Teacher-led activities in preschool provide structured learning experiences that promote foundational skills such as literacy, numeracy, and social behavior through guided instruction. Child-initiated activities foster creativity, independence, and decision-making by allowing children to explore and engage with materials at their own pace. Balancing both approaches supports holistic development, ensuring children gain essential knowledge while nurturing their natural curiosity and self-expression.
Table of Comparison
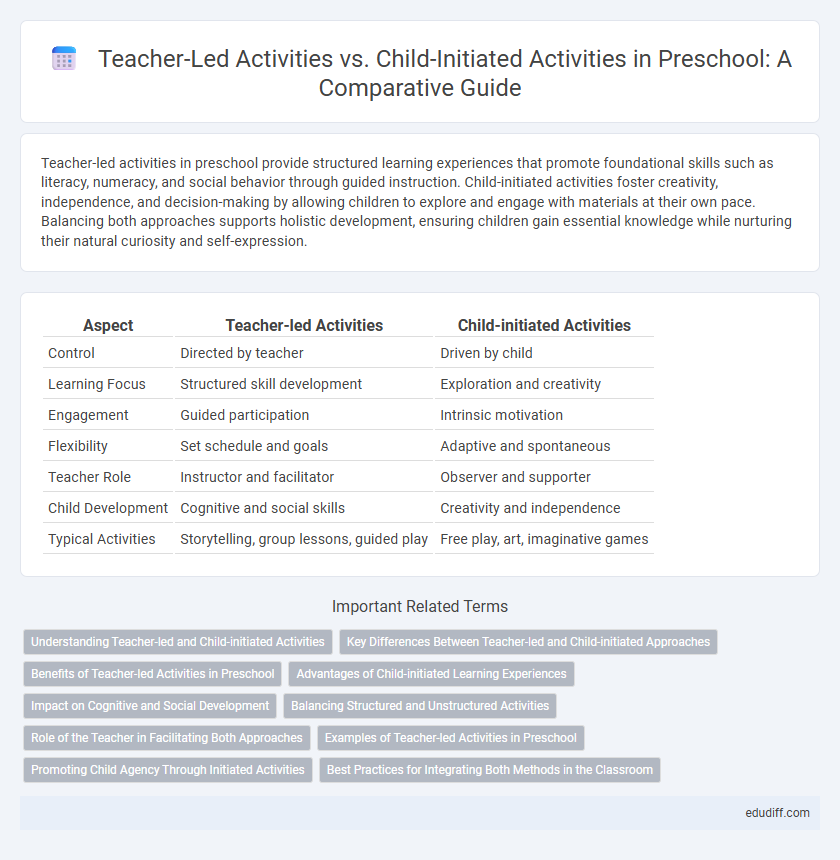
| Aspect | Teacher-led Activities | Child-initiated Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Directed by teacher | Driven by child |
| Learning Focus | Structured skill development | Exploration and creativity |
| Engagement | Guided participation | Intrinsic motivation |
| Flexibility | Set schedule and goals | Adaptive and spontaneous |
| Teacher Role | Instructor and facilitator | Observer and supporter |
| Child Development | Cognitive and social skills | Creativity and independence |
| Typical Activities | Storytelling, group lessons, guided play | Free play, art, imaginative games |
Understanding Teacher-led and Child-initiated Activities
Teacher-led activities in preschool involve structured guidance where educators design specific learning tasks to develop skills such as literacy and numeracy, fostering academic growth and classroom management. Child-initiated activities emphasize fostering creativity and independence by allowing children to explore interests freely, promoting social-emotional development and problem-solving abilities. Balancing teacher-led and child-initiated approaches enhances cognitive and social outcomes, supporting holistic early childhood education.
Key Differences Between Teacher-led and Child-initiated Approaches
Teacher-led activities in preschool are structured sessions directed by educators, focusing on specific learning outcomes through guided instruction and planned tasks. Child-initiated activities allow children to explore and learn based on their interests, promoting autonomy, creativity, and intrinsic motivation. The key differences lie in control and structure, where teacher-led approaches emphasize curriculum alignment and skill acquisition, while child-initiated methods prioritize self-expression and experiential learning.
Benefits of Teacher-led Activities in Preschool
Teacher-led activities in preschool provide structured learning environments that enhance cognitive development through targeted skill-building exercises. These activities support early literacy, numeracy, and social skills by offering clear instructions and immediate feedback from educators. Consistent teacher guidance promotes classroom discipline and prepares children for future academic expectations.
Advantages of Child-initiated Learning Experiences
Child-initiated activities in preschool foster autonomy and creativity by allowing children to explore their interests at their own pace, enhancing cognitive and social development. These experiences encourage problem-solving skills and intrinsic motivation, leading to deeper engagement and retention of knowledge. Research shows that child-initiated learning promotes self-regulation and confidence, essential for lifelong learning success.
Impact on Cognitive and Social Development
Teacher-led activities in preschool provide structured learning environments that enhance cognitive skills such as memory, language, and problem-solving through guided instruction. Child-initiated activities promote social development by encouraging autonomy, creativity, and peer interaction, fostering emotional regulation and collaborative skills. Balancing both approaches optimizes cognitive growth and social competence, supporting holistic development in early childhood education.
Balancing Structured and Unstructured Activities
Balancing teacher-led activities with child-initiated activities in preschool supports holistic development by combining structured learning goals with opportunities for creativity and autonomy. Structured activities guided by teachers provide essential foundational skills in literacy and numeracy, while unstructured play allows children to explore, problem-solve, and develop social-emotional skills in a self-directed manner. Integrating both approaches fosters a dynamic learning environment that addresses cognitive, emotional, and physical growth effectively.
Role of the Teacher in Facilitating Both Approaches
The teacher plays a crucial role in balancing teacher-led activities and child-initiated activities by guiding structured learning while fostering creativity and independence. In teacher-led activities, educators provide clear instructions and targeted goals to develop foundational skills, whereas in child-initiated activities, teachers observe and support children's choices to enhance exploration and problem-solving abilities. Effective facilitation involves adapting strategies to individual needs, encouraging curiosity, and promoting active engagement in both learning modes within the preschool environment.
Examples of Teacher-led Activities in Preschool
Teacher-led activities in preschool include structured group lessons such as circle time, where children participate in reading stories, singing songs, and practicing counting. Other examples involve guided art projects that develop fine motor skills and teacher-directed science experiments introducing basic concepts like mixing colors or exploring textures. These activities promote focused learning, social skills, and cognitive development through adult guidance and clear objectives.
Promoting Child Agency Through Initiated Activities
Child-initiated activities in preschool settings significantly enhance child agency by allowing children to explore interests, make decisions, and engage creatively, fostering autonomy and confidence. These activities encourage problem-solving and self-regulation, contrasting with teacher-led sessions that often prioritize structured learning outcomes. Promoting child agency through initiated activities supports developmental milestones in cognitive, social, and emotional domains.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Methods in the Classroom
Effective preschool classrooms balance teacher-led activities, which provide structure and guided learning, with child-initiated activities that foster creativity and independence. Best practices include creating flexible schedules that allocate time for both methods, using observation to tailor support to individual children's interests, and designing learning environments rich in open-ended materials that encourage exploration. Integrating scaffolding techniques during child-initiated play ensures developmental goals are met while promoting autonomy.
Teacher-led Activities vs Child-initiated Activities Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com