Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes cognitive skills into hierarchical levels from remembering to creating, emphasizing the complexity of thinking processes. Webb's Depth of Knowledge assesses the complexity of tasks based on the depth of understanding required, focusing on the application of knowledge across four levels. Comparing the two frameworks helps professionals design educational activities that target both cognitive complexity and depth of understanding for optimal learning outcomes.
Table of Comparison
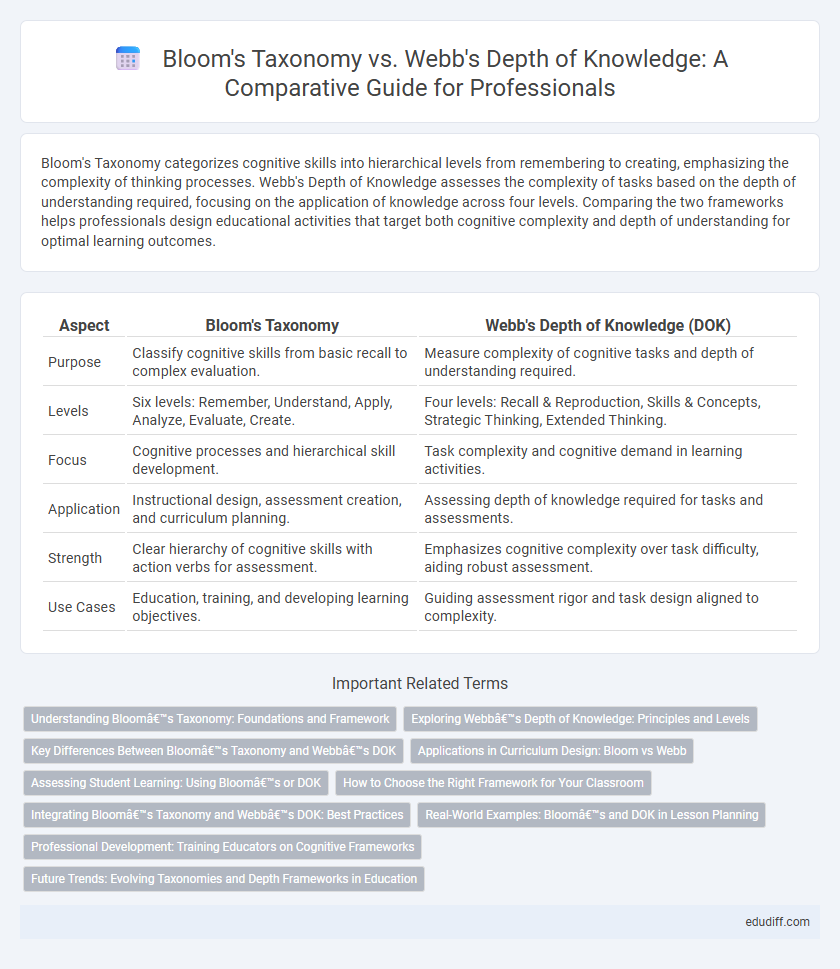
| Aspect | Bloom's Taxonomy | Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Classify cognitive skills from basic recall to complex evaluation. | Measure complexity of cognitive tasks and depth of understanding required. |
| Levels | Six levels: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, Create. | Four levels: Recall & Reproduction, Skills & Concepts, Strategic Thinking, Extended Thinking. |
| Focus | Cognitive processes and hierarchical skill development. | Task complexity and cognitive demand in learning activities. |
| Application | Instructional design, assessment creation, and curriculum planning. | Assessing depth of knowledge required for tasks and assessments. |
| Strength | Clear hierarchy of cognitive skills with action verbs for assessment. | Emphasizes cognitive complexity over task difficulty, aiding robust assessment. |
| Use Cases | Education, training, and developing learning objectives. | Guiding assessment rigor and task design aligned to complexity. |
Understanding Bloom’s Taxonomy: Foundations and Framework
Bloom's Taxonomy provides a hierarchical framework categorizing cognitive skills from basic recall to complex evaluation and creation, essential for designing curriculum and assessments that build higher-order thinking skills. This taxonomy's foundational structure--Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating--guides educators in targeting specific learning objectives and measuring student progress effectively. By systematically developing cognitive abilities, Bloom's Taxonomy supports instructional strategies that foster deep comprehension and critical thinking across educational contexts.
Exploring Webb’s Depth of Knowledge: Principles and Levels
Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK) categorizes cognitive tasks into four distinct levels, emphasizing the complexity and rigor required for each. Level 1 involves recall and reproduction, focusing on basic understanding, while Level 2 requires skills and concepts demonstrated through mental processing beyond simple recall. Levels 3 and 4 demand strategic thinking and extended reasoning, challenging learners to analyze, synthesize, and apply knowledge in complex, real-world situations.
Key Differences Between Bloom’s Taxonomy and Webb’s DOK
Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes cognitive skills into hierarchical levels: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create, emphasizing the complexity of thinking processes. Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK) focuses on the depth of content mastery required, categorizing tasks into four levels of cognitive demand: Recall and Reproduction, Skills and Concepts, Strategic Thinking, and Extended Thinking. The key difference lies in Bloom's emphasis on the type of cognitive process, while Webb's DOK assesses the complexity and rigor of knowledge application within a learning context.
Applications in Curriculum Design: Bloom vs Webb
Bloom's Taxonomy emphasizes hierarchical cognitive skills from remembering to creating, guiding curriculum designers to structure learning objectives that progressively build knowledge and critical thinking. Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK) categorizes tasks by complexity levels, encouraging educators to design assessments and activities that deepen analytical skills through application, strategic thinking, and extended reasoning. Integrating Bloom's Taxonomy with Webb's DOK enhances curriculum development by aligning learning goals with the cognitive rigor required for subject mastery and real-world problem-solving.
Assessing Student Learning: Using Bloom’s or DOK
Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes cognitive skills from basic recall to higher-order thinking, providing educators a framework to design assessments targeting specific learning objectives. Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK) emphasizes the complexity of cognitive tasks, categorizing assessment items by the depth of understanding required, from recall to extended strategic thinking. Using Bloom's Taxonomy or DOK enables precise alignment of assessment design with educational goals, improving measurement of student learning outcomes.
How to Choose the Right Framework for Your Classroom
Choosing the right framework for your classroom depends on aligning educational goals with student learning outcomes. Bloom's Taxonomy emphasizes cognitive skill development through hierarchical levels such as remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating, making it ideal for designing lesson objectives and assessments. Webb's Depth of Knowledge focuses on the complexity of tasks and cognitive demand, offering a valuable tool for measuring the rigor of assignments and ensuring students engage in deeper, critical thinking.
Integrating Bloom’s Taxonomy and Webb’s DOK: Best Practices
Integrating Bloom's Taxonomy and Webb's Depth of Knowledge enhances instructional design by aligning cognitive processes with complexity levels to foster deeper learning outcomes. Effective integration involves mapping Bloom's hierarchical cognitive domains--Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, Create--onto Webb's four DOK levels, ensuring tasks are designed with appropriate rigor and cognitive demand. Best practices include using this combined framework for curriculum development, formative assessments, and differentiated instruction to promote critical thinking and mastery of content.
Real-World Examples: Bloom’s and DOK in Lesson Planning
Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes cognitive skills from remembering to creating, enabling educators to structure lessons that progressively build higher-order thinking. Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK) assesses the complexity of tasks, emphasizing the depth of understanding needed for real-world problem-solving scenarios. Combining Bloom's levels with DOK frameworks in lesson planning promotes rigorous learning experiences by aligning cognitive processes with task complexity in authentic classroom activities.
Professional Development: Training Educators on Cognitive Frameworks
Professional development for educators benefits significantly from integrating Bloom's Taxonomy and Webb's Depth of Knowledge to enhance cognitive framework understanding. Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes learning objectives by cognitive complexity, aiding in the design of curriculum and assessment strategies that promote higher-order thinking skills. Webb's Depth of Knowledge complements this by emphasizing cognitive demand and task complexity, which helps educators develop instructional practices that scaffold student learning across varied content depths.
Future Trends: Evolving Taxonomies and Depth Frameworks in Education
Emerging educational frameworks build on Bloom's Taxonomy and Webb's Depth of Knowledge by integrating cognitive complexity with real-world problem-solving skills to meet 21st-century learning demands. Adaptive learning technologies and data analytics are driving the evolution of these taxonomies towards personalized, competency-based education models. Future trends emphasize dynamic assessment tools that capture deeper semantic understanding and critical thinking across interdisciplinary curricula.
Bloom’s Taxonomy vs Webb’s Depth of Knowledge Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com