Brain breaks improve focus and cognitive function by allowing students to rest and reset during lessons, preventing mental fatigue. Continuous instruction, while keeping momentum, can lead to decreased attention and reduced retention over time. Implementing short, frequent brain breaks enhances overall learning efficiency and classroom behavior.
Table of Comparison
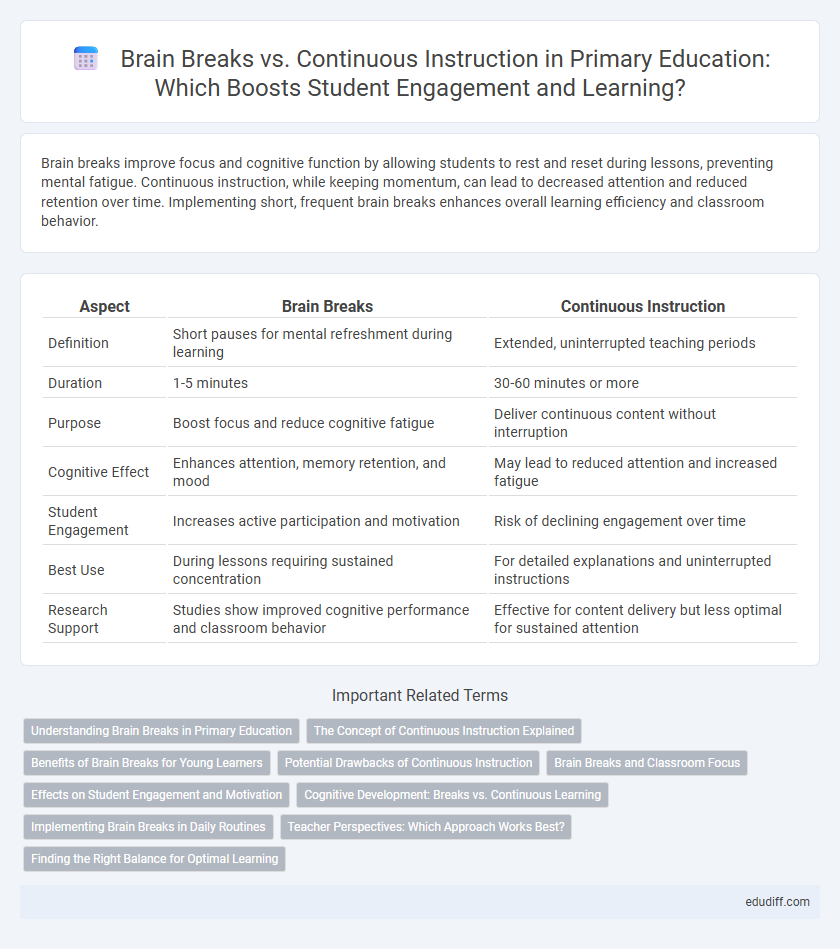
| Aspect | Brain Breaks | Continuous Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short pauses for mental refreshment during learning | Extended, uninterrupted teaching periods |
| Duration | 1-5 minutes | 30-60 minutes or more |
| Purpose | Boost focus and reduce cognitive fatigue | Deliver continuous content without interruption |
| Cognitive Effect | Enhances attention, memory retention, and mood | May lead to reduced attention and increased fatigue |
| Student Engagement | Increases active participation and motivation | Risk of declining engagement over time |
| Best Use | During lessons requiring sustained concentration | For detailed explanations and uninterrupted instructions |
| Research Support | Studies show improved cognitive performance and classroom behavior | Effective for content delivery but less optimal for sustained attention |
Understanding Brain Breaks in Primary Education
Brain breaks in primary education involve short, structured pauses that help students reset attention and improve cognitive processing during learning sessions. Research shows these breaks enhance memory retention, reduce fatigue, and promote positive classroom behavior compared to continuous instruction. Incorporating brain breaks every 20-30 minutes aligns with children's developmental needs, supporting sustained engagement and overall academic performance.
The Concept of Continuous Instruction Explained
Continuous instruction involves delivering educational content without interruptions, aiming to maintain student engagement through sustained focus and momentum. This teaching method emphasizes consistent exposure to new material, which can enhance cognitive flow and reduce transition times between topics. However, the absence of breaks may lead to decreased attention spans and increased mental fatigue among primary students.
Benefits of Brain Breaks for Young Learners
Brain breaks enhance focus and cognitive function by allowing young learners to relax and reset their attention spans during lessons. Short, active intervals improve memory retention and reduce behavioral issues by providing physical movement that stimulates brain activity. Incorporating brain breaks in primary education supports emotional regulation and increases overall classroom engagement compared to continuous instruction.
Potential Drawbacks of Continuous Instruction
Continuous instruction in primary education may lead to decreased student attention and increased cognitive fatigue, undermining learning efficiency. Prolonged focus without breaks can result in reduced information retention and lower engagement levels among young learners. Incorporating brain breaks enhances cognitive processing and helps maintain optimal mental energy throughout lessons.
Brain Breaks and Classroom Focus
Brain breaks significantly enhance primary students' classroom focus by providing short, purposeful pauses that recharge cognitive resources and reduce mental fatigue. Research indicates that incorporating brain breaks every 20-30 minutes improves attention spans, engagement, and information retention compared to continuous instruction. Effective brain breaks involve physical movement or mindfulness activities tailored to children's developmental needs, promoting sustained academic performance and classroom behavior.
Effects on Student Engagement and Motivation
Brain breaks significantly enhance student engagement and motivation by providing short, purposeful pauses that help refresh cognitive focus and reduce mental fatigue. Continuous instruction, while promoting content immersion, often leads to decreased attention spans and increased disengagement during extended learning periods. Implementing brain breaks in primary classrooms supports sustained motivation and active participation, contributing to improved academic outcomes.
Cognitive Development: Breaks vs. Continuous Learning
Cognitive development in primary students benefits significantly from brain breaks, which enhance memory retention and executive functioning by reducing mental fatigue. Continuous instruction without pauses can decrease attentional control and increase cognitive overload, leading to diminished learning efficiency. Incorporating short, frequent brain breaks optimizes neural processing and supports sustained cognitive engagement during lessons.
Implementing Brain Breaks in Daily Routines
In primary classrooms, implementing brain breaks enhances student focus by incorporating short, structured activities between continuous instruction periods. Research shows that 5-minute brain breaks, such as stretching or mindfulness exercises, boost cognitive function and decrease behavioral issues. Integrating these breaks every 25-30 minutes promotes sustained attention and improves overall academic performance in young learners.
Teacher Perspectives: Which Approach Works Best?
Teachers report that brain breaks enhance student focus and behavior by providing short, structured pauses during lessons, promoting cognitive reset and improved engagement. Continuous instruction, while efficient for covering curriculum, often leads to diminished attention spans and increased classroom restlessness over time. Educators tend to favor integrating brain breaks within primary classrooms to balance instructional time and maintain optimal learning conditions.
Finding the Right Balance for Optimal Learning
In primary education, integrating brain breaks strategically enhances cognitive retention and prevents mental fatigue during continuous instruction. Research indicates that short, frequent breaks stimulate neural connections, improve attention span, and support information processing, leading to more effective learning outcomes. Balancing instructional time with planned brain breaks cultivates an engaging classroom environment that optimizes student focus and academic performance.
Brain Breaks vs Continuous Instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com