Teacher-directed learning in preschool provides structured activities that guide children through specific skills and concepts, ensuring foundational knowledge is systematically developed. Child-initiated learning empowers children to explore their interests, promoting creativity, motivation, and independent problem-solving skills. Combining both approaches creates a balanced environment that supports cognitive and social-emotional growth.
Table of Comparison
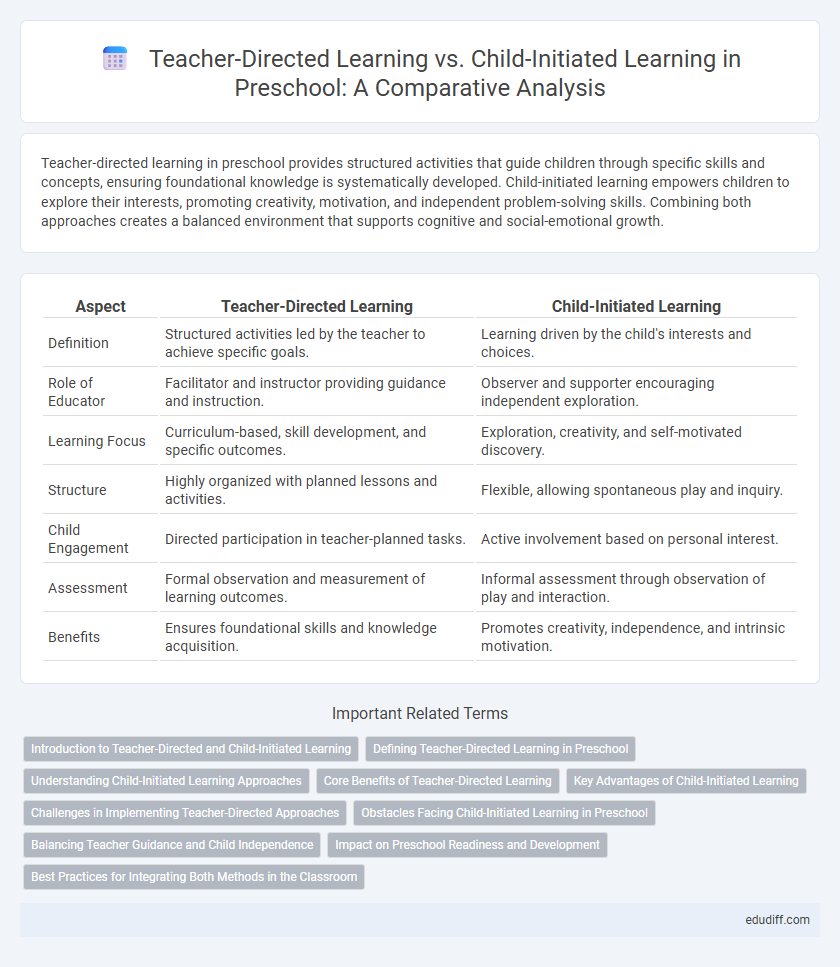
| Aspect | Teacher-Directed Learning | Child-Initiated Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured activities led by the teacher to achieve specific goals. | Learning driven by the child's interests and choices. |
| Role of Educator | Facilitator and instructor providing guidance and instruction. | Observer and supporter encouraging independent exploration. |
| Learning Focus | Curriculum-based, skill development, and specific outcomes. | Exploration, creativity, and self-motivated discovery. |
| Structure | Highly organized with planned lessons and activities. | Flexible, allowing spontaneous play and inquiry. |
| Child Engagement | Directed participation in teacher-planned tasks. | Active involvement based on personal interest. |
| Assessment | Formal observation and measurement of learning outcomes. | Informal assessment through observation of play and interaction. |
| Benefits | Ensures foundational skills and knowledge acquisition. | Promotes creativity, independence, and intrinsic motivation. |
Introduction to Teacher-Directed and Child-Initiated Learning
Teacher-directed learning in preschool centers on structured activities led by educators to achieve specific learning outcomes, emphasizing curriculum goals and skill development through direct instruction and guidance. Child-initiated learning encourages exploration and creativity, allowing children to choose activities based on their interests, which fosters independence and intrinsic motivation. Understanding the balance between these approaches supports optimal cognitive, social, and emotional growth during early childhood education.
Defining Teacher-Directed Learning in Preschool
Teacher-directed learning in preschool involves structured activities planned and led by the educator to guide children's knowledge acquisition and skill development. This approach emphasizes clear objectives, direct instruction, and teacher control over the learning environment to ensure foundational concepts in literacy, numeracy, and social skills are effectively taught. Research shows that teacher-directed learning supports early cognitive growth and prepares children for academic expectations in primary education.
Understanding Child-Initiated Learning Approaches
Child-initiated learning in preschool emphasizes exploration and creativity, where children actively choose activities that interest them, fostering autonomy and intrinsic motivation. This approach contrasts with teacher-directed learning, as it promotes cognitive and social development through hands-on experiences and peer interaction, enhancing problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Understanding child-initiated learning highlights the importance of providing a flexible environment that supports individual learning styles and encourages self-regulation.
Core Benefits of Teacher-Directed Learning
Teacher-directed learning in preschool enhances structured skill development by providing clear guidance and focused instruction on foundational concepts such as literacy, numeracy, and social skills. This approach supports consistent classroom management and helps ensure curriculum alignment with educational standards. It also fosters early acquisition of discipline and routine, crucial for children's readiness for formal schooling.
Key Advantages of Child-Initiated Learning
Child-initiated learning in preschool promotes autonomy, creativity, and intrinsic motivation by allowing children to explore topics that interest them at their own pace. This approach enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through experiential discovery rather than structured instruction. Research shows that child-initiated activities contribute to higher engagement levels and foster social-emotional development by encouraging cooperation and communication among peers.
Challenges in Implementing Teacher-Directed Approaches
Teacher-directed learning in preschool often faces challenges such as limited engagement from children who may feel less autonomy in structured settings and potential difficulties in addressing diverse learning paces within a single classroom. Strict adherence to teacher-led activities can reduce opportunities for creativity and critical thinking, impacting overall developmental outcomes. Balancing curriculum goals with individual needs remains a significant obstacle for educators aiming to implement effective teacher-directed strategies.
Obstacles Facing Child-Initiated Learning in Preschool
Child-initiated learning in preschool often faces obstacles such as limited classroom resources and insufficient teacher training to support child autonomy. Rigid curriculum requirements and standardized assessments restrict opportunities for spontaneous exploration and creativity. Additionally, balancing safety concerns with freedom of expression can hinder the natural development of child-initiated activities.
Balancing Teacher Guidance and Child Independence
Balancing teacher-directed learning and child-initiated learning in preschool supports both structured skill development and creative exploration. Effective early childhood education integrates teacher guidance to introduce foundational concepts while allowing children autonomy to foster critical thinking and social-emotional growth. This harmonious approach enhances cognitive outcomes by combining intentional instruction with opportunities for self-directed discovery.
Impact on Preschool Readiness and Development
Teacher-directed learning in preschool enhances structured skill acquisition, promoting early literacy and numeracy crucial for school readiness. Child-initiated learning fosters creativity, social-emotional development, and problem-solving abilities by encouraging exploration and autonomy. Balancing both approaches optimizes cognitive, emotional, and social outcomes essential for comprehensive preschool development.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Methods in the Classroom
Effective preschool classrooms balance teacher-directed learning and child-initiated learning by incorporating structured lessons alongside opportunities for free play and exploration. Best practices include using thematic units guided by educators while allowing children to choose related activities that foster autonomy and creativity. Integrating formative assessments helps teachers tailor instruction to children's interests and developmental stages, optimizing engagement and learning outcomes.
Teacher-directed learning vs Child-initiated learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com