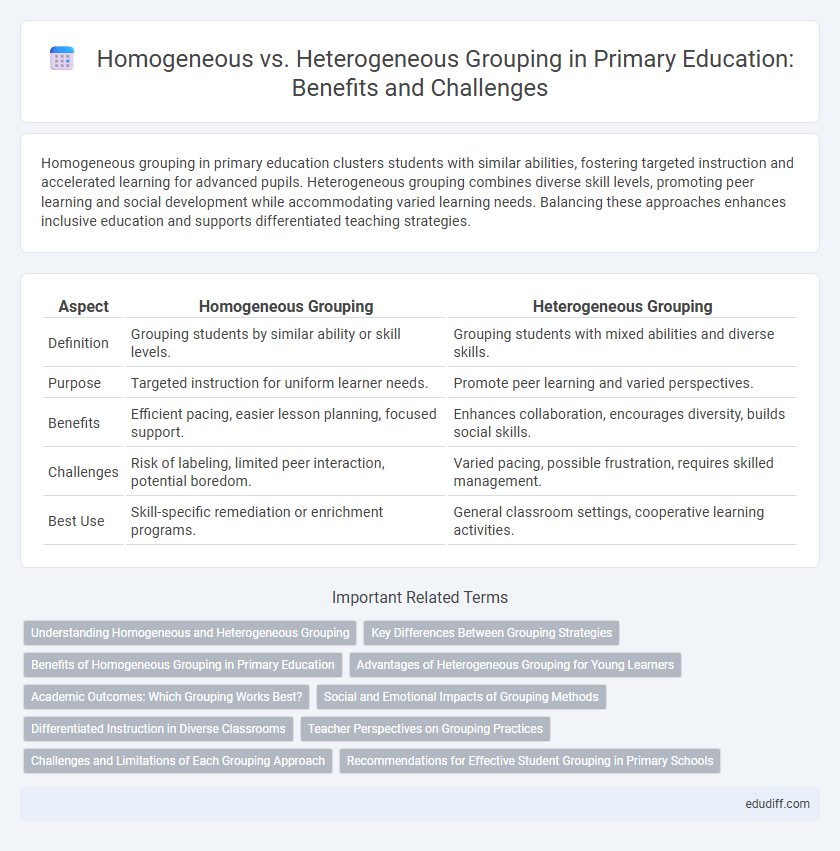
Homogeneous grouping in primary education clusters students with similar abilities, fostering targeted instruction and accelerated learning for advanced pupils. Heterogeneous grouping combines diverse skill levels, promoting peer learning and social development while accommodating varied learning needs. Balancing these approaches enhances inclusive education and supports differentiated teaching strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Homogeneous Grouping | Heterogeneous Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Grouping students by similar ability or skill levels. | Grouping students with mixed abilities and diverse skills. |
| Purpose | Targeted instruction for uniform learner needs. | Promote peer learning and varied perspectives. |
| Benefits | Efficient pacing, easier lesson planning, focused support. | Enhances collaboration, encourages diversity, builds social skills. |
| Challenges | Risk of labeling, limited peer interaction, potential boredom. | Varied pacing, possible frustration, requires skilled management. |
| Best Use | Skill-specific remediation or enrichment programs. | General classroom settings, cooperative learning activities. |
Understanding Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Grouping
Homogeneous grouping involves organizing students with similar abilities or learning levels together, which can streamline instruction and target specific skill development more effectively. Heterogeneous grouping mixes students with varied abilities and backgrounds, fostering collaboration, peer learning, and diverse perspectives within the classroom. Understanding the benefits and challenges of both grouping strategies is essential for tailoring teaching methods to meet diverse educational needs in primary education.
Key Differences Between Grouping Strategies
Homogeneous grouping clusters primary students based on similar abilities, promoting targeted instruction that addresses specific learning needs, while heterogeneous grouping mixes diverse ability levels to encourage peer learning and social development. Homogeneous groups streamline lesson planning and allow teachers to focus on precise skill gaps, whereas heterogeneous groups foster collaboration, communication skills, and exposure to varied perspectives. Selecting the optimal strategy depends on educational goals, classroom dynamics, and student diversity in primary education settings.
Benefits of Homogeneous Grouping in Primary Education
Homogeneous grouping in primary education enhances targeted instruction by aligning student abilities, allowing educators to tailor lessons that address specific learning needs and accelerate academic progress. It fosters a supportive and focused classroom environment where students with similar skill levels can collaborate effectively, boosting confidence and motivation. This approach simplifies assessment and intervention, enabling more precise identification of learning gaps and timely support.
Advantages of Heterogeneous Grouping for Young Learners
Heterogeneous grouping in primary education promotes inclusive learning by pairing students with diverse abilities, enhancing peer support and collaborative problem-solving. Young learners benefit from exposure to multiple perspectives, which fosters social skills and empathy while catering to varied learning styles. This approach encourages higher engagement and motivation by creating a dynamic classroom environment that supports individualized growth.
Academic Outcomes: Which Grouping Works Best?
Research indicates homogeneous grouping in primary education often leads to improved academic outcomes by allowing teachers to tailor instruction to students' specific skill levels, thereby enhancing mastery of content. Conversely, heterogeneous grouping fosters diverse peer interactions that can promote critical thinking and collaborative learning but may dilute targeted skill development. Optimal academic achievement depends on balancing these approaches with curriculum goals and individual student needs, suggesting a flexible use of grouping strategies is most effective.
Social and Emotional Impacts of Grouping Methods
Homogeneous grouping in primary education often fosters a sense of belonging and self-confidence among students with similar abilities, reducing anxiety and encouraging peer support. Heterogeneous grouping promotes social skills development by exposing children to diverse perspectives and helping them build empathy and cooperation. Both methods influence emotional well-being, with homogeneous groups supporting comfort and competence, while heterogeneous groups enhance adaptability and inclusiveness.
Differentiated Instruction in Diverse Classrooms
Homogeneous grouping allows teachers to tailor instruction to students with similar skill levels, promoting targeted support and acceleration in primary classrooms. In contrast, heterogeneous grouping fosters diversity and peer learning, encouraging collaboration and social development across varying abilities. Effective differentiated instruction in diverse classrooms leverages both grouping strategies to address individual needs and maximize student engagement and growth.
Teacher Perspectives on Grouping Practices
Teachers perceive homogeneous grouping as beneficial for targeting instruction to students with similar skill levels, enabling tailored lesson plans and pacing. In contrast, heterogeneous grouping is often valued for promoting social interaction and peer learning, which can enhance collaborative skills and expose students to diverse perspectives. Educators weigh the balance between academic differentiation and social development when selecting grouping strategies in primary classrooms.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Grouping Approach
Homogeneous grouping often limits peer learning opportunities due to similar skill sets, which can lead to repetitive challenges and reduced student engagement. Heterogeneous grouping poses difficulties in managing diverse learning paces, potentially causing frustration for both advanced and struggling students within the same group. Effective differentiation and teacher facilitation remain critical hurdles in maximizing the benefits of either grouping strategy in primary education.
Recommendations for Effective Student Grouping in Primary Schools
Effective student grouping in primary schools involves balancing homogeneous and heterogeneous grouping strategies based on learning objectives and student needs. Homogeneous groups enable targeted instruction for students with similar abilities, enhancing skill mastery, while heterogeneous groups promote peer learning, social development, and diverse perspectives. Teachers should regularly assess student progress and adapt groupings to optimize engagement and academic growth.
Homogeneous Grouping vs Heterogeneous Grouping Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com