizes child-led exploration, creativity, and strong community involvement, while HighScope focuses on active learning through structured, hands-on experiences and consistent daily routines. Selecting the appropriate method depends on your child's learning style, your educational goals, and the preschool environment that best supports holistic development.
Reggio Emilia vs HighScope Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com