Literacy centers enhance reading and writing skills by providing targeted activities that engage students in phonics, vocabulary, and comprehension practice. Math manipulatives support hands-on learning by allowing students to visualize and explore mathematical concepts such as addition, subtraction, and fractions. Both tools foster active learning but focus on different skill sets essential for early childhood education development.
Table of Comparison
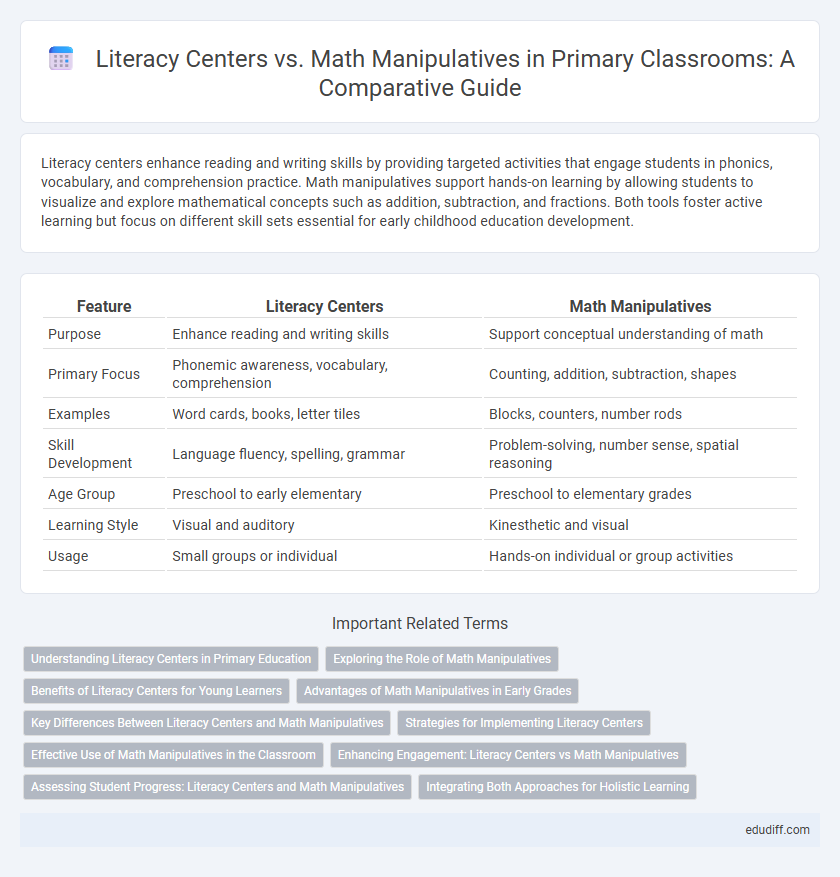
| Feature | Literacy Centers | Math Manipulatives |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance reading and writing skills | Support conceptual understanding of math |
| Primary Focus | Phonemic awareness, vocabulary, comprehension | Counting, addition, subtraction, shapes |
| Examples | Word cards, books, letter tiles | Blocks, counters, number rods |
| Skill Development | Language fluency, spelling, grammar | Problem-solving, number sense, spatial reasoning |
| Age Group | Preschool to early elementary | Preschool to elementary grades |
| Learning Style | Visual and auditory | Kinesthetic and visual |
| Usage | Small groups or individual | Hands-on individual or group activities |
Understanding Literacy Centers in Primary Education
Literacy centers in primary education provide targeted environments that enhance reading, writing, and comprehension skills through interactive activities tailored to young learners' developmental stages. These centers often incorporate thematic books, phonics games, and vocabulary exercises that promote individualized learning and peer collaboration, fostering a comprehensive language foundation. Understanding the role of literacy centers helps educators design effective curricula that support early literacy acquisition and long-term academic success in primary students.
Exploring the Role of Math Manipulatives
Math manipulatives play a crucial role in enhancing conceptual understanding by providing hands-on experiences that bridge abstract math concepts with tangible learning. In literacy centers, integrating math manipulatives fosters cross-disciplinary skills, promoting numerical literacy alongside reading and writing development. Utilizing tools like counting blocks, fraction tiles, and geometric shapes supports differentiated instruction, catering to diverse learning styles and improving student engagement in primary education.
Benefits of Literacy Centers for Young Learners
Literacy centers provide young learners with engaging, hands-on activities that develop critical reading and writing skills through interactive storytelling, phonics games, and vocabulary exercises. These centers foster individualized learning, allowing children to progress at their own pace while enhancing comprehension and fluency. Research shows that literacy centers boost motivation and confidence, which are essential for foundational language acquisition and long-term academic success.
Advantages of Math Manipulatives in Early Grades
Math manipulatives enhance early grade learning by providing hands-on experiences that improve number sense, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving skills. Unlike literacy centers that primarily focus on letter recognition and phonics, manipulatives foster conceptual understanding through tactile engagement and visual representation of abstract math concepts. These tools support differentiated instruction, allowing students of varying abilities to explore mathematics at their own pace and build foundational numeracy skills essential for future academic success.
Key Differences Between Literacy Centers and Math Manipulatives
Literacy centers primarily focus on developing reading, writing, and language skills through targeted activities like phonics games and vocabulary exercises, whereas math manipulatives emphasize hands-on learning of mathematical concepts such as counting, addition, and geometric shapes using physical objects. Literacy centers promote comprehension and fluency by engaging students with text-based materials, while math manipulatives enhance conceptual understanding and problem-solving through tactile interaction. The key difference lies in their instructional goals: literacy centers cultivate language proficiency, whereas math manipulatives support quantitative reasoning and spatial awareness.
Strategies for Implementing Literacy Centers
Effective strategies for implementing literacy centers include organizing materials by skill level, incorporating diverse reading and writing activities, and using data-driven assessments to guide instruction. Teachers should create clear, focused station tasks that promote phonemic awareness, vocabulary development, and comprehension skills to maximize student engagement and learning outcomes. Integrating technology tools alongside hands-on resources enhances differentiation and supports individualized literacy growth.
Effective Use of Math Manipulatives in the Classroom
Math manipulatives enhance student understanding by providing hands-on experiences that facilitate the grasp of abstract mathematical concepts. Integrating tools like counting blocks, number lines, and geometric shapes supports development of problem-solving skills and deepens cognitive connections. Effective use of math manipulatives in the classroom promotes active engagement, improves conceptual clarity, and boosts overall math achievement among diverse learners.
Enhancing Engagement: Literacy Centers vs Math Manipulatives
Literacy centers enhance engagement by providing interactive, hands-on activities that foster reading, writing, and comprehension skills in a dynamic environment. Math manipulatives boost student involvement through tactile exploration of mathematical concepts like counting, geometry, and problem-solving, making abstract ideas concrete. Both strategies increase active participation, with literacy centers focusing on language development and math manipulatives emphasizing numerical understanding.
Assessing Student Progress: Literacy Centers and Math Manipulatives
Assessing student progress in literacy centers involves tracking reading fluency, comprehension, and writing skills through targeted activities and observational checklists. Math manipulatives enable hands-on assessment of conceptual understanding, problem-solving strategies, and number sense by allowing students to demonstrate math principles physically. Both tools provide formative data essential for differentiating instruction and addressing individual learning needs effectively.
Integrating Both Approaches for Holistic Learning
Integrating literacy centers and math manipulatives creates a multidimensional learning environment that enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills across subjects. Literacy centers promote language development and comprehension, while math manipulatives offer hands-on experiences to solidify numerical concepts, together fostering holistic cognitive growth. This combined approach supports differentiated instruction and addresses diverse learning styles, maximizing student engagement and academic achievement.
Literacy Centers vs Math Manipulatives Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com