A mentor provides long-term guidance by sharing personal experiences and industry insights to foster professional growth. A coach focuses on specific skills and performance improvement through structured feedback and goal-setting. Understanding the distinction helps professionals choose the right support for their career development.
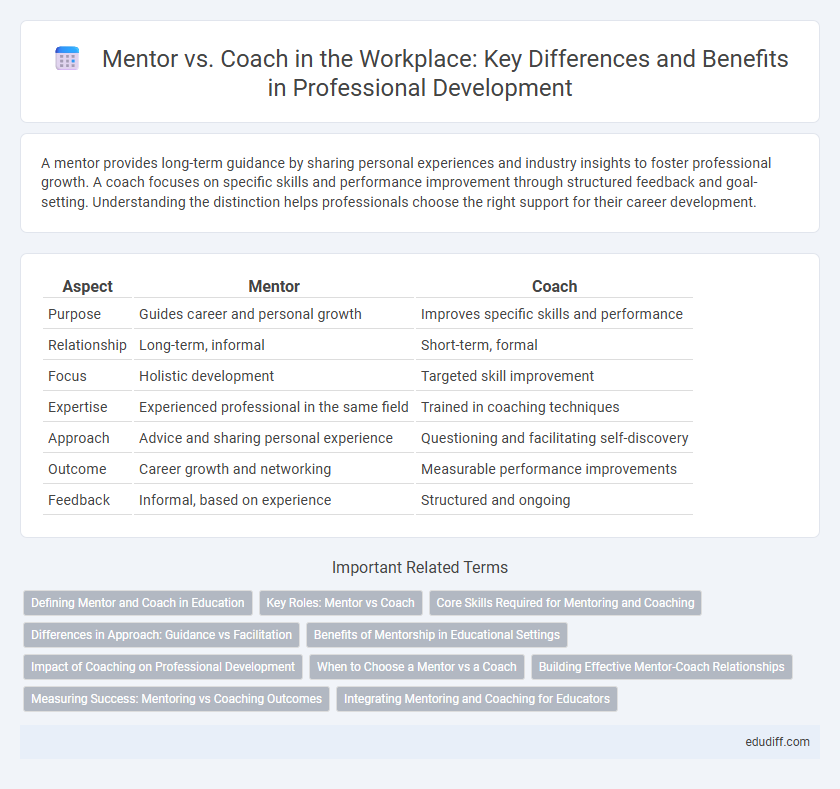
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mentor | Coach |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Guides career and personal growth | Improves specific skills and performance |
| Relationship | Long-term, informal | Short-term, formal |
| Focus | Holistic development | Targeted skill improvement |
| Expertise | Experienced professional in the same field | Trained in coaching techniques |
| Approach | Advice and sharing personal experience | Questioning and facilitating self-discovery |
| Outcome | Career growth and networking | Measurable performance improvements |
| Feedback | Informal, based on experience | Structured and ongoing |
Defining Mentor and Coach in Education
A mentor in education provides long-term guidance, sharing expertise and personal experiences to support a learner's professional and personal growth. A coach focuses on specific skills and performance improvement through targeted feedback and goal-oriented sessions. Both roles aim to enhance development, but mentors build relationships over time while coaches drive immediate, strategic progress.
Key Roles: Mentor vs Coach
Mentors provide guidance by sharing their experience and wisdom to support long-term personal and professional growth, often fostering a deeper relationship based on trust and encouragement. Coaches focus on enhancing specific skills and performance, using targeted techniques and feedback to help individuals achieve short-term goals and measurable outcomes. Both roles contribute to development, with mentors emphasizing knowledge transfer and coaches prioritizing skill-building and accountability.
Core Skills Required for Mentoring and Coaching
Mentoring requires strong interpersonal communication, active listening, and the ability to provide constructive feedback tailored to long-term professional growth. Coaching demands expertise in goal-setting, motivational techniques, and performance assessment to drive measurable improvements. Both roles emphasize empathy and adaptability but differ in their focus on guidance versus skill development.
Differences in Approach: Guidance vs Facilitation
Mentors provide direct guidance based on their experience, offering specific advice and sharing knowledge to help mentees navigate their career paths. Coaches focus on facilitation by asking powerful questions that encourage self-discovery and enhance problem-solving skills. This distinction in approach emphasizes mentors as advisors and coaches as catalysts for personal growth and development.
Benefits of Mentorship in Educational Settings
Mentorship in educational settings cultivates personalized learning experiences that enhance student engagement and academic achievement by fostering long-term relationships with experienced educators. Access to mentors provides students with tailored guidance, skill development, and emotional support, which significantly boosts confidence and motivation. Research shows that mentored students demonstrate higher retention rates and improved career readiness compared to those without mentorship.
Impact of Coaching on Professional Development
Coaching significantly enhances professional development by fostering personalized skill growth and improving performance through targeted feedback and goal-setting. Unlike traditional mentoring, coaching emphasizes active collaboration and accountability, driving measurable improvements in leadership abilities and decision-making. Research shows professionals who engage in coaching report increased confidence, productivity, and career advancement opportunities.
When to Choose a Mentor vs a Coach
Choose a mentor when seeking long-term guidance from an experienced professional who can provide career insights, industry knowledge, and personal development advice. Opt for a coach when requiring focused support to improve specific skills, achieve short-term goals, or enhance performance through structured feedback and accountability. Understanding these distinctions ensures selecting the right expert to maximize professional growth and success.
Building Effective Mentor-Coach Relationships
Building effective mentor-coach relationships requires clear communication of goals and expectations to align both parties' objectives. Establishing trust through consistent feedback and active listening enhances collaboration and fosters a growth-oriented environment. Integrating personalized development plans ensures targeted skill improvement and long-term professional success.
Measuring Success: Mentoring vs Coaching Outcomes
Measuring success in mentoring focuses on long-term personal and professional growth achieved through guidance and knowledge transfer, often assessed via mentee career progression and skill development. Coaching outcomes prioritize short-term performance improvements and goal attainment, with success quantified by specific metrics such as productivity increases and behavior changes. Organizations track mentoring effectiveness through qualitative feedback and retention rates, while coaching impact is evaluated using performance data and achievement of predefined objectives.
Integrating Mentoring and Coaching for Educators
Integrating mentoring and coaching in education enhances professional development by combining personalized guidance with skill-building strategies. Educators benefit from mentors' experience-driven insights while leveraging coaches' goal-oriented techniques to improve instructional effectiveness. This hybrid approach fosters continuous growth, reflective practice, and collaborative learning within academic environments.
Mentor vs Coach Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com