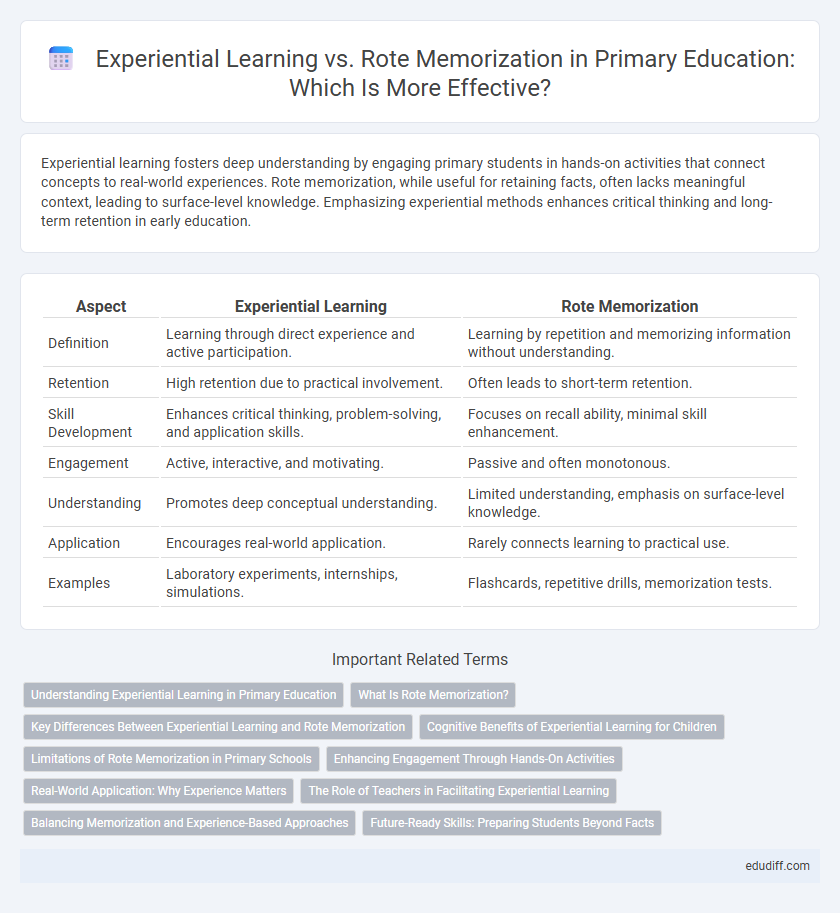
Experiential learning fosters deep understanding by engaging primary students in hands-on activities that connect concepts to real-world experiences. Rote memorization, while useful for retaining facts, often lacks meaningful context, leading to surface-level knowledge. Emphasizing experiential methods enhances critical thinking and long-term retention in early education.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Rote Memorization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and active participation. | Learning by repetition and memorizing information without understanding. |
| Retention | High retention due to practical involvement. | Often leads to short-term retention. |
| Skill Development | Enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and application skills. | Focuses on recall ability, minimal skill enhancement. |
| Engagement | Active, interactive, and motivating. | Passive and often monotonous. |
| Understanding | Promotes deep conceptual understanding. | Limited understanding, emphasis on surface-level knowledge. |
| Application | Encourages real-world application. | Rarely connects learning to practical use. |
| Examples | Laboratory experiments, internships, simulations. | Flashcards, repetitive drills, memorization tests. |
Understanding Experiential Learning in Primary Education
Experiential learning in primary education engages students through hands-on activities and real-world problem-solving, fostering deeper comprehension and retention. This approach contrasts with rote memorization by encouraging critical thinking and the practical application of knowledge. Research supports that experiential learning enhances cognitive development and keeps young learners motivated by making education relevant and interactive.
What Is Rote Memorization?
Rote memorization is a learning method centered on repetitive practice and recall of information without understanding its meaning or context. This technique emphasizes memorizing facts, formulas, or procedures through repetition to ensure quick retrieval from memory. While efficient for short-term recall, rote memorization often lacks deep comprehension and critical thinking engagement compared to experiential learning methods.
Key Differences Between Experiential Learning and Rote Memorization
Experiential learning involves active engagement and real-world experience, fostering critical thinking and deeper understanding, whereas rote memorization relies on repetitive practice and memorization without context or comprehension. Experiential learning promotes long-term retention by connecting knowledge to practical application, while rote memorization often leads to short-term recall with limited cognitive skill development. Key differences include the emphasis on meaningful interaction in experiential learning compared to the passive, mechanical nature of rote memorization.
Cognitive Benefits of Experiential Learning for Children
Experiential learning enhances children's cognitive development by promoting critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper understanding through hands-on activities and real-world experiences. Unlike rote memorization, which emphasizes passive repetition, experiential learning engages multiple senses and encourages active participation, leading to better retention and application of knowledge. This approach fosters creativity and adaptability, essential cognitive benefits that support lifelong learning and intellectual growth.
Limitations of Rote Memorization in Primary Schools
Rote memorization in primary schools restricts students' ability to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for lifelong learning. This method often leads to superficial understanding, limiting retention and application of knowledge in real-world contexts. Without engaging hands-on experiences, young learners struggle to connect concepts meaningfully, reducing overall academic motivation and creativity.
Enhancing Engagement Through Hands-On Activities
Experiential learning enhances student engagement by involving hands-on activities that promote active participation and critical thinking, improving knowledge retention and real-world application. Research shows that learners retain up to 75% of information through experiential methods compared to 10-20% via rote memorization. This approach fosters deeper understanding and motivation, making education more effective and meaningful for primary students.
Real-World Application: Why Experience Matters
Experiential learning fosters deeper understanding by engaging learners in hands-on activities that mirror real-world challenges, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. In contrast, rote memorization emphasizes repetition without context, often leading to short-term retention and limited practical application. Real-world experience bridges the gap between theory and practice, making knowledge more meaningful and transferable across diverse situations.
The Role of Teachers in Facilitating Experiential Learning
Teachers play a crucial role in facilitating experiential learning by designing immersive activities that promote critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills. They guide students through reflection and collaborative discussions, enabling deeper understanding beyond memorization. By creating supportive environments, educators transform passive content absorption into active, meaningful learning experiences that enhance retention and application.
Balancing Memorization and Experience-Based Approaches
Balancing memorization and experience-based approaches enhances cognitive retention by combining the strengths of rote memorization's factual accuracy with experiential learning's practical application. Incorporating active engagement and real-world problem-solving alongside traditional memorization techniques fosters deeper understanding and long-term knowledge retention. Educators should design curricula that integrate both methods, optimizing student outcomes through diverse instructional strategies.
Future-Ready Skills: Preparing Students Beyond Facts
Experiential learning cultivates critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills that rote memorization fails to develop, equipping students with competencies vital for the future workforce. Engaging in hands-on projects, simulations, and real-world challenges fosters adaptability and collaboration, attributes increasingly valued in evolving industries. Emphasizing experiential methods prepares learners not just to recall information but to apply knowledge effectively in dynamic environments.
Experiential Learning vs Rote Memorization Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com