Classroom management involves organizing the physical environment, establishing rules, and routines to create a productive learning space. Behavior management focuses on understanding and guiding students' social-emotional behaviors to promote positive interactions and reduce disruptions. Effective teaching requires integrating both strategies to maintain order and support student growth.
Table of Comparison
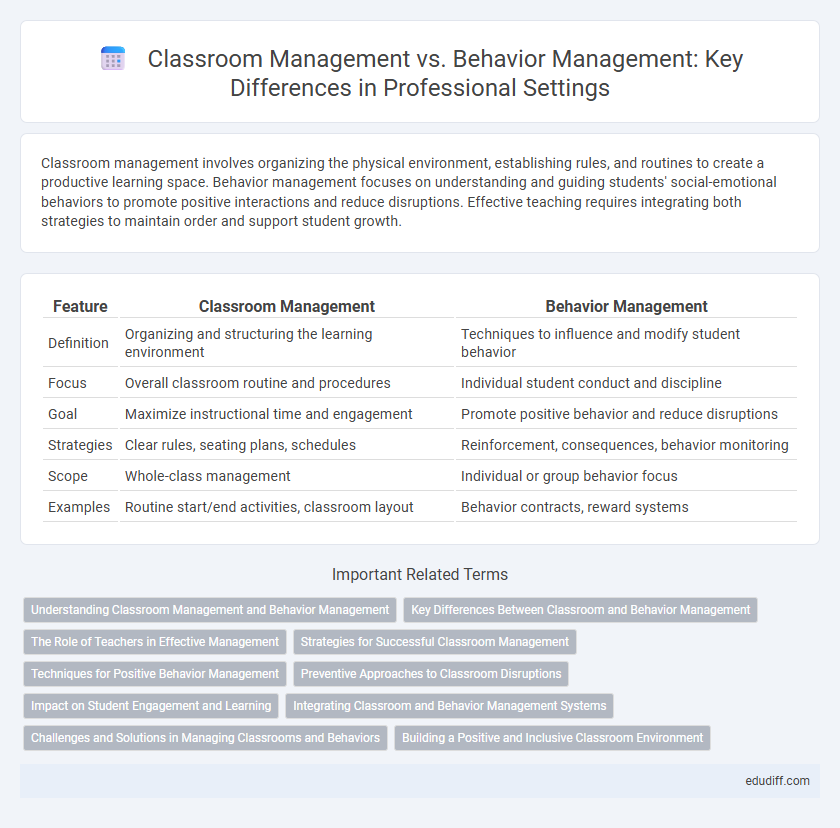
| Feature | Classroom Management | Behavior Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organizing and structuring the learning environment | Techniques to influence and modify student behavior |
| Focus | Overall classroom routine and procedures | Individual student conduct and discipline |
| Goal | Maximize instructional time and engagement | Promote positive behavior and reduce disruptions |
| Strategies | Clear rules, seating plans, schedules | Reinforcement, consequences, behavior monitoring |
| Scope | Whole-class management | Individual or group behavior focus |
| Examples | Routine start/end activities, classroom layout | Behavior contracts, reward systems |
Understanding Classroom Management and Behavior Management
Classroom management involves organizing the learning environment to promote effective instruction, including setting rules, routines, and procedures that foster student engagement. Behavior management specifically targets students' conduct by implementing strategies to prevent and address disruptive behaviors, ensuring a positive and respectful classroom climate. Understanding both concepts is essential for educators to create an orderly, supportive space that maximizes academic achievement and social development.
Key Differences Between Classroom and Behavior Management
Classroom management primarily centers on organizing the physical environment, establishing routines, and maintaining instructional flow to optimize learning conditions. Behavior management focuses specifically on addressing and modifying students' individual conduct through strategies like positive reinforcement and consistent consequences. While classroom management creates a structured setting, behavior management targets specific behavioral issues to promote self-discipline and social-emotional growth.
The Role of Teachers in Effective Management
Teachers play a crucial role in both classroom management and behavior management by establishing clear expectations and consistent routines that foster a positive learning environment. Effective classroom management involves organizing physical space and instructional activities to minimize disruptions, while behavior management focuses on reinforcing positive behaviors and addressing misbehavior through proactive strategies. Mastery of these interconnected skills enhances student engagement, promotes respect, and supports academic success.
Strategies for Successful Classroom Management
Effective classroom management strategies emphasize clear expectations, consistent routines, and positive reinforcement to foster an environment conducive to learning. Behavior management techniques incorporate proactive interventions, individualized support plans, and restorative practices to address disruptions constructively. Integrating these approaches enhances student engagement, minimizes conflicts, and promotes a respectful classroom culture.
Techniques for Positive Behavior Management
Effective positive behavior management techniques prioritize clear expectations, consistent reinforcement, and proactive engagement strategies to foster a respectful learning environment. Utilizing methods such as positive reinforcement, restorative practices, and collaborative problem-solving encourages student accountability and intrinsic motivation. These approaches reduce disruptions, promote social-emotional skills, and enhance overall classroom climate.
Preventive Approaches to Classroom Disruptions
Effective classroom management emphasizes establishing clear expectations, structured routines, and engaging instructional strategies to proactively minimize disruptions. Behavior management focuses on identifying triggers and consistently applying positive reinforcement techniques to shape student conduct before issues escalate. Preventive approaches integrate both methods, fostering a supportive environment that reduces the likelihood of behavioral problems through anticipation and early intervention.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning
Classroom management establishes a structured environment that minimizes disruptions and supports instructional flow, directly enhancing student engagement by promoting consistent routines and clear expectations. Behavior management targets specific student behaviors through interventions and reinforcement strategies, which help maintain focus and motivation, thereby positively influencing learning outcomes. Both approaches interplay to create a conducive learning atmosphere where students remain attentive and academically productive.
Integrating Classroom and Behavior Management Systems
Integrating classroom management and behavior management systems enhances overall student engagement and reduces disruptions by creating consistent expectations and reinforcing positive behavior. Effective integration involves aligning instructional strategies with behavioral interventions to promote a supportive learning environment. Utilizing data-driven approaches and collaborative teacher-student relationships further strengthens the efficacy of combined management systems.
Challenges and Solutions in Managing Classrooms and Behaviors
Classroom management challenges often stem from maintaining engagement and order, while behavior management focuses on addressing individual student conduct issues. Effective solutions include establishing clear expectations, consistent routines, and proactive interventions tailored to diverse student needs. Implementing positive reinforcement strategies and ongoing teacher training enhances both classroom and behavior management outcomes.
Building a Positive and Inclusive Classroom Environment
Classroom management emphasizes creating structured routines and clear expectations to foster a positive learning environment, while behavior management focuses on addressing individual student behaviors to maintain order and promote respect. Effective integration of both strategies supports an inclusive classroom culture where diverse needs are met and students feel valued and safe. Implementing proactive communication, consistent reinforcement, and culturally responsive practices enhances engagement and reduces disruptions.
Classroom Management vs Behavior Management Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com