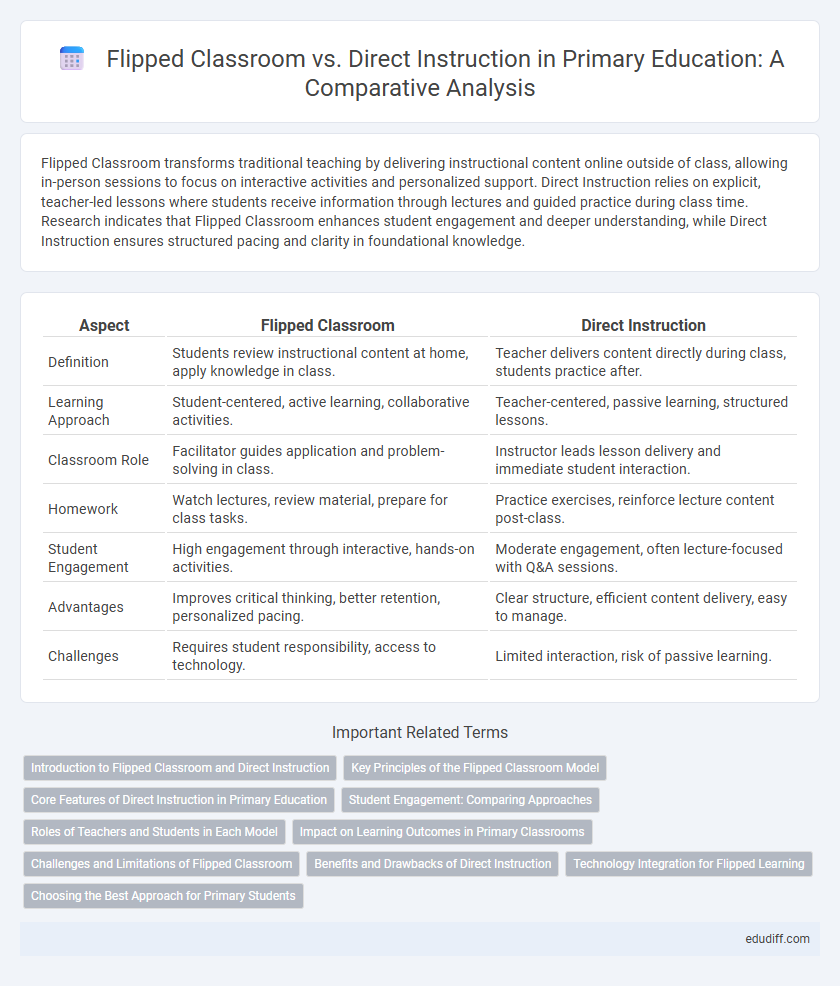
Flipped Classroom transforms traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive activities and personalized support. Direct Instruction relies on explicit, teacher-led lessons where students receive information through lectures and guided practice during class time. Research indicates that Flipped Classroom enhances student engagement and deeper understanding, while Direct Instruction ensures structured pacing and clarity in foundational knowledge.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Direct Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students review instructional content at home, apply knowledge in class. | Teacher delivers content directly during class, students practice after. |
| Learning Approach | Student-centered, active learning, collaborative activities. | Teacher-centered, passive learning, structured lessons. |
| Classroom Role | Facilitator guides application and problem-solving in class. | Instructor leads lesson delivery and immediate student interaction. |
| Homework | Watch lectures, review material, prepare for class tasks. | Practice exercises, reinforce lecture content post-class. |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through interactive, hands-on activities. | Moderate engagement, often lecture-focused with Q&A sessions. |
| Advantages | Improves critical thinking, better retention, personalized pacing. | Clear structure, efficient content delivery, easy to manage. |
| Challenges | Requires student responsibility, access to technology. | Limited interaction, risk of passive learning. |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Direct Instruction
Flipped Classroom is an instructional strategy where students engage with instructional content, such as video lectures or readings, outside of class, allowing classroom time for interactive activities and personalized support. Direct Instruction involves teacher-led lessons with explicit teaching of concepts, step-by-step guidance, and immediate feedback, focusing on mastery of specific skills. Both methods aim to enhance student understanding but differ in delivery and classroom dynamics.
Key Principles of the Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model emphasizes active learning by delivering instructional content, often online, outside of the classroom, allowing in-class time for interactive activities and personalized support. Key principles include student-centered learning, where learners engage with pre-recorded lectures or materials at their own pace, and collaborative problem-solving during class sessions. This approach contrasts with direct instruction, which relies on teacher-led lectures and passive student reception, aiming to boost engagement and deeper understanding through flipped methodologies.
Core Features of Direct Instruction in Primary Education
Direct Instruction in primary education emphasizes structured lessons with clear, specific objectives and systematic teaching methods that promote skill mastery. It relies on teacher-led demonstrations, guided practice, and frequent assessments to ensure student understanding and immediate feedback. Core features include explicit teaching of foundational skills, step-by-step instructions, and repetitive practice to reinforce learning outcomes in young learners.
Student Engagement: Comparing Approaches
Flipped classroom models significantly enhance student engagement by promoting active learning through pre-class video lectures and in-class collaborative activities, enabling deeper understanding. Direct instruction, while structured and teacher-centered, can limit student participation but provides clear guidance and immediate feedback. Research shows that flipped classrooms foster higher motivation and sustained attention, particularly in primary education settings.
Roles of Teachers and Students in Each Model
In the flipped classroom model, teachers act as facilitators, guiding students through interactive activities and personalized support, while students take on an active role by engaging with instructional content independently before class. In contrast, direct instruction centers on teachers delivering structured lessons and controlling the learning pace, with students primarily receiving information and practicing skills under teacher supervision. This shift in roles influences student autonomy, engagement, and the methods teachers use to assess understanding and provide feedback.
Impact on Learning Outcomes in Primary Classrooms
Flipped Classroom models in primary classrooms enhance student engagement and improve retention by allowing pupils to review instructional content at their own pace outside class, which increases active learning during face-to-face time. Studies indicate that Direct Instruction often results in higher immediate mastery of foundational skills due to its structured and teacher-led approach, yet it may limit opportunities for critical thinking compared to flipped models. Integrating flipped techniques with Direct Instruction strategies has shown positive impacts on primary students' academic performance and motivation across subjects like literacy and mathematics.
Challenges and Limitations of Flipped Classroom
Flipped Classroom faces challenges such as unequal access to technology and reliable internet, which can hinder students' ability to engage with pre-recorded lessons at home. Limited student motivation and self-discipline may result in incomplete preparation for in-class activities, reducing the effectiveness of active learning strategies. Teachers often require additional training and time to create quality instructional videos and redesign lesson plans to ensure alignment with learning objectives.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction offers a structured learning environment that enhances student focus and provides clear, explicit teaching of fundamental skills, which can improve academic performance in core subjects. However, it may limit opportunities for student-led inquiry, creativity, and critical thinking, potentially reducing engagement and personalized learning experiences. Despite its efficiency in delivering content, Direct Instruction may not accommodate diverse learning styles as effectively as more interactive approaches like the Flipped Classroom.
Technology Integration for Flipped Learning
Flipped Classroom leverages technology tools such as video tutorials, interactive quizzes, and learning management systems to enhance student engagement and provide personalized learning experiences. This integration allows students to access instructional content asynchronously, enabling more in-class time for collaborative activities and individualized support. Direct Instruction, while effective for structured teaching, typically relies less on digital platforms, leading to limited opportunities for technology-driven interactivity and self-paced learning.
Choosing the Best Approach for Primary Students
Flipped Classroom empowers primary students to engage with learning materials at their own pace, promoting active participation and critical thinking skills outside traditional classroom hours. Direct Instruction offers a structured, teacher-led approach that ensures clear guidance and immediate feedback, which is beneficial for young learners requiring step-by-step support. Selecting the best approach depends on individual student needs, classroom resources, and the specific learning objectives targeted in primary education.
Flipped Classroom vs Direct Instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com