Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, allowing students to benefit from flexible access to resources while maintaining direct teacher interaction. Face-to-face instruction emphasizes in-person communication, immediate feedback, and social engagement, which are crucial for young learners' developmental needs. Balancing these methods can enhance engagement, personalize learning experiences, and improve educational outcomes in primary education.
Table of Comparison
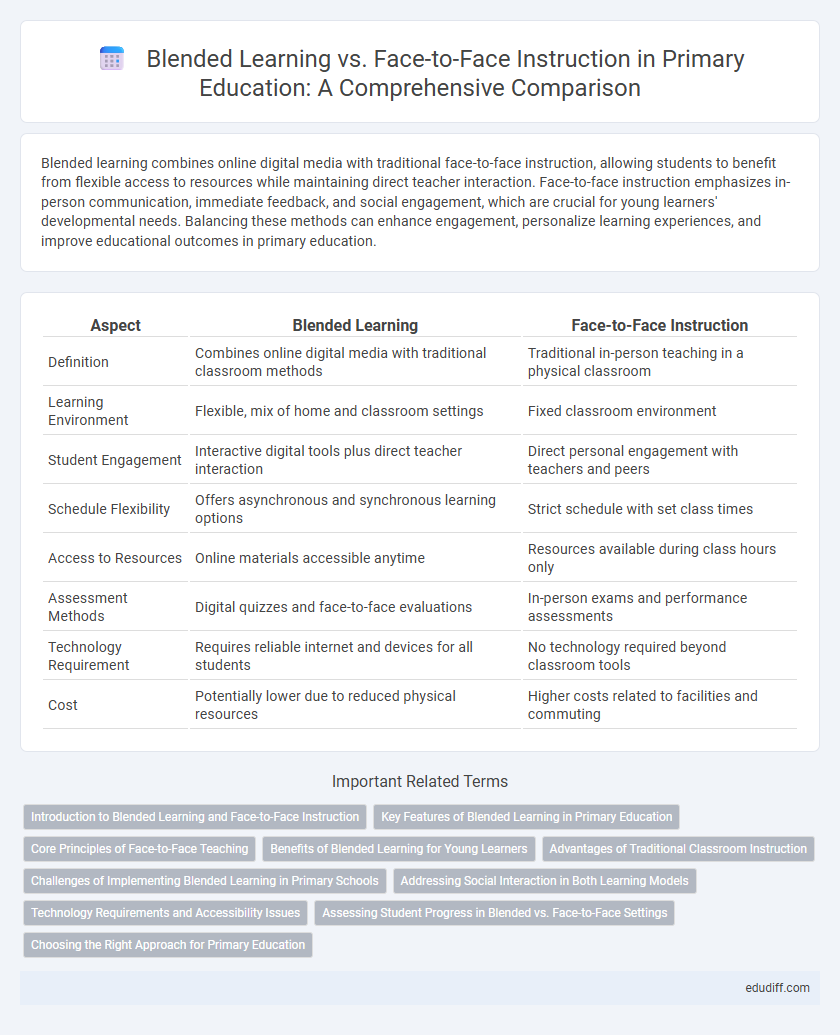
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Face-to-Face Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods | Traditional in-person teaching in a physical classroom |
| Learning Environment | Flexible, mix of home and classroom settings | Fixed classroom environment |
| Student Engagement | Interactive digital tools plus direct teacher interaction | Direct personal engagement with teachers and peers |
| Schedule Flexibility | Offers asynchronous and synchronous learning options | Strict schedule with set class times |
| Access to Resources | Online materials accessible anytime | Resources available during class hours only |
| Assessment Methods | Digital quizzes and face-to-face evaluations | In-person exams and performance assessments |
| Technology Requirement | Requires reliable internet and devices for all students | No technology required beyond classroom tools |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to reduced physical resources | Higher costs related to facilities and commuting |
Introduction to Blended Learning and Face-to-Face Instruction
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, allowing students to control aspects of their learning pace and style while benefiting from face-to-face interaction. Face-to-face instruction relies solely on in-person teaching, fostering direct engagement, immediate feedback, and social interaction within a structured environment. Understanding the distinct advantages of each approach is essential for optimizing educational outcomes in primary education settings.
Key Features of Blended Learning in Primary Education
Blended learning in primary education integrates digital tools with traditional classroom instruction, offering personalized learning paths and interactive content tailored to young students. This approach enhances engagement through multimedia resources and allows for flexible pacing, accommodating diverse learning needs. Data analytics within blended platforms enable teachers to monitor progress in real-time and adjust instruction accordingly for improved educational outcomes.
Core Principles of Face-to-Face Teaching
Face-to-face instruction emphasizes direct interpersonal interaction, immediate feedback, and active classroom engagement, fostering a dynamic learning environment. Core principles include personalized support, non-verbal communication cues, and hands-on activities that enhance student comprehension and motivation. These elements create a structured setting where teachers can adapt teaching strategies in real time to meet diverse learner needs effectively.
Benefits of Blended Learning for Young Learners
Blended learning enhances young learners' engagement by integrating interactive digital content with traditional face-to-face instruction, promoting active participation and personalized pacing. This approach supports diverse learning styles and facilitates immediate feedback through technology, boosting retention and comprehension. Studies indicate that blended models improve motivation and foster self-regulation skills, essential for early academic success.
Advantages of Traditional Classroom Instruction
Traditional classroom instruction fosters direct interaction between teachers and primary students, enhancing immediate feedback and personalized support crucial for early learning. The structured environment promotes social skills development and motivation through peer collaboration and teacher-led activities. Face-to-face settings also enable hands-on learning experiences that are essential for cognitive and motor skill growth in young learners.
Challenges of Implementing Blended Learning in Primary Schools
Implementing blended learning in primary schools faces challenges such as limited access to reliable technology and internet connectivity for young students, impacting consistent engagement and participation. Teachers often require specialized training to effectively integrate digital tools with traditional teaching methods, which can strain existing professional development resources. Ensuring equitable learning experiences remains difficult due to varying home environments and parental support levels in primary education settings.
Addressing Social Interaction in Both Learning Models
Blended learning integrates digital tools with traditional face-to-face instruction to enhance social interaction by facilitating collaborative online discussions and group projects alongside in-person activities. Face-to-face instruction promotes immediate, dynamic social exchanges through verbal and non-verbal cues, fostering deeper interpersonal connections and real-time feedback. Both models address social interaction uniquely, with blended learning leveraging technology for flexible communication and face-to-face instruction emphasizing direct human engagement.
Technology Requirements and Accessibility Issues
Blended learning demands reliable internet access, compatible devices such as tablets or laptops, and user-friendly learning management systems to facilitate seamless integration of digital content. Face-to-face instruction requires minimal technological resources but depends heavily on physical classroom environments and in-person teacher availability. Accessibility challenges in blended learning include disparities in technology access among students, while face-to-face instruction may encounter limitations due to geographic location and infrastructural constraints.
Assessing Student Progress in Blended vs. Face-to-Face Settings
Assessing student progress in blended learning environments combines digital tools like online quizzes and real-time analytics with traditional teacher evaluations, offering a multifaceted view of student performance. Face-to-face instruction relies heavily on in-person assessments, immediate feedback, and observational insights, which foster direct teacher-student interactions but may limit continuous data tracking. Blended models allow for continuous, data-driven progress monitoring while face-to-face settings emphasize personalized, immediate response to student needs.
Choosing the Right Approach for Primary Education
Blended learning integrates digital tools with traditional face-to-face instruction, enhancing engagement and catering to diverse learning styles in primary education. Face-to-face instruction remains crucial for developing social skills, immediate feedback, and hands-on activities essential for young learners' cognitive development. Selecting the right approach depends on factors like technology access, teacher expertise, and individual student needs to optimize learning outcomes in early education settings.
Blended Learning vs Face-to-Face Instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com