Inquiry-based instruction in professional pet training fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by engaging learners in hands-on experiences and real-world scenarios. Lecture-based instruction primarily delivers information through direct teaching, which may limit interaction and practical application. Emphasizing inquiry-based methods enhances skill retention and adaptability essential for effective pet care and behavior management.
Table of Comparison
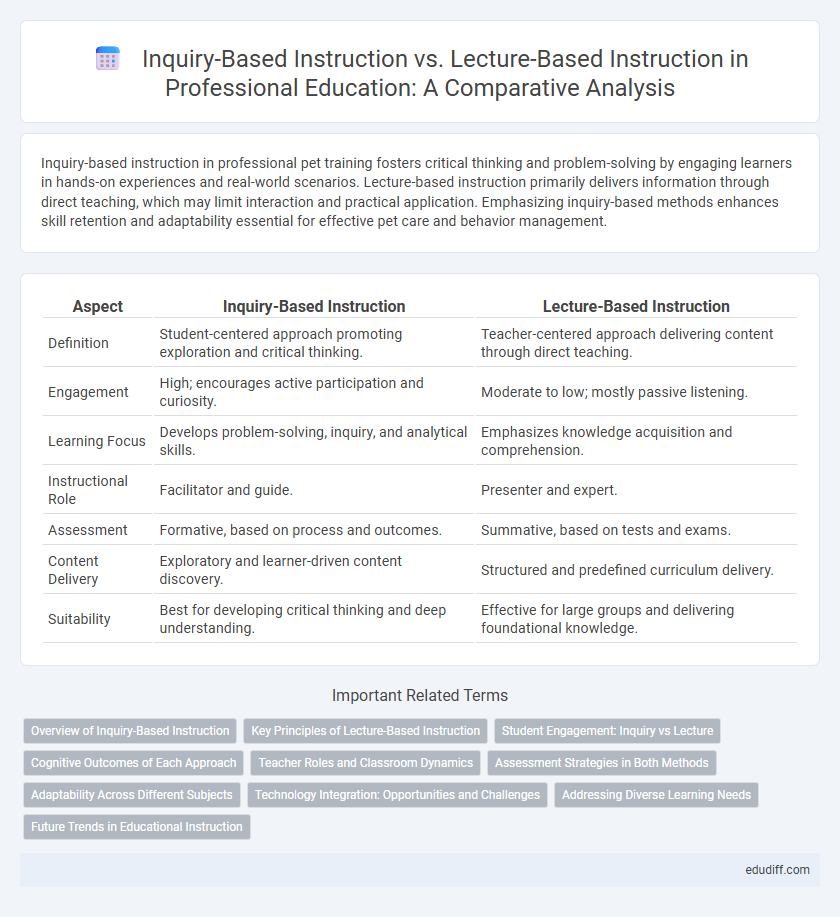
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Instruction | Lecture-Based Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach promoting exploration and critical thinking. | Teacher-centered approach delivering content through direct teaching. |
| Engagement | High; encourages active participation and curiosity. | Moderate to low; mostly passive listening. |
| Learning Focus | Develops problem-solving, inquiry, and analytical skills. | Emphasizes knowledge acquisition and comprehension. |
| Instructional Role | Facilitator and guide. | Presenter and expert. |
| Assessment | Formative, based on process and outcomes. | Summative, based on tests and exams. |
| Content Delivery | Exploratory and learner-driven content discovery. | Structured and predefined curriculum delivery. |
| Suitability | Best for developing critical thinking and deep understanding. | Effective for large groups and delivering foundational knowledge. |
Overview of Inquiry-Based Instruction
Inquiry-based instruction emphasizes student-centered learning through exploration, questioning, and problem-solving, promoting critical thinking and deep understanding. This method engages learners in active investigation, fostering skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Research indicates inquiry-based models improve retention and adaptability compared to traditional lecture-based approaches.
Key Principles of Lecture-Based Instruction
Lecture-based instruction centers on structured content delivery where the instructor actively imparts knowledge while students primarily listen and take notes. Key principles include clarity of explanation, organized presentation of material, and effective use of verbal and visual aids to reinforce understanding. This method emphasizes a systematic approach to transmitting information, ensuring comprehensive coverage of essential topics within a fixed timeframe.
Student Engagement: Inquiry vs Lecture
Inquiry-based instruction significantly enhances student engagement by promoting active exploration, critical thinking, and hands-on problem-solving, which fosters deeper understanding and retention. Lecture-based instruction often results in passive learning, where students are more likely to disengage due to limited interaction and one-way communication. Research indicates that inquiry-based methods increase motivation and academic performance by encouraging curiosity and collaboration among students.
Cognitive Outcomes of Each Approach
Inquiry-based instruction enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by actively engaging students in the learning process, promoting deeper understanding and retention of content. Lecture-based instruction primarily supports the efficient transmission of factual knowledge but may limit opportunities for developing higher-order cognitive skills. Research indicates that inquiry-based methods tend to produce stronger gains in analytical abilities and conceptual comprehension compared to traditional lectures.
Teacher Roles and Classroom Dynamics
Inquiry-based instruction positions teachers as facilitators who guide student exploration and critical thinking, fostering a collaborative classroom dynamic where learners actively construct knowledge. In contrast, lecture-based instruction casts teachers as primary knowledge transmitters, resulting in a more passive learning environment with limited student interaction. The shift from authoritative to interactive teacher roles in inquiry-based instruction enhances student engagement and promotes deeper understanding.
Assessment Strategies in Both Methods
Inquiry-based instruction emphasizes formative assessment strategies such as observation, reflective journals, and student self-assessments to gauge understanding and promote critical thinking skills. Lecture-based instruction primarily relies on summative assessments including quizzes, exams, and standardized tests to evaluate retention of factual knowledge. Combining both methods can enhance assessment by integrating real-time feedback and comprehensive evaluation of conceptual mastery.
Adaptability Across Different Subjects
Inquiry-based instruction demonstrates high adaptability across diverse subjects by fostering critical thinking and active exploration tailored to specific content areas. Lecture-based instruction, while efficient for delivering structured information, often lacks flexibility in addressing varying subject complexities and student engagement levels. Educators seeking to enhance subject-specific understanding benefit from blending inquiry methods to accommodate diverse learning styles and curricular demands.
Technology Integration: Opportunities and Challenges
Inquiry-based instruction leverages technology to foster active learning through interactive simulations, real-time data analysis, and collaborative platforms, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Lecture-based instruction traditionally relies on technology for content delivery, such as video presentations and digital resources, but may limit student engagement and interactivity. The challenge lies in effectively integrating technology to support inquiry-driven learning environments while ensuring accessibility and addressing potential technical difficulties.
Addressing Diverse Learning Needs
Inquiry-based instruction fosters critical thinking and adaptability by engaging students in active exploration, making it highly effective for meeting diverse learning needs. Lecture-based instruction, while efficient for delivering standardized content, may not accommodate individual learning styles or promote deep understanding. Tailoring instruction to incorporate inquiry-based methods can enhance inclusivity and support varied cognitive processes among learners.
Future Trends in Educational Instruction
Inquiry-based instruction emphasizes student engagement and critical thinking, fostering personalized learning experiences that adapt to diverse learning styles. Lecture-based instruction continues to integrate advanced technologies such as AI and virtual reality to enhance content delivery and accessibility. Future trends in educational instruction prioritize hybrid models combining inquiry and lecture methods to optimize student outcomes and prepare learners for complex problem-solving in dynamic environments.
Inquiry-based instruction vs Lecture-based instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com